Bacteria
-
Researchers have discovered a certain kind of sugar that is only found on the surface of bacteria. Targeting it could lead to an entirely new class of immunotherapeutic drugs designed to target and eliminate at least one deadly, drug-resistant bug.
-
A bacterium from the gut of Japanese tree frogs has "exhibited remarkably potent" tumor-killing abilities when administered intravenously, outperforming current standard therapies and paving the way for an entirely new approach to treating cancer.
-
Deep in the growth rings of Pyrenean trees lies the strongest evidence yet for what set the Black Death in motion – a direct link between a sudden climate shift and the plague’s arrival in Europe, where it killed millions between 1347 and 1353.
-
Instead of growing, harvesting, processing, and shipping fabric across the world, why not let non-polluting bacteria grow it and dye it in a single container? Korean scientists are taking the first steps towards doing that very thing.
-
An antibiotic primarily used in veterinary medicine was found to turn the gut into a factory that pumps out life-extending compounds. The finding could change the way we think about the development of longevity drugs.
-
A novel treatment for irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is on the horizon, with the discovery that two specific gut microbes produce serotonin that protects against inflammation and damage.
-
A study has for the first time homed in on the specific combination of temperature, acidity, and microbes involved in the fermentation process for cocoa beans. They propose an ideal microbial formulation for developing the flavors of fine chocolate.
-
Sequencing mammoth DNA has already helped scientists map out how these Ice Age giants evolved, migrated, and survived. But there's a hidden layer of history still waiting to be decoded – the microbes that lived inside them.
-
For the first time, scientists have identified 27 bacteria and fungi in our mouth that contribute to pancreatic cancer. Collectively, carrying all of these “bad” microbes increases cancer risk by 250% – 3.5 times higher than in the general population.
-
One of the problems with microplastics lies in the fact that the plastic particles can be so small, we don't even know they're present in water in the first place. A new type of engineered bacteria could help, by causing the particles to glow green.
-
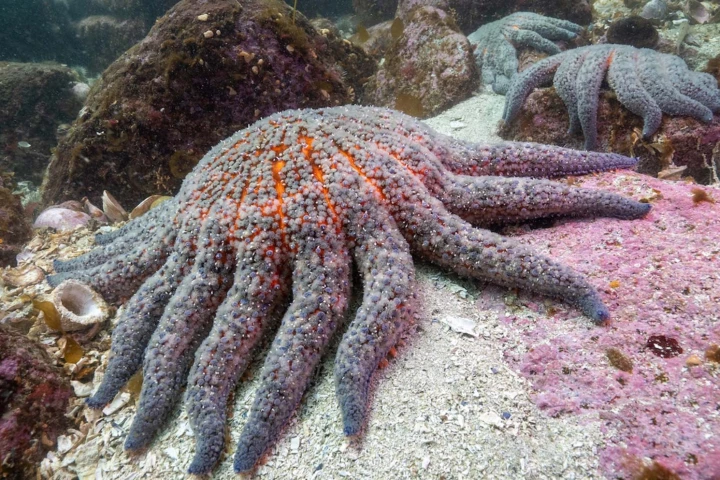
A mysterious marine epidemic has killed billions of sea stars from North America’s Pacific coast. After more than a decade of unanswered questions, scientists have finally traced the disaster to a single bacterial species.
-
What we eat, what drugs we take, and even the timing or combination of treatments could influence how bacteria respond to antibiotics. A food ingredient like caffeine or a second medication might tip the balance, making antibiotics less effective.
Load More