Cedars-Sinai
-
Scientists have uncovered an intriguing link between infection and brain health, finding that a common bacterium may advance cognitive decline. It's the latest evidence suggesting that bacteria and infections play a key role in destroying our brains.
-
After two decades in the making, scientists have cracked the code on a drug that can repair DNA, setting the scene for a new class of therapeutics that can fix tissue damage that occurs through heart attack, inflammatory disease and other conditions.
-
A new drug combination to treat advanced recurring prostate cancer has shown remarkable results in a long-term trial, lowering the risk of death after eight years by 40.3%. What's more, the drug treatments are already FDA-approved on their own.
-
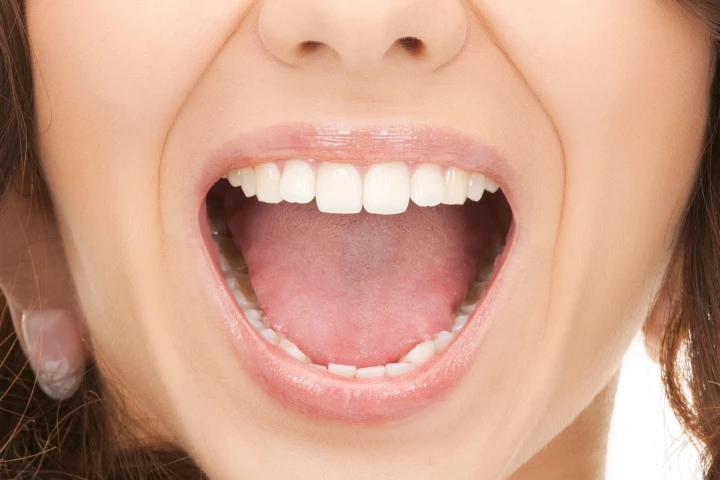
We all know that injuries inside the mouth heal quicker than those on the outside of the body. Scientists have a new understanding of why, and believe that their findings could be used in wound treatments that reduce or even eliminate scarring.
-
Researchers have created a way to guide and control the development of stem cells into specific tissues and organs, opening the door to developing a means of one day tackling complex diseases like diabetes and Parkinson’s disease.
-
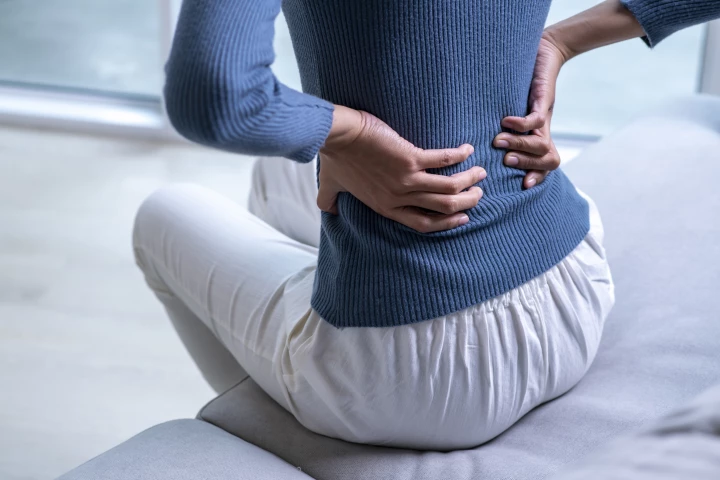
In big news for the millions who suffer from chronic lower back pain due to degraded disks, scientists have made a potentially huge breakthrough in understanding its cause at a microscopic level, paving the way for effective cell therapy to relieve it.
-
The warning signs of a deadly out-of-hospital sudden cardiac arrest differ significantly between the sexes, a study has found. Researchers hope their research will improve survival rates and educate people about when to call emergency services.
-
Research has found over the course of the pandemic heart attack deaths have spiked alongside COVID-19 infection waves. The findings cannot causally link the heart attacks to COVID, however prior studies have found SARS-CoV-2 infections can damage the heart.
-
A new AI tool can accurately measure plaque deposits in arteries and predict a patient’s risk of suffering a heart attack within five years. The tool promises to achieve in seconds what has previously taken trained experts up to 30 minutes to deliver.
-
Cedars-Sinai researchers are reporting even mild COVID-19 cases show lingering signs of an overactive immune system months after the acute disease, and experts are concerned the current wave of Omicron infections could lead to huge rates of long COVID.
-
New research suggests Parkinson's may be present in the brain right from birth, as malfunctioning neurons are always there. Thankfully, a drug that’s already on the market could help prevent the disease from taking hold if caught early enough.
-
BMI is often criticized because it doesn't take into account gender differences and doesn't distinguish between bone mass, muscle mass and excess fat. Researchers at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center have now come up with a formula they claim paints a more accurate picture of one's body fat.
Load More