China leads the world in terms of renewable energy resources like solar power. And not just by a small margin either, making over twice as much solar power as the next highest country, the USA. Where do you store any excess solar energy for use when the sun isn't shining? Answer: in ridiculously big batteries.
It's not just the 609 gigawatts of solar power capacity China had in 2023 that makes the country a world leader. China is also the global leader in wind power, having a capacity of 441 gigawatts of clean, renewable wind energy. And the country just keeps building more.
The trouble is, that's China's wind and solar capacity. And because China's grid infrastructure is still playing catch-up to the crazy amounts of renewables it keeps building, curtailment is a real issue and much of that power simply goes unused for one reason or another.
Grid-scale batteries could potentially remedy some of these issues in China and around the world.
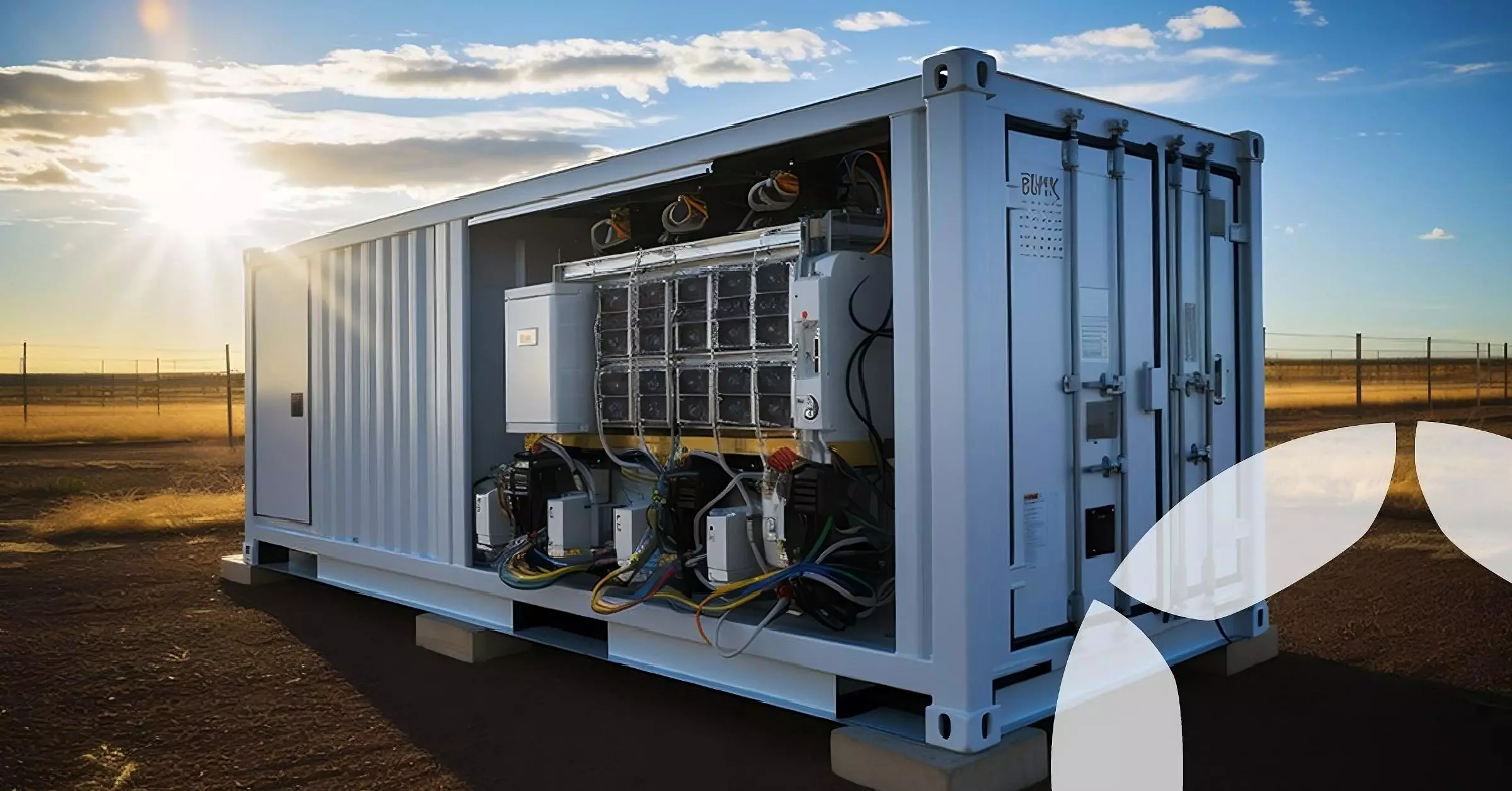
Envision Energy announced an 8-MWh, grid-scale battery that fits in a 20-ft (6-m) shipping container this week while at the third Electrical Energy Storage Alliance (EESA) exhibition held in Shanghai.
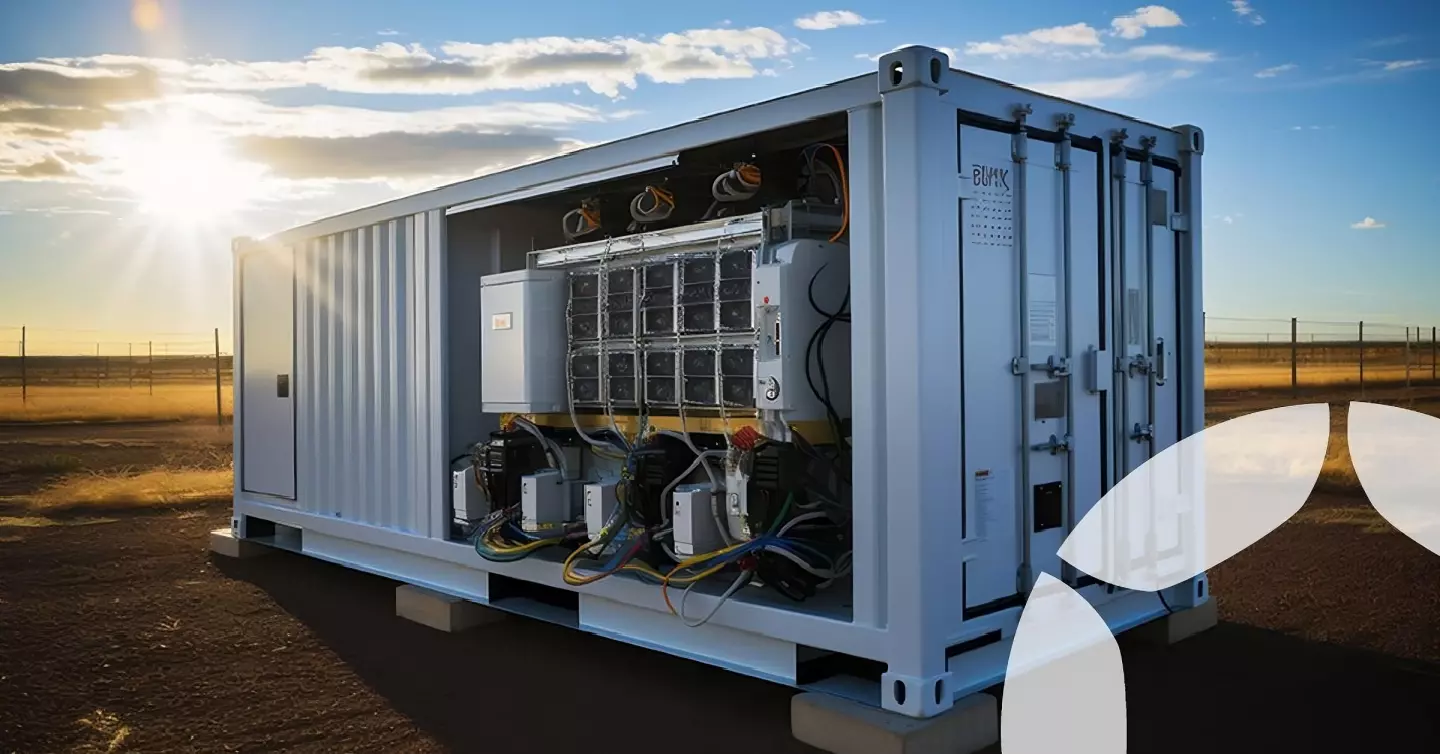
It's colossal. Not just in size, but in the 8-MWh figure. The company says its newest product uses 700-Ah lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) cells in a liquid-cooled 1,500 to 2,000-volt configuration that's good for nearly 16,000 charge cycles that all fits in half a normal shipping container. All in, the system weighs about 55 tons (50 tonnes)
To put it into simple terms, at 1,500 volts DC, it could theoretically power an average US home at 1 kW continuously for about 640 hours – a few hours shy of 27 days.
Not that this energy storage system is designed for such a thing. It's designed with a short-term charge and discharge duration configurable between two and eight hours.
Short duration plays a crucial role in balancing renewable energy sources by maintaining a stable supply of power, storing excess electricity when production is high and discharging power when production wanes. The downside to having two-hour short cycles means that at 16,000 life cycles, the battery would only last a little over three and a half years.
The battery cells are produced by AESC, a Japanese company known for supplying high-performance batteries to numerous electric vehicle manufacturers. The system's inverters and battery management system (BMS) are all made in-house by Envision.

It was only a short three months ago, in June, when Envision announced its 5-MW container battery, making this latest 8-MW iteration quite a big jump.
While LiFePO4 doesn't have the same inherent risks of "venting" as do the much more common lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries, Envision's energy storage unit features a pretty robust six-tiered suite of safety features. These include AI-powered monitoring systems to detect fires and faults, off-gas detection, aerogel pads between cells, active ventilation, and even an option water sprinkler system can be added. Deflagration panels are a must though – aka explosive vent panels.
Source: ESS News