Blood
-
Diagnosing celiac disease often means exposure to the thing that makes you sick, which can be debilitating. It may soon be simpler and pain-free, with a first-of-a-kind test that can detect and gauge the severity of the disease in a test tube instead.
-
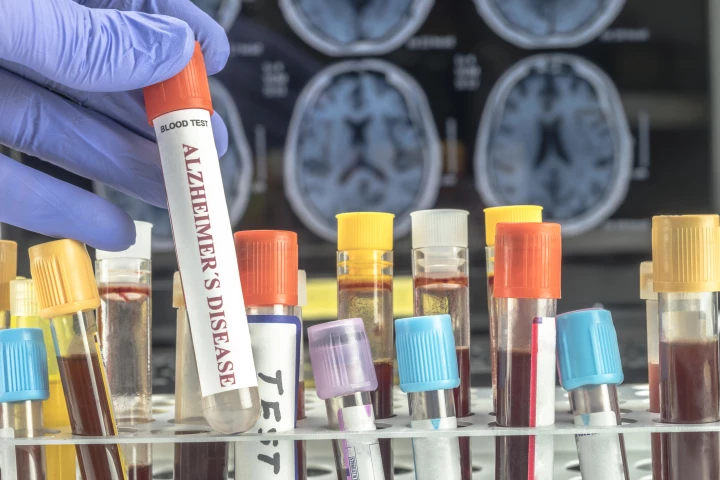
The first blood test for Alzheimer's disease detection has been green-lit by the US Food and Drug Administration, providing a simpler, quicker and less invasive method of diagnosis and speedier intervention. It's a milestone moment for medical science.
-
Scientists at Oregon Health and Science University (OHSU) have developed a new blood test for pancreatic cancer, one of the most deadly forms of the disease. Tests showed up to 85% accuracy in detection, even in early stages.
-
The body has a remarkable ability to heal injuries, but it has its limits. Now scientists have developed a way to improve on the natural process, making implants created from a patient’s own blood to regenerate injuries, even repairing bone.
-
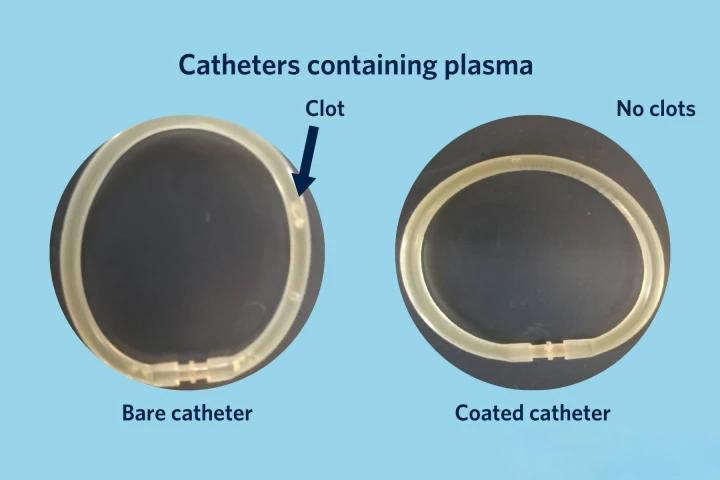
When a patient's blood flows through catheters, stents or other medical devices, there's always a risk that harmful clots may form. An experimental new bio-inspired coating could keep that from happening, without the use of blood-thinning drugs.
-
Nobody enjoys giving blood samples, but it’s a necessary part of doctor visits. Soon we might not have to, thanks to a new device that can isolate biomarkers for different diseases using sound waves, from a single drop of blood, in around an hour.
-
If a medical professional has ever had a hard time getting a needle into your veins, you'll welcome this new gizmo from Adison Technology. By effectively turning your skin transparent, it makes needle sticks more accurate and therefore less painful.
-
Toxic “forever chemicals” are a major environmental problem, and a growing body of research shows they’re also a major health problem. A new study has found people with higher levels of PFAS in their blood have poorer sleep.
-
Leeches may be creepy, but many people find hypodermic needles even creepier. That's one of the reasons why scientists have developed a new leech-inspired blood collection device, which draws blood samples without the need for a big jab.
-
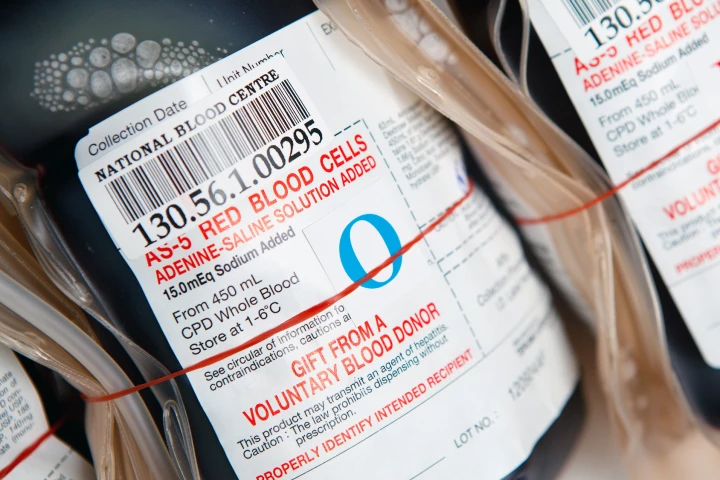
Using enzymes produced by a bacteria that almost everyone has in their gut, researchers have removed the antigens from red blood cells that determine blood type, putting us within reach of producing universal donor blood.
-
Researchers have developed a blood test that can accurately detect whether someone has been awake for 24 hours or more. They foresee the test being used like those that measure alcohol concentration or test for the presence of drugs in drivers.
-
A new technique, which involves melting bacterial DNA found in blood samples, could deliver diagnoses of potentially fatal infections faster than ever before. Results may be obtained in a few hours, instead of days.
Load More