Dwarf galaxy
-
The endless expanse of space is a beautiful and fascinating subject for photography. From the dramatic births and deaths of stars, to galactic glamor shots and planetary close-ups, here are some of the most breathtaking space photos of 2021.
-
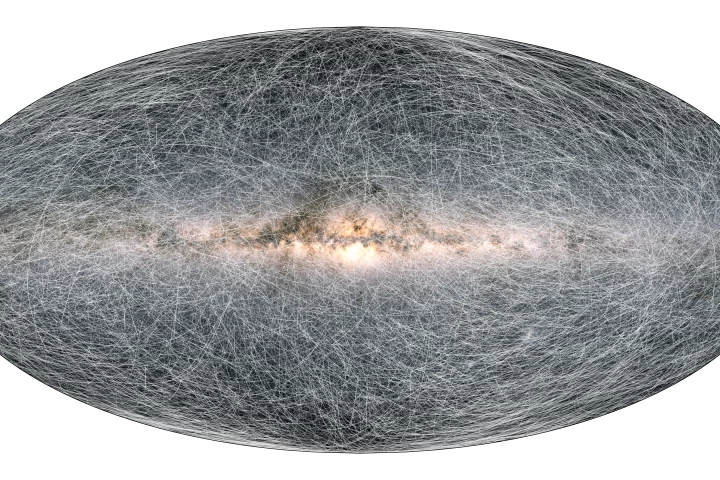
ESA has published a colossal data release from the agency’s Gaia observatory, which is currently engaged in a mission to survey 1 billion stars orbiting in the Milky Way. The data has already shed light on the motion of our galaxy and solar system.
-
A star that shined with 2.5 million times the light of our Sun has disappeared from the night sky. It is possible that the star collapsed into a black hole without first triggering a supernova – a rare event, even in the context of dying stars.
-
The Hubble Space Telescope has captured a view of a stellar laboratory that is being used to understand how truly gargantuan stars come to form. The image features a colorful starfield and a substructure of the famous Tarantula Nebula.
-
A new study has revealed the violent past of the Andromeda galaxy, by identifying the remains of its galactic victims.
-
Last year astronomers discovered a gigantic “ghost” galaxy, named Antlia 2, orbiting the Milky Way. Now, new research led by Rochester University has found that the bizarre galaxy may have been involved in a hit-and-run that left the Milky Way with a wobbly galactic disc.
-
Astronomers have discovered a star in the Milky Way that doesn’t belong. Known as J1124+4535, the star has a chemical composition unlike any others ever observed in our home galaxy, suggesting it’s an intergalactic interloper that may have come from a dwarf galaxy swallowed up by the Milky Way.
-
According to a new study, the Large Magellanic Cloud, a nearby dwarf galaxy, is on a collision course with the Milky Way. But there’s no need to worry just yet – the starry smashup won’t begin for another two billion years or so.
-
Astronomers have spotted a mysterious “ghost” galaxy orbiting the Milky Way. Huge but extremely faint, the oddball galaxy has been named Antlia 2, and it might just be weird enough to force us to rethink what we know about galactic physics and dark matter.
-
Astronomers have discovered a population of incredibly fast-moving stars bearing down on the Milky Way. It is possible that these newly found "hypervelocity" stellar bodies were created in another galaxy, before being hurled out into intergalactic space on a collision course with the Milky Way.
-
An international team of astronomers has now found evidence of a celestial smash-up between the Milky Way and an unknown dwarf galaxy that took place around eight to 10 billion years ago, and forever changed the face of our home galaxy.
-
Astronomers have captured the most detailed view to date of the region of space surrounding the famous Tarantula Nebula – a 1,000 light-year wide swirling cloud of cosmic gas, the core of which is illuminated by some of the brightest and most massive stars ever detected.
Load More