Drugs
-
For the first time, scientists have identified ancient cannabis enzymes dating back millions of years – and discovered they were more efficient at producing the plant’s bioactive compounds like THC and CBD. The team then resurrected them in the lab.
-
Millions of Americans can now look forward to a better time traveling, with the US Food and Drug Administration approving a novel oral pill that helps prevent motion-induced vomiting – the first of its kind in more than 40 years.
-
A new review reveals finasteride users face higher risks of depression, anxiety, and suicidal thoughts. Concerns about the drug's underreported mental health side effects prompt calls for stricter regulation.
-
Researchers have identified specific regions of the human genome connected to cannabis use, which means the propensity to get addicted to weed may be encoded in our DNA.
-
People with cannabis use disorder had more than triple the odds of developing oral cancer, a large five-year study found, raising red flags about the carcinogenic risks of heavy cannabis use, especially in its smoked form.
-
Traces of a psychoactive compound has been found in the dental plaque of a woman buried 4,000 years ago, making it the earliest direct chemical evidence of humans chewing betel nut – the world's fourth biggest drug, after tobacco, caffeine and alcohol.
-
While it's very important to know if a "date rape" drug has been sneaked into your drink, whipping out a full test kit in a bar may be time-consuming. That's why scientists have developed a temporary tattoo that can detect such drugs in one second.
-
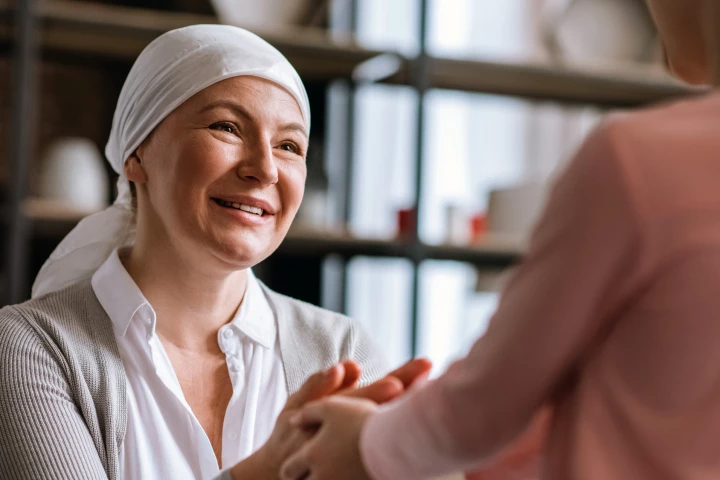
A common anti-nausea drug used during chemotherapy may do more than ease discomfort, it could help women with aggressive breast cancers live longer, cutting the risk of death by up to 39% in some cases, according to a new study.
-
In the ongoing search to find an intervention that does away with opioids, a new game-based system has shown huge promise in tackling chronic neuropathic pain. Using a game and a headset, it "trains" patients to rewire brain signals to relieve pain.
-
A new study has found that smoking marijuana and ingesting THC edibles over the long term can reduce blood vessel function at levels similar to those seen in cigarette smokers, posing a risk to heart health.
-
The first once-daily oral GLP-1 medication could be on shelves by this time next year, making the weight-loss drug easier to take and potentially cheaper. In the race to be the first, Novo Nordisk has scored a huge win, while Pfizer has failed again.
-
For some common medical conditions, timing is everything when it comes to taking medications. Now, a customizable capsule engineered at UC San Diego could simplify complicated dosing schedules thanks to a unique staged release system.
Load More