Vision
-
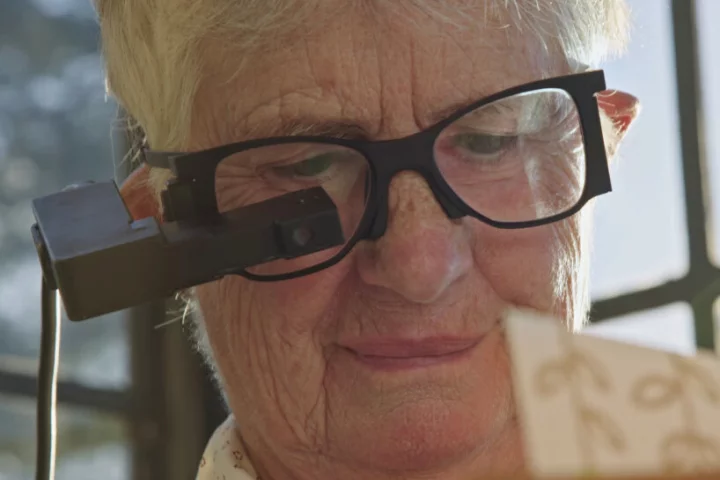
An upcoming wearable device for the legally blind could help them navigate public and outdoor spaces independently, acting as 'glasses' that guide them through their surroundings. Maker .Lumen is accepting reservations now.
-
A new study shows that briefly and reversibly anesthetizing the retina of the amblyopic eye for just a few days can restore the brain's visual responses to that eye, even in adults.
-
In a major breakthrough in human tissue replication, for the first time ever a 3D-printed cornea has been transplanted onto a legally blind patient's eye, successfully restoring their sight.
-
Pickleball’s boom has brought an unexpected side effect: a surge in serious eye injuries. A new study has revealed a sharp rise in pickleball-related eye trauma, promoting calls for protective eyewear standards.
-
Stanford researchers and global collaborators have developed a wireless retinal implant called PRIMA that's helping people with untreatable eyesight loss see not just light, but actual shapes and patterns – what scientists call form vision.
-
Despite what some movies may suggest, it's currently impossible to transplant functional, seeing human eyeballs. Scientists are taking a big step in that direction, however, with the development of an eye-transplant device known as the eye-ECMO.
-
Forget carrots. Researchers have determined that one of the most common amino acids has the power to keep retinas thick and healthy. The finding has the potential to fight vision loss and blindness through this newly discovered metabolic pathway.
-
Although there already are "smart" contact lenses that monitor the eyes for signs of glaucoma, the devices are typically only worn when the patient is awake. A new type of contact lens, however, watches over the eyes throughout the night, too.
-
A breakthrough treatment has allowed damaged retinal cells to regenerate themselves. The current research has been conducted on mice, but the pathways are the same in humans, which opens hope for a new way to treat certain kinds of blindness.
-
A team of researchers at Rice University has developed a haptic feedback vest and camera system for a blind dog known as Kunde. The vest helps guide the dog through daily obstacles and the hope is that it will soon do the same for other pups.
-
It certainly sounds like something from a new sci-fi series, but a power-free set of contact lenses impregnated with nanoparticles has proven successful in allowing humans to see what has previously been invisible – even when their eyes are closed.
-
Just when you think you've seen it all, researchers claim to have developed a way for people to see a color the human eye has previously never seen before. They're calling this new hue 'Olo.'
Load More