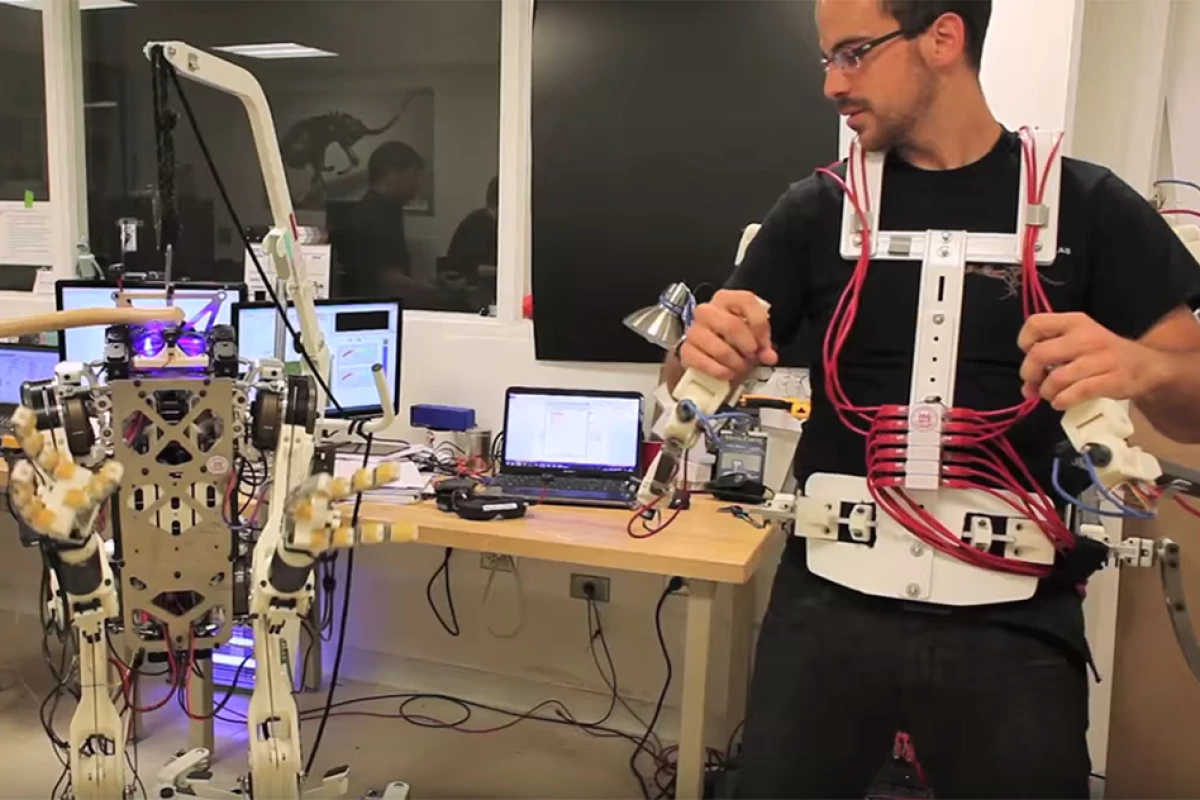
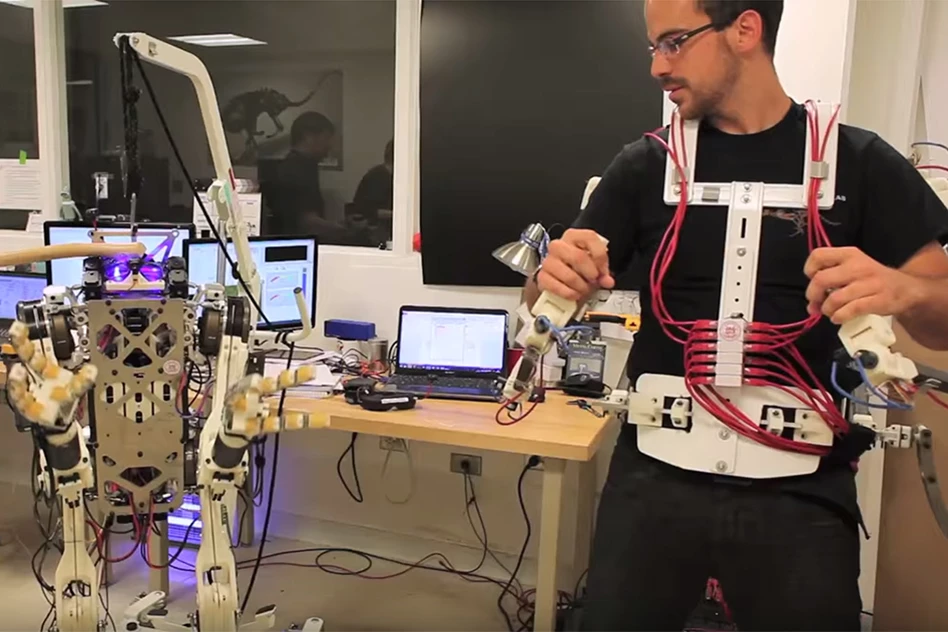
Engineers at MIT and the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign are developing a teleoperated robot that uses a special operator vest to give it human-like balance and reflexes. Called Little Highly Efficient Robotic Mechanisms and Electromechanical System (HERMES), the small-scale bipedal robot is a third of the size of an adult person and can run, jump, and mostly move in sync with the operator.
When it comes to dealing with disasters, robots have a lot of obvious attractions as responders and rescuers, but there's still a long way to go before we see humanoid robotic firefighters dashing into collapsed burning buildings.
One of the biggest problems is that though robots today can run, jump, and do backflips like a parkour artist, they are still terrible at balancing. So if a bipedal robot tries something like forcing open a door, it's very likely to simply slip and end up on the floor.
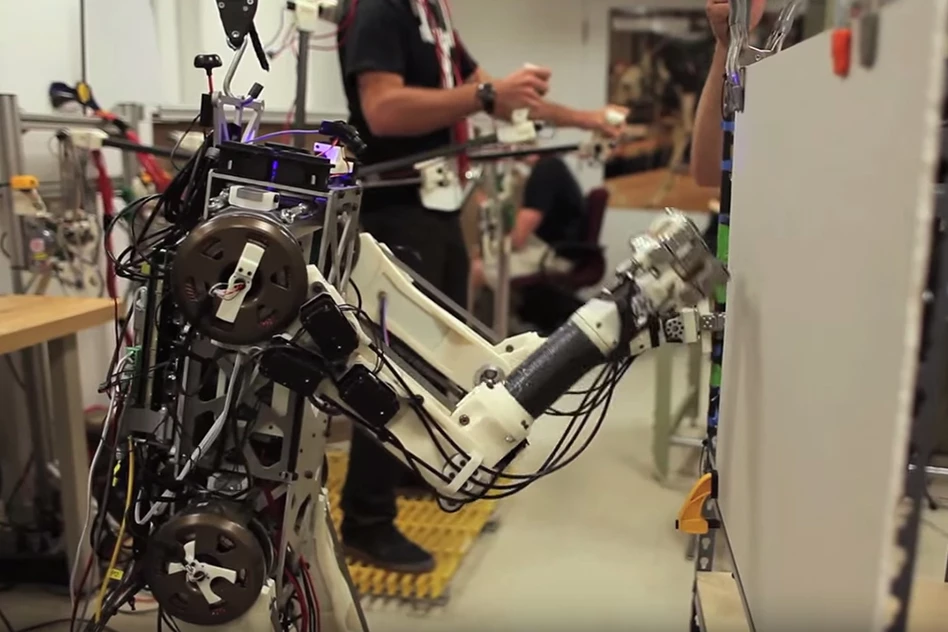
This is because, although we do them every day without thinking, tasks like standing, walking, running, and forcing open a door or swinging a hammer are actually very complex processes of balancing forces, centers of gravity and centers of pressure.
To help bipedal robots keep their balance and "root" themselves to handle vigorous activities, University of Illinois mechanical science and engineering professor João Ramos and Professor Sangbae Kim at MIT developed Little HERMES.
"We were motivated by watching the 2011 Tohoku, Japan, earthquake, tsunami and subsequent Fukushima Dai-ichi nuclear plant disaster unfold," says Ramos. "We thought that if a robot could have entered the power plant after the disaster, things could have ended differently. This incident was a wake-up call for the robotics community."
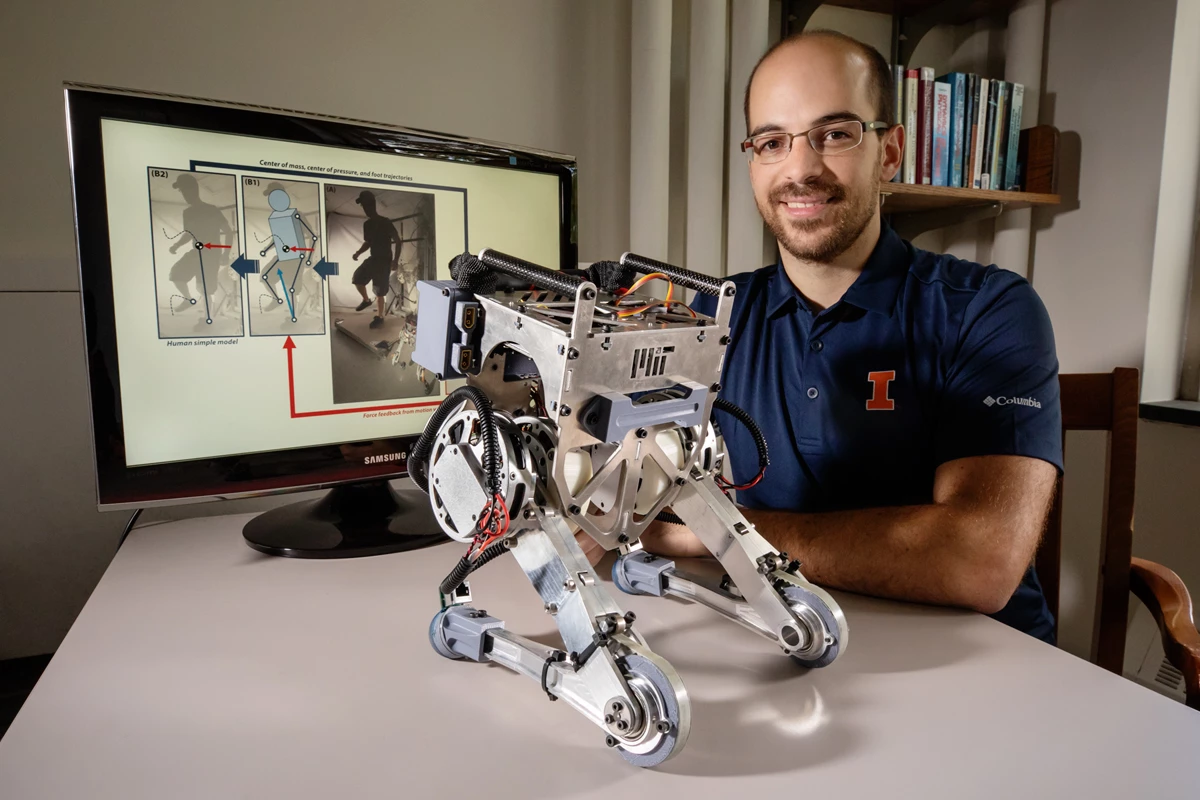
The key to Little HERMES is a forced feedback mechanism. The operator wears a vest that not only makes the robot move in sync with the operator, but also allows the operator to feel the forces working on the robot in near real-time and react instinctively – sharing the human sense of balance with the machine.
Key to this is a vest worn by the operator that pushes and tugs as the robot loses it balance. In such circumstances, the operator reflexively compensates and so does the machine. This means it can not only walk and stand with more confidence but to also brace itself to push or use a tool.
“If the robot begins to fall, the operator feels a push in that direction through the vest,” Ramos said. “Naturally, the operator's reaction is to take a step to balance themselves, and the robot does the same, synchronously, preventing it from tipping over.”
Currently, Little HERMES works by direct wire control, though the next step is to introduce wireless control as well as expanding the scope of the forced feedback technology.
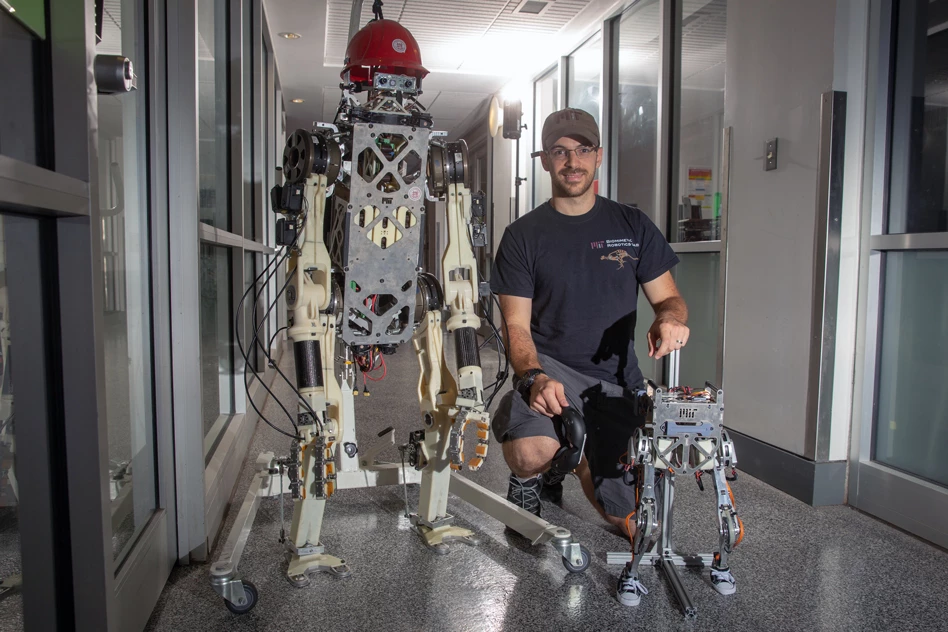
"We also plan to develop robot-to-human force-feedback devices to other parts of the body like the feet and hands," says Ramos. "Additionally, everything we have developed so far is not constrained to bipedal robots; any of the technology transfers easily to other mobile systems like quadrupedal and wheeled robots."
The research was published in Science Robotics.
The video below shows Little HERMES in action.
Sources: University of Illinois, MIT






