Diabetes
-
Synching your daily calories with your own circadian rhythm can improve glucose metabolism, protecting against type 2 diabetes and obesity. A new study uncovers the relationship between metabolic health and our personal, inherent biological clock.
-
A new study reveals that Americans are confused about what “processed food” actually means, and which types pose health risks. Researchers found major gaps between public perception and science, highlighting the need for more comprehensive education.
-
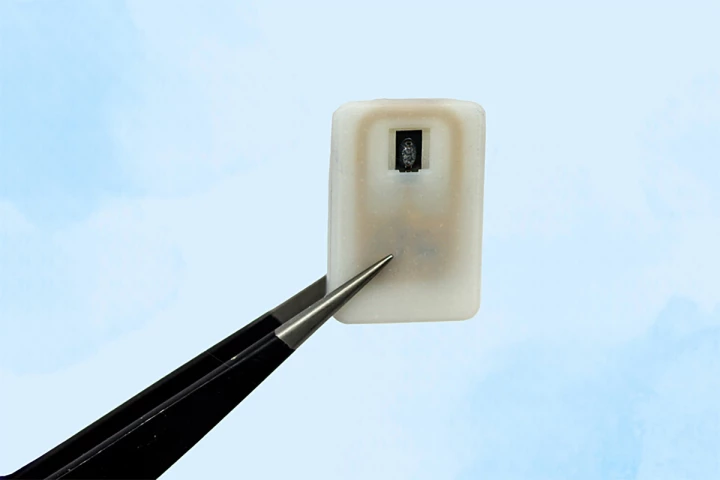
Engineers at MIT have developed a coin-sized device that can be safely implanted in the body to automatically deliver a dose of glucagon when a sensor notices blood glucose levels dropping too low – and potentially save the user's life.
-
If you have a high level of interaction with patients, students, clients or the general public in your work, you might be at much higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes. And, if you also have poor support at work, it could worsen your odds further.
-
Over the weekend, Novo Nordisk dropped a pile of scientific data on three new experimental weight-loss drugs, including an oral one, showing what appears to be a strategic "something for everyone" plan of attack from the pharmaceutical giant.
-
A novel weight loss drug in the same class as semaglutide has successfully met its targets in the largest clinical trial yet, with nearly 90% of participants losing at least 5% of their body weight. The results strengthen its case for FDA approval.
-
Diabetic foot ulcers are prone to recurring, even when they look healed. A new study used an existing method to assess the degree of water loss from the skin and found that it was a good diagnostic tool for predicting a foot ulcer’s comeback.
-
The first once-daily oral GLP-1 medication could be on shelves by this time next year, making the weight-loss drug easier to take and potentially cheaper. In the race to be the first, Novo Nordisk has scored a huge win, while Pfizer has failed again.
-
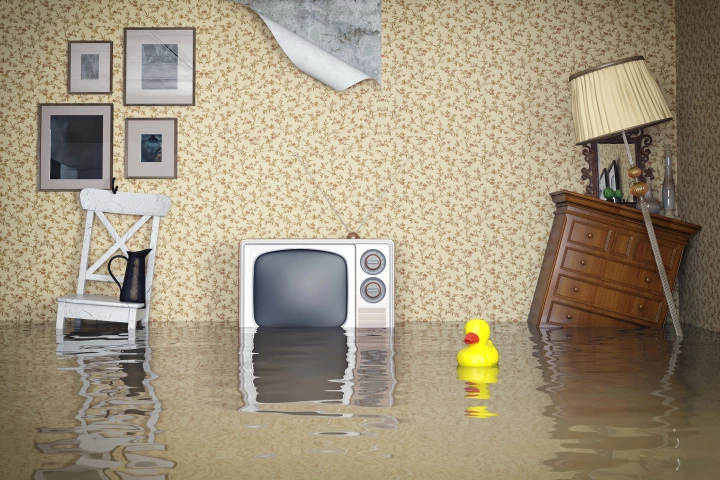
The world's largest study into the long-term health impact of floods has found that there are surges in hospitalizations for months after an event – and current responses are inadequate when it comes to treating cancer, diabetes, mental health and more.
-
Scientists have developed smart insoles that accurately measure the forces created when a foot hits the ground in the real world. The tech has a range of applications, from assisting in rehabilitating patients to helping athletes prevent injuries.
-
Researchers at the National University of Singapore have hit upon new technologies to deliver a double whammy to chronic wounds in diabetics, using tiny needles barely visible to the human eye.
-
It was only a matter of time until the GLP-1 receptor agonist drugs like Ozempic and Wegovy were superseded, and now it looks like we'll have the next generation of these breakthrough weight loss and diabetes medicines on shelves by early next year.
Load More