Heart Disease
-
A new study has found that, for most of us, the fiber we eat can protect our heart health, lowering the risk of high blood pressure, heart disease or stroke by up to 20%. It’s more evidence showing that a healthy gut leads to a healthy heart.
-
A study examined how managing multiple heart disease risk factors reduced the likelihood of premature death faced by people with high blood pressure. Its findings highlight the need for a broad approach to preventing or treating hypertension.
-
Valvular heart disease (VHD) is a potentially fatal condition, yet it's hard to diagnose with a regular stethoscope. A possibly life-saving new stethoscope is claimed to be much better at the job, plus it can be used by just about anyone.
-
One of the ketogenic diet's major perceived drawbacks is an increase in LDL, or so-called bad cholesterol. A new study, though, says that this cholesterol spike doesn't fit the conventional science in terms of its disease-causing ability.
-
If someone is afflicted with heart disease, it's important that their cardiac activity be monitored as accurately as possible. An experimental new wearable device is designed to make that happen, by copying the body structure of the starfish.
-
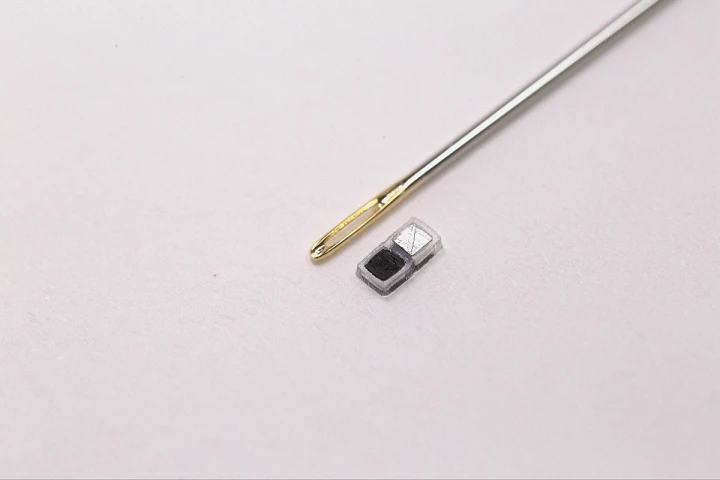
Engineers at Illinois' Northwestern University have developed the tiniest pacemaker you'll ever see. It's several times smaller than a regular pacemaker, and it's designed for patients several times smaller than the average pacemaker user.
-
A man has lived for more than 100 days with a maglev heart beating inside his chest. In a landmark moment, he was discharged earlier this year, becoming the first person in the world to leave the hospital with the device embedded in his body.
-
Aspartame has long been marketed as a guilt-free alternative to sugar in products like Diet Coke and sugar-free Jell-O. However, the sweetener has now been linked to an increased risk of heart attacks in mice. Should you ditch your fizzy drinks?
-
A new study has found that eating between one and six eggs each week significantly reduces the risk of dying from any cause but particularly from heart disease – even in people who have been diagnosed with high cholesterol levels.
-
Most people know that body fat stored around the midsection can spell disaster for cardiovascular health. But Harvard researchers have now discovered another problematic fat-storage location in the body that's been largely overlooked.
-
From fighting memory decline to warding off some cancers, drinking coffee continues to emerge as a way to improve your health. Now, a new study says that the time of day during which you drink your daily brew is key to boosting some of its effects.
-
A naturally occurring fat molecule reduced heart inflammation and scarring caused by diabetes, thereby improving cardiac function, according to new research. The findings open the door to developing a new treatment for diabetes-induced heart disease.
Load More