Exercise
-
Choosing a type of exercise that matches your personality might mean you’re happier working out and achieve better results, according to a new study. The research highlights the benefits of a “psychologically personalized” approach to fitness.
-
Harnessing the power of a metabolite produced in the kidneys and absorbed from certain foods can mimic the health benefits delivered by exercise, regulating inflammation and promoting an array of anti-aging processes without any physical activity.
-
Water-based exercise not only improved muscle strength in people with chronic low back pain, but it also improved quality of life, according to a new study. Aquatic therapy could be a viable alternative for those who fear moving or exercising due to pain.
-
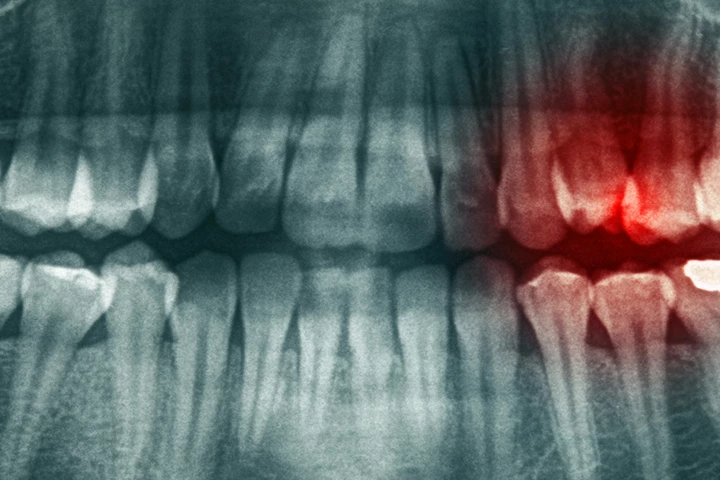
A new study found that combining exercise with omega-3 supplements reduced inflammation and, thereby, the severity of a chronic tooth infection. It suggests a simple means of controlling these infections, which can result in bone and tooth loss.
-
The simple act of walking every day can significantly reduce a person’s risk of developing chronic low back pain, according to a new study. But, its effectiveness depends on how long you walk for, and the speed at which you walk.
-
A landmark study has found that a workable exercise plan significantly improves survival and health of people who have survived colorectal cancer. So much so that, as one researcher notes, "Our findings will change the way we treat colon cancer."
-
From raw eggs at the crack of dawn to whey shakes after workouts – there's a whole lot of advice about the best way to optimize your muscle growth. Has new research settled the debate once and for all, or will it spark even more?
-
A new study of nearly 15,000 people found that the window of late-night workouts in which sleep is impacted is actually much larger than previously thought, showing that exercising within four hours of bedtime can have a detrimental effect on shut-eye.
-
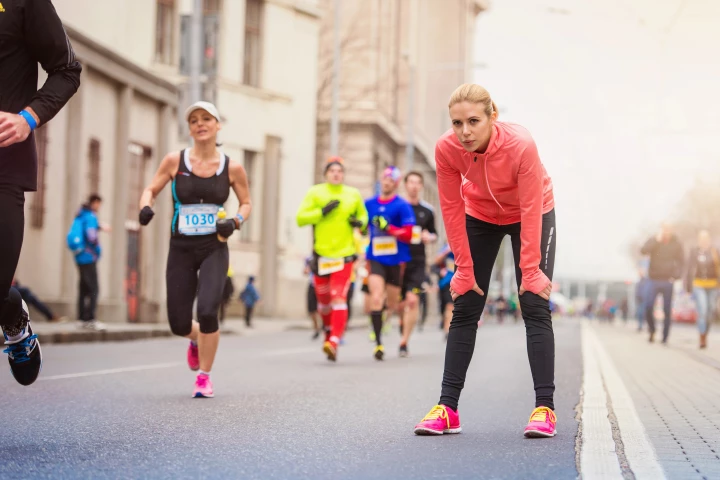
More than a million people of nearly all ages lace up their trainers and hit the pavement in a marathon every year. And while running has a suite of health benefits, a long-distance race may not be such good news for the brain in the weeks that follow.
-
A new study has debunked a popular TikTok wellness trend called cycle syncing, which claims that tailoring a workout routine to match the hormonal changes that occur during the different phases of the menstrual cycle provides a fitness benefit.
-
A new study has ranked the best types of exercise for improving sleep quality. The findings demonstrate that exercise is an easy-to-implement, relatively cheap, and particularly effective way of treating insomnia, a common problem for older adults.
-
A study is building on a body of evidence showing a common supplement used to build muscle may also confer beneficial mental health outcomes. The clinical trial suggests the effects of psychotherapy can be amplified by adding this nutritional supplement.
Load More