Diagnosis
-
Researchers engineered a probiotic bacteria to release a marker that can be detected in the urine after it comes into contact with bowel cancer, even when it's in the early stages. The novel test may mean avoiding messy poo-based screening tests.
-
A study has found that a rectal exam alone or in combination with a blood test doesn't improve prostate cancer detection, suggesting the exams could be omitted from prostate cancer screening in men who don’t have clinical signs and symptoms.
-
MIT scientists have developed an easier method for diagnosing lung cancer – breathe in some inhalable nanoparticle sensors, then pee on a stick. The method should be less invasive than CT scans, and easier to perform in low-income regions.
-
Researchers have found that inexperienced doctors performing AI-assisted colonoscopies significantly improved their detection of polyps. Using AI in this way could lower the chances of missing these potential precursors to colorectal cancer.
-
In a finding that could have a significant impact on personalized medicine, scientists have identified five blood compounds linked to suicidal ideation. It could prove crucial in assessing risk factors and for new targeted treatment of depression.
-
Researchers have developed a simple blood test that improves the diagnosis of bipolar disorder, a commonly misdiagnosed condition. The test could ensure that people receive the correct treatment and identify potential drug targets for mood disorders.
-
A new study has found that globally, the rates of new cancer cases and associated deaths in people under 50 increased alarmingly between 1990 and 2019, highlighting the importance of education on the incidence of certain cancers in younger people.
-
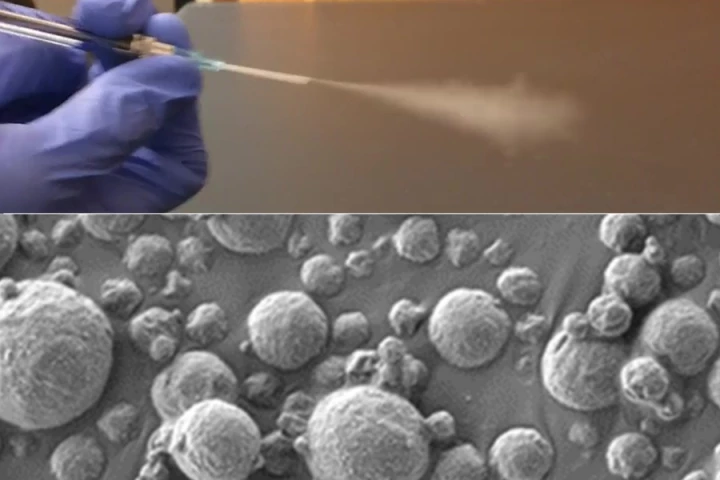
Certain gut bacteria have been linked to colon cancer, but now they might get a chance at redemption. Scientists have engineered “pickpocket” bacteria to detect colorectal cancer, with a 100% success rate in mouse tests.
-
For the first time, through brain scans, assessments and therapies, researchers have identified a subtype of depression that features more pronounced cognitive dysregulation, with common treatment missing the mark on combatting debilitating symptoms.
-
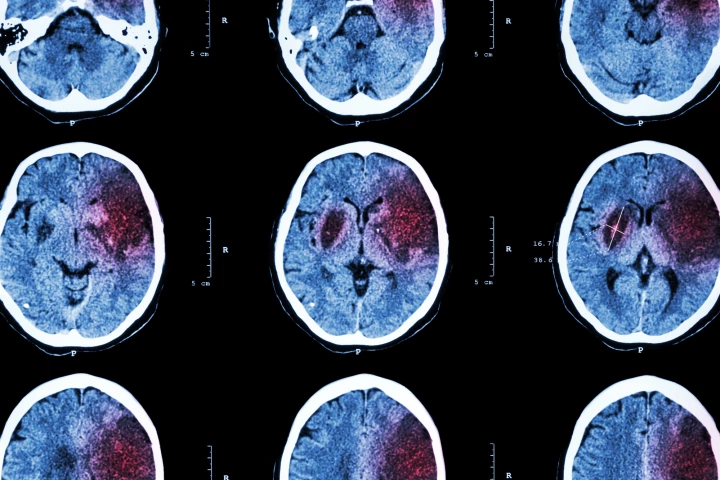
Stroke can be tricky to diagnose as patients don’t always present with classic symptoms, and other conditions can mimic it. Researchers have now developed a machine-learning model that accurately predicts stroke and may make diagnosis easier.
-
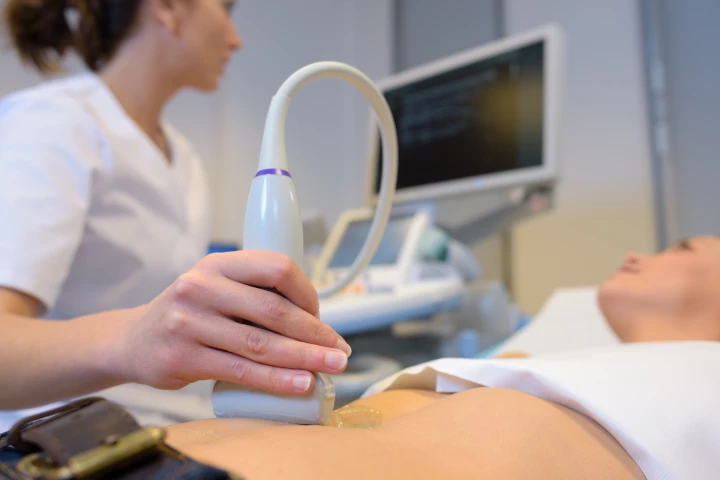
Researchers have developed a breakthrough ultrasound method that uses shear waves to, for the first time, measure tension in human tissue. The discovery has to the potential to revolutionize disease diagnosis.
-
In a new study published in Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, researchers propose urine tests as a potential way to detect Alzheimer's disease. The study suggests formic acid levels in urine could be a useful early-stage biomarker for the disease.
Load More