Disease
-
A new study challenges the idea MS is just one single disease presenting evidence it may actually follow two distinct biological pathways. It’s a shift that could reshape how clinicians think about diagnoses, disease progression and treatment strategy.
-
Deep in the growth rings of Pyrenean trees lies the strongest evidence yet for what set the Black Death in motion – a direct link between a sudden climate shift and the plague’s arrival in Europe, where it killed millions between 1347 and 1353.
-
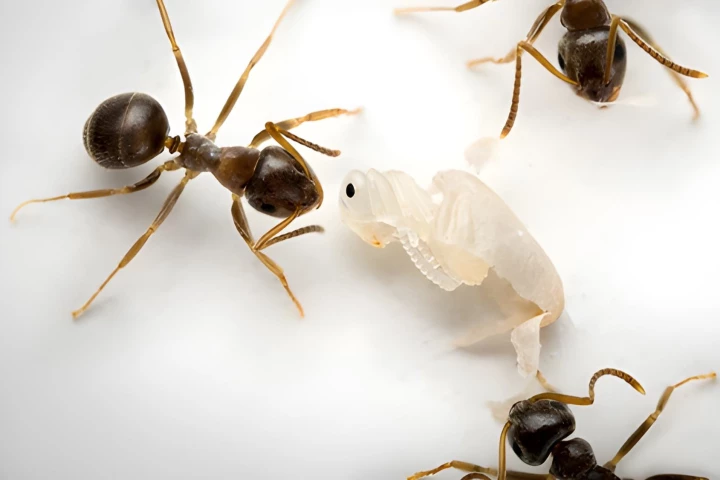
In a wide range of social species, when an animal is sick, it takes itself away from its group. Ant pupae are unable to move, however, so they've developed a unique mechanism that leads them to sacrifice their own life for the betterment of the nest.
-
One of the first events to signal the collapse of Napoleon's reign was his crushing defeat after an invasion of Russia in 1812. Researchers have long thought that the disease typhus played a role, but modern DNA analysis paints a different picture.
-
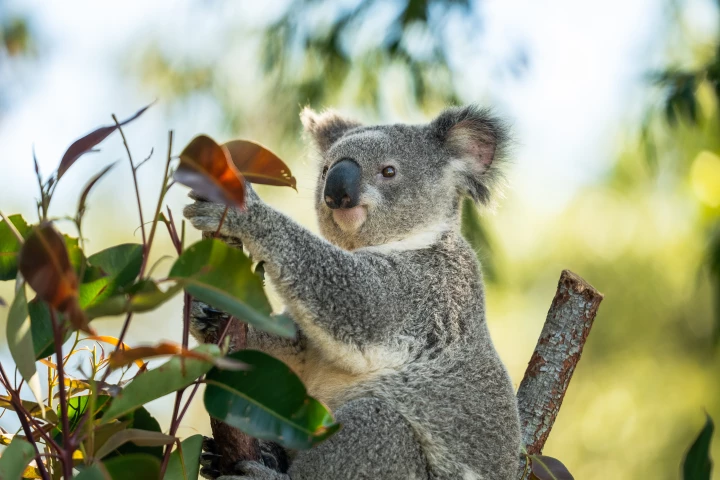
Australia's embattled koalas have been given some good news for once, with the approval of the world's first chlamydia vaccine. More than a decade in the making, a single jab will now protect koalas from the disease decimating their populations.
-
In a landmark move, the FDA has given biotech company eGenesis the go-ahead to conduct a wider trial of pig-to-human kidney transplants, marking a significant step forward in addressing the critical organ shortage now facing thousands of Americans.
-
Got asthma? Then you might also go on to get Parkinson's. Celiac? You'll want to watch out for lung cancer. That's the kind of information you can get on a new website that uncovers the links between common conditions based on genetic analysis.
-
A novel way to prevent the spread of malaria by directly targeting the proteins that enable the infectious parasite to reproduce could soon be realized, thanks to scientists at WEHI in Australia.
-
The fitness community regularly touts the health benefits of getting in 10,000 steps per day. But a new study says that a good deal fewer steps can still deliver significant benefits, including a 47% reduction in dying prematurely.
-
A massive study of over 1.2 million children has found no link between aluminum-containing vaccines and 50 chronic childhood conditions, including autism, ADHD, asthma, and diabetes, delivering a reassuring message about vaccine safety.
-
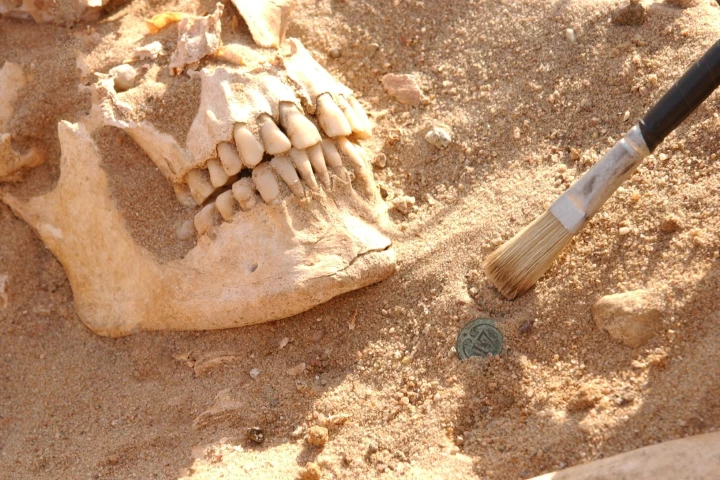
Humans have been getting infected by ancient bacteria and viruses for at least 37,000 years. Now, for the first time, pathogen DNA has uncovered a pivotal disease "turning point" that happened 6,500 years ago, which would forever change our lives.
-
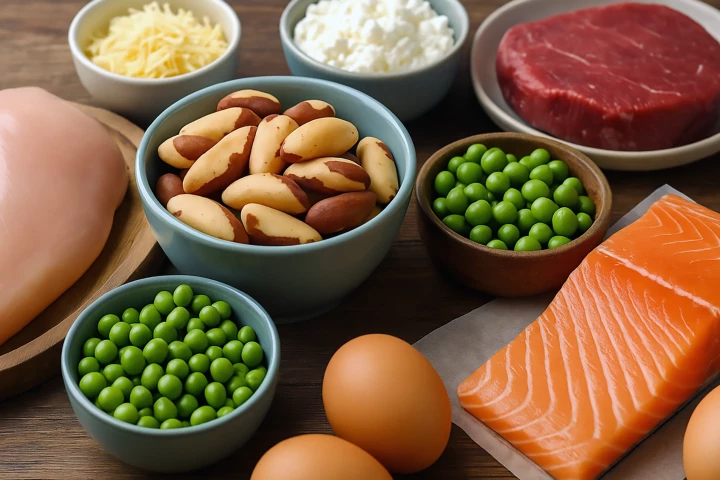
Reducing our intake of a single amino acid called methionine, which we get from the food we eat, could help protect against disease and promote healthy aging. Now, scientists have a better method for studying the effects of this critical compound.
Load More