Immunotherapy
-
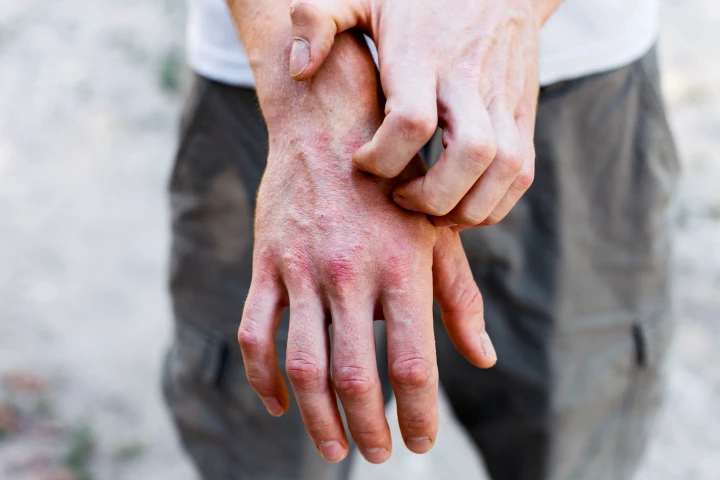
A new immune-modulating treatment has shown promising results for treating moderate to severe eczema, delivering fast itch relief and clear skin for many patients in a clinical trial, without the common side effects associated with other therapies.
-
Taking inspiration from the CAR T-cell technology used to provide personalized cancer treatments, researchers have conducted a proof-of-concept study showing how similar compounds can precisely target protein tangles and plaques in the brain.
-
Positive results from trials of an immune therapy in dogs with bone cancer have been used to fast-track the development of the drug to treat children with the same cancer. It highlights how leveraging our genetic similarity can advantage both species.
-
Recent human trials of a new one-year-long immune-based treatment for post-polio syndrome, which can strike polio survivors years after the initial infection and be very debilitating, have produced positive results.
-
Scientists have uncovered a mechanism for reinvigorating the immune system to stop it from flagging when it’s fighting long-term conditions like chronic infections and cancer. It could make treatments more effective and improve clinical outcomes.
-
A phase 3 clinical trial has shown that adding an immunotherapy drug to chemotherapy almost doubled the cure rate for patients with the most common kind of breast cancer. The findings suggest that a new treatment paradigm should be adopted.
-
Hugely promising cancer immunotherapy drug dostarlimab is one step closer to being widely available, after the Food and Drug Administration granted it Breakthrough Therapy Designation status that, if successful, will expedite its path to market.
-
A new kind of cancer gene therapy can be remotely activated at a specific part of the body. The team developed a version of CRISPR that responds to ultrasound, and demonstrated how it can be used to clear cancer in mice.
-
Scarring of heart tissue can be slowed but not stopped, and can lead to heart failure. But a new study has shown that an existing immunotherapy could stop scar tissue formation after heart attacks.
-
Global healthcare company Grifols has partnered with BARDA, the Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority, to develop the first immune therapy eye drops to prevent the long-term effects of exposure to sulfur mustard, commonly called ‘mustard gas.’
-
T cells are our first line of defense against cancer, but the battle tends to exhaust them. Now, scientists have found a way to give them extra “batteries” to keep them fighting longer, with promising early results in mice.
-
A 67-year-old London man with lung cancer is the first to receive a new cancer vaccine as part of an international trial. The early-stage research will test the immune therapy’s safety and whether it can be used together with existing cancer treatments.
Load More