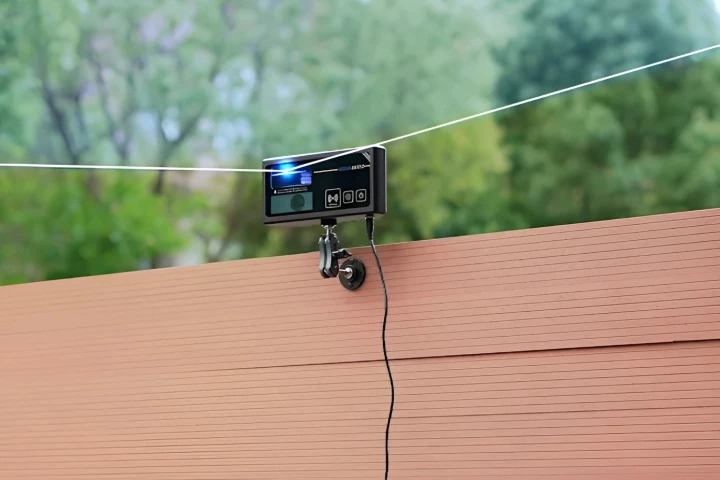
In what it is claiming as a world record and breakthrough for solar thermal energy, researchers at Australia's CSIRO have used solar energy to generate "supercritical" steam at its solar thermal test plant in Newcastle, Australia. Using a field of more than 600 directional mirrors (heliostats) directed at two towers housing solar receivers and turbines, the researchers generated steam at a pressure of 23.5 MPa (3,400 psi) and 570° C (1,058° F).
Generating supercritical steam, an ultra-hot, ultra-pressurized steam that’s used to drive the world’s most advanced power plant turbines, has previously only been possible using fossil fuels, such as coal or gas. The CSIRO is touting its generation using solar technology as a breakthrough for solar energy production, with Dr Alex Wonhas, CSIRO's Energy Director, seeing it as a potential revolution for the renewable energy industry.
"It's like breaking the sound barrier; this step change proves solar has the potential to compete with the peak performance capabilities of fossil fuel sources," Dr Wonhas said. "Instead of relying on burning fossil fuels to produce supercritical steam, this breakthrough demonstrates that the power plants of the future could instead be using the free, zero emission energy of the sun to achieve the same result."
Commercial solar thermal power plants that currently exist use subcritical steam that is generated at similar temperatures to the CSIRO experiment, but at lower pressures. The difference between subcritical and supercritical power plants is that the former operate at lower pressures, which allows bubbles to form when heating takes place, leading to inefficiencies.
However, by increasing the pressure, the boiling temperature also increases and the latent heat of vaporization decreases. Supercritical steam powerplants operate at such high pressure that the latent heat of vaporization is zero; in other words, liquid water is converted directly to steam. Modifying subcritical plants to operate on supercritical steam would vastly increase their efficiency and could help significantly lower the cost of generating solar electricity while negating the need to use fossil fuels to achieve the same result.
Supported by the Australian Renewable Energy Agency (ARENA) the research program is part of a wider collaboration with one solar thermal electricity supplier, Abengoa Solar. ARENA CEO Ivor Frischknecht in recognizing the importance of the realization of CSIRO’s work, said, "this breakthrough brings solar thermal energy a step closer to cost competitiveness with fossil fuel generated power."
The CSIRO says that although commercial development of the technology could still be a fair way off, the breakthrough is a big step in paving the way for a low cost, low emission energy future.
The video below shows the setup at its Energy Centre in Newcastle used to achieve the breakthrough.
Source: CSIRO