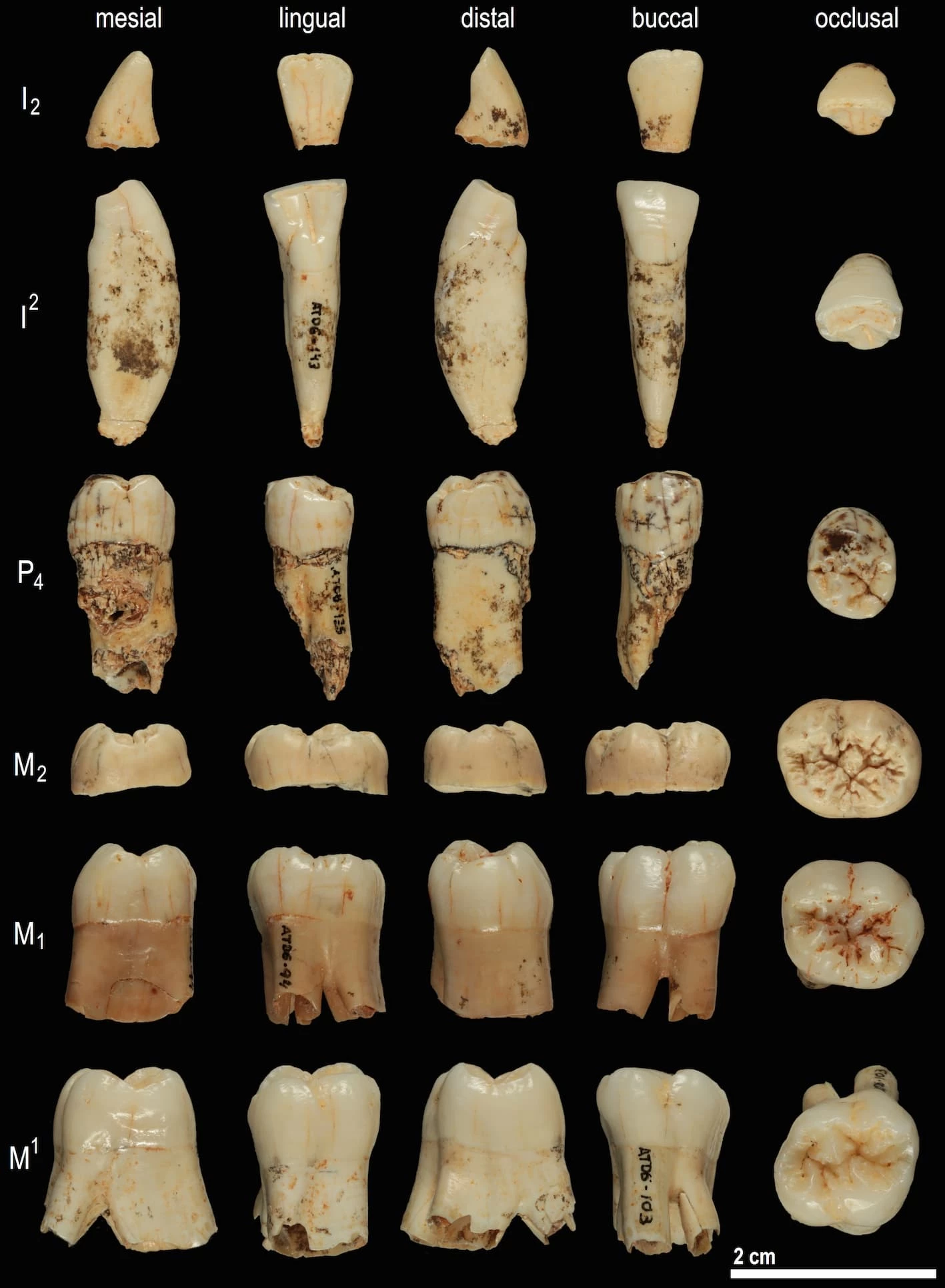
It’s hard to piece together the full history of human evolution from piles of old bones. But now, scientists have made use of a new method to study proteins in dental enamel of an 800,000-year-old human species, helping place it in the family tree.
Although Homo sapiens is the only human species still alive today, the road to get here is paved with extinct relatives. And untangling how they’re all related to each other is a task that scientists continue to wrestle with. The timeline is usually determined through various dating processes, both on the bones themselves and the sediment layers they’re found in. Relationships between species are then determined from this timeline, and by examining the structures and features of the bones to track the progress of evolution.
For the new study, researchers at the University of Copenhagen have used a new tool called palaeoproteomics to get a more precise picture. This involves sequencing proteins from ancient remains, and it works on samples that are far too old to have intact DNA. In this case, the team applied it to the 800,000-year-old teeth of a mysterious, archaic human species called Homo antecessor.

“Using state of the art mass spectrometry, we determine the sequence of amino acids within protein remains from Homo antecessor dental enamel,” says Jesper Velgaard Olsen, co-author of the study. “We can then compare the ancient protein sequences we ‘read’ to those of other hominins, for example Neanderthals and Homo sapiens, to determine how they are genetically related.”
With this process, the team managed to pin down Homo antecessor’s place in the family tree with greater precision than ever before. It had previously been put forward that this species was the last common ancestor for us modern humans, Neanderthals, and Denisovans. But the new study suggests that while we are closely related, we aren’t directly derived from Homo antecessor – it was less of a great grandfather and more of a great uncle.
“Ancient protein analysis provides evidence for a close relationship between Homo antecessor, us (Homo sapiens), Neanderthals, and Denisovans,” says Frido Welker, first author on the study. “Our results support the idea that Homo antecessor was a sister group to the group containing Homo sapiens, Neanderthals, and Denisovans.”
The team says that applying palaeoproteomics to other fossils could reveal other new details about human ancestors. We doubt the family tree has seen its last revision.
The research was published in the journal Nature.
Source: University of Copenhagen