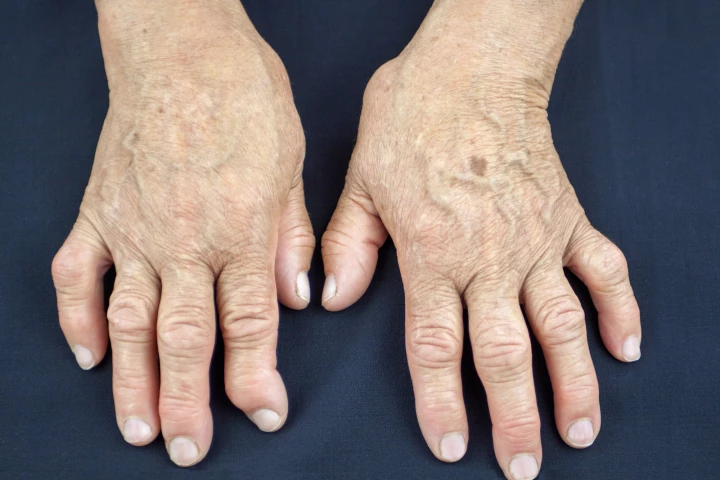
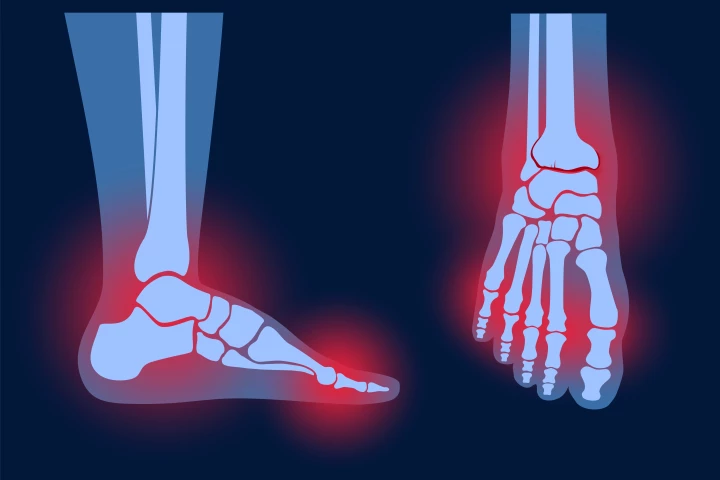
Arthritis
-
Researchers have developed a 3D organ-on-a-chip that mimics the human joint. The discovery will help researchers understand the pathology of joint diseases better and assist with the development and testing of new treatments for arthritis.
-
Researchers have called for a review of the recommendations for the treatment of hand arthritis, after a large study revealed that injections were as ineffective as a placebo for pain relief. Injections are considered the most effective pain reliever.
-
In a world first, Budapest Zoo gorilla Liesel has received stem-cell therapy for her arthritis. It's hoped that this groundbreaking procedure, which aims to rejuvenate her damaged joint cartilage, will not just help her but be adapted for human use too.
-
Scientists investigating new treatments for hand osteoarthritis have made promising new inroads through research on a drug originally developed for acne and psoriasis, with work now underway to ascertain its potential as a new clinical therapy.
-
A common diabetes drug has been linked to a reduction in the need for joint replacement surgery. The observational study suggests the drug could be helpful for patients with osteoarthritis, although further clinical work is needed to validate the association.
-
Immune suppression can help relieve symptoms of autoimmune diseases, but it can cause complications. A new nanoparticle therapy selectively targets problematic immune cells, and was able to significantly delay and even prevent arthritis in mice.
-
A pair of new studies have revealed evidence corticosteroid injections can hasten progression of knee osteoarthritis. The research, yet to be peer-reviewed and published, indicates hyaluronic acid injections may be a better pain relief option.
-
New data suggests long-term use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as naproxen or ibuprofen, can be associated with hastened progression of osteoarthritis symptoms. The researchers are cautious to stress the link is still observational.
-
A new study has provided more evidence gut bacteria plays a role in the development of rheumatoid arthritis. The research suggests an abnormal immune response to a common species of gut bacteria could influence the development of the disease.
-
A research team has discovered a novel mechanism in which a key protein drives the inflammatory damage associated with rheumatoid arthritis. The foundational finding could lead to entirely new pathways to treat this autoimmune disease affecting millions.
-
Positive Phase 3 trial results for a new antibody treatment targeting rheumatoid arthritis have recently been reported. The therapy is hoped to offer a new option to patients struggling with current treatments and should be available within the next year.
-
When it comes to the different ways of exercising the human body, walking is about as accessible as they come, and new research suggests it could be a powerful way to tackle osteoarthritis in the knees.
Load More