Diagnostic tools
-
Scientists have developed a new rapid test for hepatitis C. It is easy to use, highly sensitive, and made for point-of-care places like clinics and community centers. The speed allows clinicians to diagnose and start treatment in the same visit.
-
Thermal imaging has become wildly accessible, thanks to technological advancements that have made it more affordable than ever. Thermal Master's Thor 002 sits squarely in that sweet spot. And it's about a third of the price of its main competitors.
-
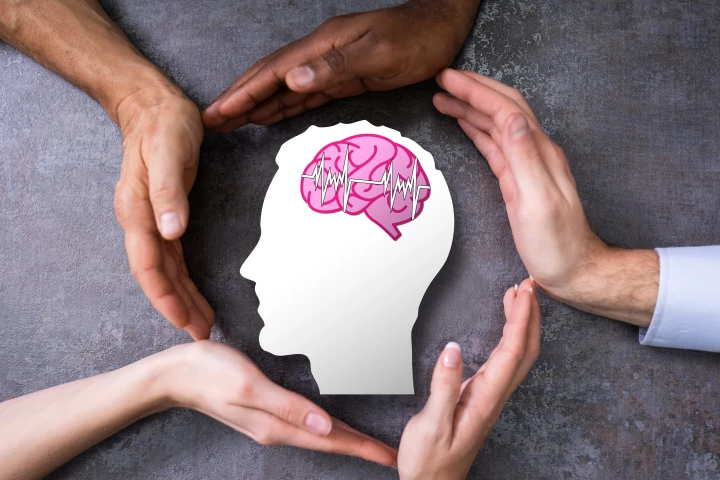
Groundbreaking research has uncovered three gene variants that increase the risk of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder by up to 15 times. It's a remarkable finding, considering that thousands of mutations only come with a nominal elevated risk.
-
In a breakthrough for diagnostics, scientists have created an effective and easy test that identifies a heart failure biomarker in saliva, opening the door to more rapid and accessible life-saving medical interventions for this disease – and others.
-
Researchers believe they have developed the first blood test to diagnose chronic fatigue syndrome, or myalgic encephalomyelitis, and it has the potential to be a game-changer for millions around the globe suffering with the debilitation condition.
-
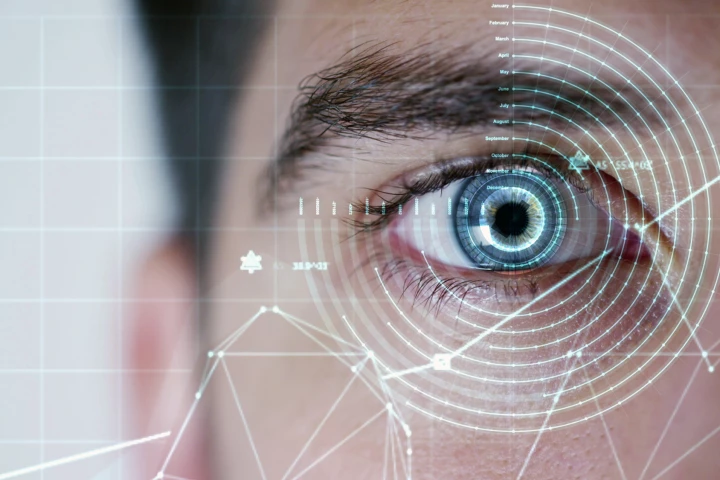
Scientists have developed a powerful new dual-imaging tool that maps the retina’s structure and oxygen use in unprecedented detail. This breakthrough could one day help doctors spot sight-stealing diseases long before symptoms appear.
-
Among the many problems with the flu is the fact that you can spread the virus before you even know you've got it. An experimental new "sensor" could one day keep you from doing so, by causing you to taste thyme in your mouth.
-
Scientists have rejected claims that acetaminophen is a key driver of autism spectrum disorder, cautioning that research is inconclusive and excludes genetics and a suite of other influences. What's more, it focuses on a "cure," not understanding.
-
A new study significantly strengthens the case that attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder brains are structurally unique, thanks to a new scanning technique known as traveling-subject method. It isn't down to new technology – but better use of it.
-
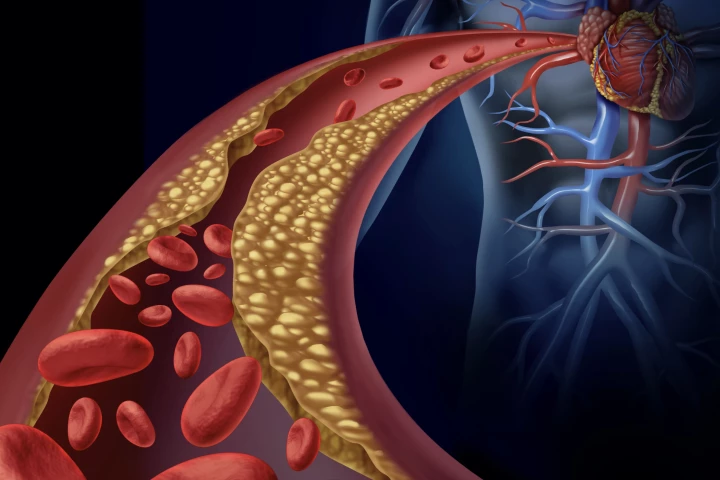
A new generation of nanoparticles can detect, shrink and clear plaques in the arteries, lowering inflammation and drawing out harmful cholesterol to be cycled via the liver. They offer a new way of diagnosing and fighting heart disease without drugs.
-
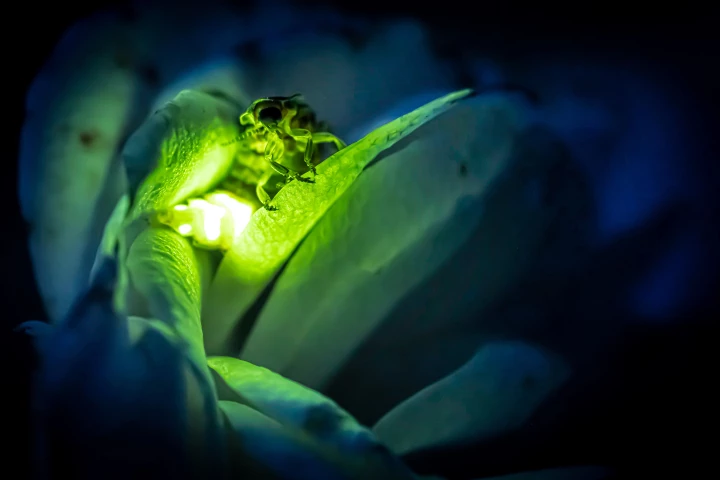
Animals that produce their own light source, through an internal chemical reaction, are a true wonder of nature – and something biotechnology scientists have been working hard to replicate and adapt for human use. They've now made a huge breakthrough.
-
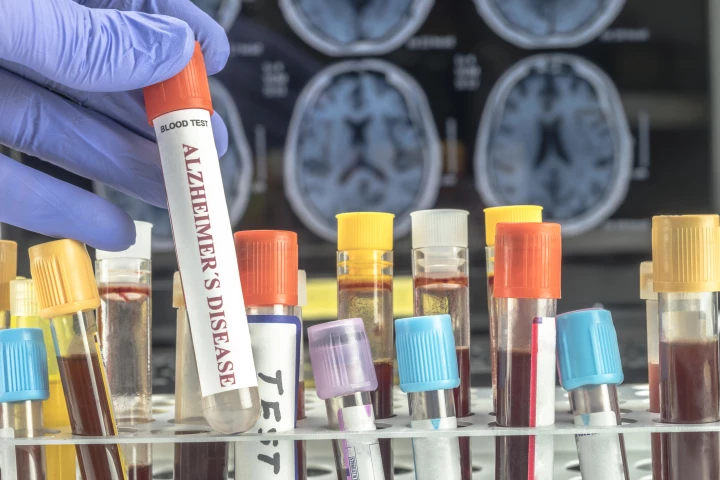
The first blood test for Alzheimer's disease detection has been green-lit by the US Food and Drug Administration, providing a simpler, quicker and less invasive method of diagnosis and speedier intervention. It's a milestone moment for medical science.
Load More