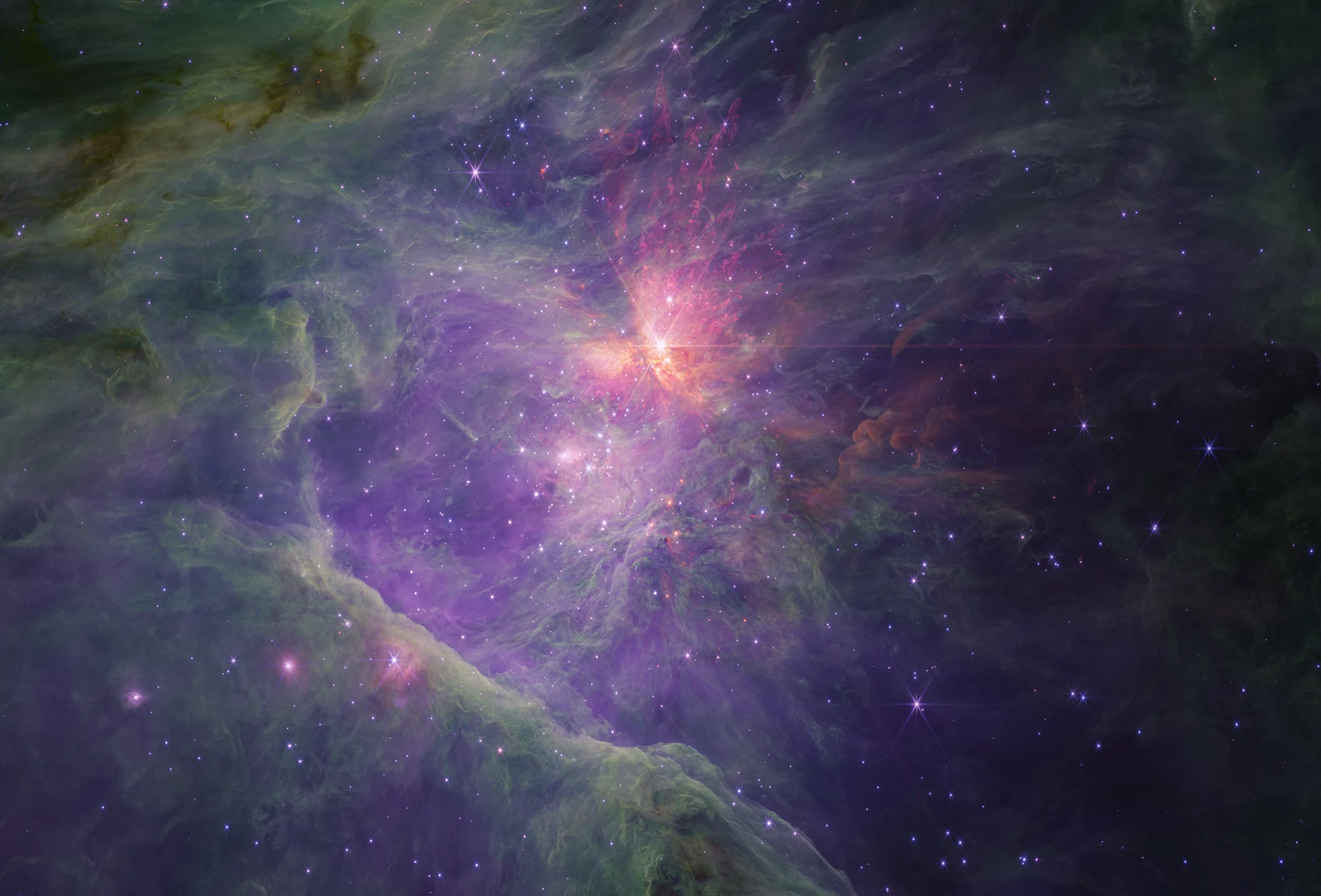
Hiding within new images of a nebula captured by the James Webb Space Telescope, astronomers have made a puzzling discovery – dozens of Jupiter-sized objects that defy explanation.
The discovery was made in Messier 42, the bright nebula located within the constellation of Orion. James Webb, being an infrared telescope, is perfect for peering through big clouds of dust and gas such as nebulae, so astronomers trained it on this one to see what they could find.
Maps of the region are now fully explorable in ESASky, the European Space Agency’s online astronomical data visualization system. Scientists and general users alike can scroll around high-definition images of the night sky, view it in different wavelengths of light, and zoom way in on any random spot to see what’s there.
The expected (but no less spectacular) finds included still-forming protostars and young stars with dusty disks around them, as well as incredible structures carved into the nebula through the interplay between radiation and chemistry.
But zoom in on certain areas and you might spot pairs of tiny dots. They don’t look like much to the untrained eye, but the existence of these mysterious new objects doesn’t really make sense, and might usher in a new category of astronomical entity.

The team has dubbed them Jupiter-mass binary objects (JUMBOs), and that tells you pretty much everything you need to know about them. They have masses from about half to a few times that of Jupiter, and most of them are found in binary pairs for some reason. Their most perplexing feature though is that they’re free-floating through space, not orbiting any star.
While free-floating or “rogue” planets have been discovered before, the sheer number of objects in this region – more than 30 pairs – raises some difficult questions. How did they form? Where did they come from? And how did they end up so consistently in pairs?
Usually planets are thought to form in the dusty disks around young stars, and it’s always possible that a game of gravitational billiards knocks some of them out into interstellar space. But for this to happen so many times in one region of space seems unlikely, and even in that scenario the chaotic interactions should make it nigh on impossible for so many of them to buddy up.
Currently, our best models for how stars and planets form can’t explain these JUMBOs. Even though they’re planet-sized, technically they can’t yet be classified as planets. Future observations might help provide new clues, but in doing so we may need to revise some fairly fundamental models.
The JUMBOs and other features of the Orion Nebula can be explored in ESASky.
Source: ESA via The Guardian