Carbon
-
Scientists at KIST have built a working electric motor with metal-free windings, replacing copper entirely. It's much lighter and could reshape the future of EVs, drones, and electric aircraft.
-
Using machine learning, a team of researchers in Canada has created ultrahigh-strength carbon nanolattices, resulting in a material that's as strong as carbon steel, but only as dense as Styrofoam.
-
Using principles from rocket science, researchers have created carbon with a record-breaking surface area. The material can soak up about twice the amount of CO2 as current activated carbon materials and has impressive energy-storage capabilities.
-
A 3,775-year-old log discovery has lent credence to the idea of burying wood to sequester the carbon it contains. Known as a wood vault, the concept helps keep CO2 out of the atmosphere while allowing the soil to be used for crops and other purposes.
-
BC8 superdiamonds are harder than any known material, but they likely only exist in the cores of giant exoplanets. Now, the Frontier supercomputer has unraveled the secret of their formation, a finding that could lead to their production on Earth.
-
Using biowaste from cassava plants, scientists have created a coating that virtually eliminates friction in metal parts. The breakthrough has the potential to deliver better fuel economy and deliver enormous savings in myriad industries.
-
Despite evidence that indicates we're now living beneath unprecedented levels of atmospheric greenhouse gases, a lack of historical records has meant we've had little to compare it to. So scientists decided to consult the planet's own record books.
-
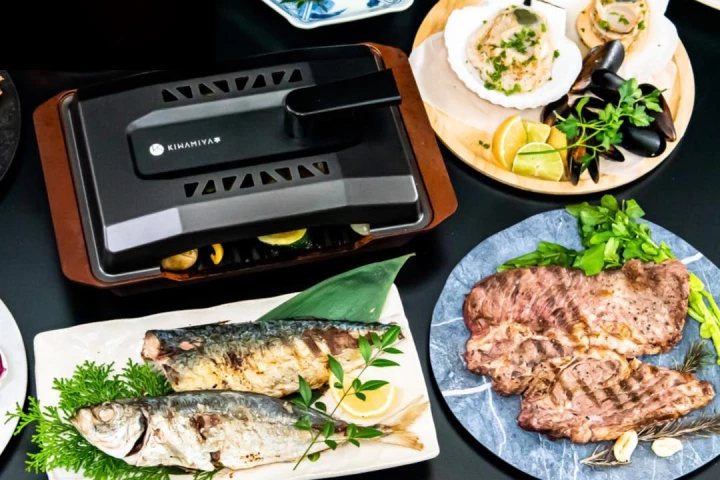
For many people who live in places that get "real" winters, barbecuing is an activity that gets put on hold once the snow flies. The Grill-X was designed with that fact in mind, as it reportedly brings a charcoal flavor to foods grilled indoors.
-
Researchers have developed a new, lightweight foam made from carbon nanotubes that, when used as a helmet liner, absorbed the kinetic energy caused by an impact almost 30 times better than liners currently used in US military helmets.
-
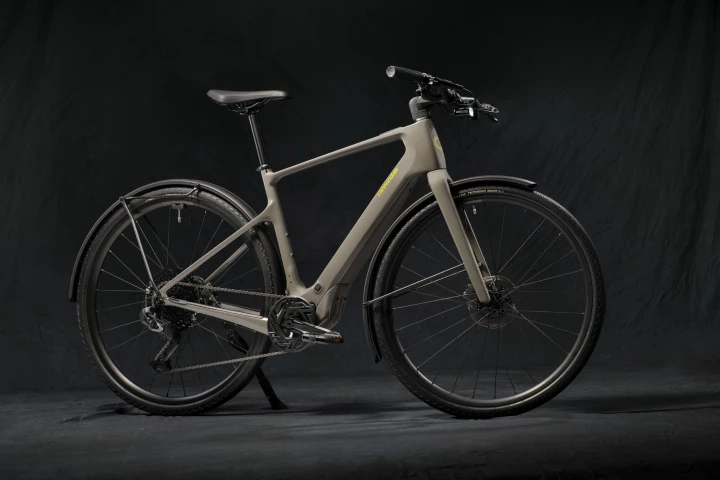
Cannondale has dissected the DNA of its Synapse road bike to create a tasty carbon-framed "commuter bike that would make a pro cyclist smile." The Tesoro Neo Carbon ebike is a Europe-only release, and rides out with Bosch power.
-
Our Sun is capable of terrifying outbursts – and now scientists have discovered evidence of its biggest tantrum on record. Tree rings dating back 14,000 years contain a radiocarbon spike twice as powerful as the previous biggest known solar storm.
-
The best places to search for life beyond Earth aren’t planets like Mars – they’re icy moons like Europa. The case for life on this watery world just got stronger, as the James Webb Space Telescope has detected a fresh carbon source there.
Load More