Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
-
There may be a new use for that urine you've been so thoughtlessly flushing. Scientists say it could be an alternate source of a valuable bone- and tooth-repair material, with a little help from a genetically modified type of yeast.
-
Under the right circumstances, electrons can actually “freeze” into a bizarre solid form. Now, physicists at Berkeley Lab have created and taken the first ever direct images of this structure.
-
Scientists at Berkeley Lab have used a titanium beam to make atoms of element 116. This new way to make the super rare element stands as a proof-of-concept that they could soon potentially create the undiscovered element 120, which may be stable.
-
Scientists have discovered that a once-in-a-billion-years evolutionary event is underway, as two lifeforms have merged into one organism that boasts abilities its peers would envy. Last time this happened, Earth got plants.
-
Climate change will trigger stronger storms more often, and the threat may not be properly communicated. Now, scientists at Berkeley Lab suggest there’s room for a Category 6 on the scale – with five storms in the past decade reaching that strength.
-
For all its uses, plastic is unfortunately one of our least sustainable materials. Now, scientists at Berkeley Lab have developed a way to engineer bacteria to produce raw materials that can be made into plastics that are completely recyclable.
-
Heating and cooling systems are among the biggest guzzlers of energy. Berkeley Lab has now developed a new technology that heats and cools by switching a material between solid and liquid states, inducing a large temperature change from a small voltage.
-
A simple alloy has claimed the crown for toughest material ever recorded. A team led by Berkeley Lab discovered not only its incredible toughness, but high strength and ductility that improve in colder temperatures, unlike most known materials.
-
The fastest internet network in the US just got a bit faster. The Energy Sciences Network has been upgraded to ESnet6, boasting a blistering bandwidth of 46 Terabits per second (Tbps). But don’t get too excited yet – it’s strictly scientists only.
-
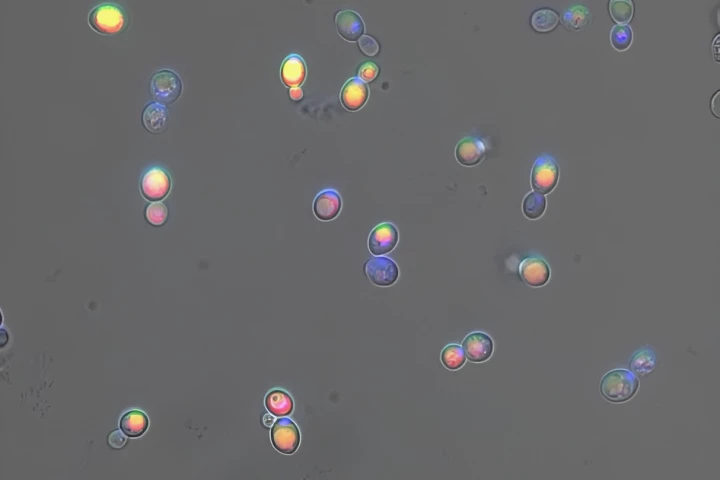
It takes tons of plant matter to make each gram of the cancer drug vinblastine. To find an alternative source, scientists have engineered yeast to produce the precursors of vinblastine, which could help make this vital drug more available and affordable.
-
Old electronics are tricky to recycle, meaning they clog up landfills while locking valuable metals away. Now scientists have demonstrated printed circuits that can be degraded on demand, returning their materials to reusable forms.
-
As effective as fossil fuels may be, their impact on the planet cannot be overstated. Now researchers at Berkeley Lab have coaxed bacteria into directly producing a new biofuel with an energy density significantly higher than jet fuel.
Load More