Lund University
-
A new blood test is not only able to identify Alzheimer's disease, but it can also indicate how far the disease has progressed with a 92% rate of accuracy. The finding offers hope for new personalized treatment and care options.
-
You might think that by now, we would have learned all we're ever going to know about plesiosaurs. Such is not the case, however, as a recent study indicates that the creatures had smooth skin on some parts of their body, and hard scales on others.
-
We naturally pick up microorganisms as we move about the world. Now, researchers have developed an AI tool that accurately links you to a particular location using a sample of the bugs you’ve collected on your travels – like a bacterial satellite navigation system.
-
A new injectable, temporary pacemaker could help correct a heart arrhythmia in an emergency. This nanoparticle gel can regulate the heart’s electrical signals for up to five days before dissolving harmlessly in the body.
-
Getting a tattoo, regardless of its size, increases the risk of developing lymphoma by 21%, according to a new study. The researchers say they’re not trying to dissuade people from getting inked, they just want to ensure the procedure is safe.
-
An organic electrode that doesn’t require invasive surgery to implant and is resorbed by the body over time may be a novel way of using electrical stimulation to treat non-chronic conditions such as cancer, nerve injuries and pain.
-
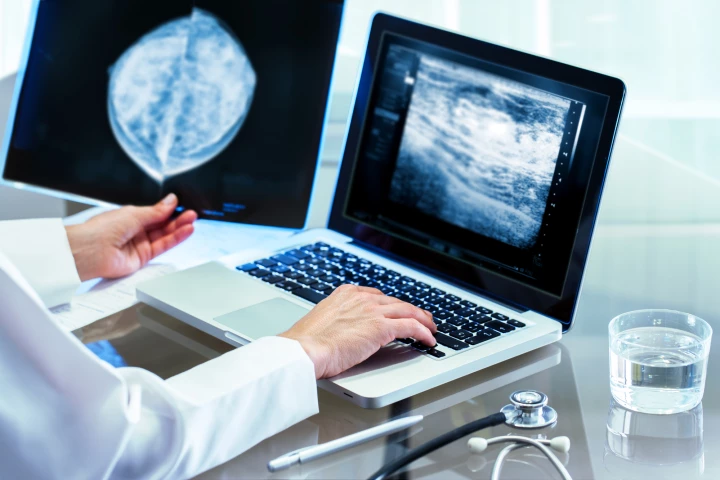
A new study found that a single radiologist screening mammograms picked up more incidents of breast cancer when supported by AI. The researchers say an AI-supported approach would be a safe alternative to having two radiologists read the scans.
-
Chlorine has long been used to disinfect drinking water but has been linked to health problems. In a new study, researchers looked at how the bacteria the purification process was designed to remove responded when chlorine was removed from the equation.
-
With the incidence of type 2 diabetes on the rise, science is looking to genetics for answers. A new study has isolated a gene not previously associated with the disease that appears to impair insulin production in type 2 diabetics.
-
A new study has tugged photosynthesis research in an interesting new direction, with a team at Sweden’s Lund University demonstrating how carefully spaced mirrors can be used to trap light and supercharge its effects.
-
One in five people diagnosed with type 2 diabetes are of a normal weight. A new test could help identify such people by looking for patterns of molecules in blood samples that correspond with obesity-related metabolic changes, regardless of weight.
-
In ice cores from both ends of the planet, scientists have discovered evidence of an extreme solar storm that struck Earth around 9,200 years ago, and strangely it seemed to have occurred during a period when the Sun should have been rather quiet.
Load More