Massachusetts General Hospital
-
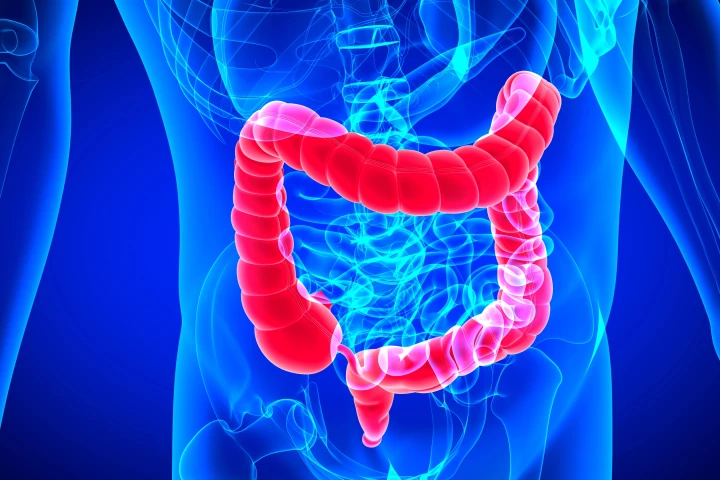
By age 50, you have a 50/50 chance of your gut being primed for developing diverticulitis, a painful condition that sends 200,000 Americans to hospital each year. But the good news is, you can reduce your risk with even just one lifestyle tweak.
-
Pupil dilation and subtle facial changes in response to sound can reveal how severe tinnitus is. Through this, researchers have discovered a new way to objectively gauge how bad the condition is, more accurately diagnosing tinnitus and treating it.
-
Eye injuries that damage the cornea are usually irreversible and cause blindness. But a new clinical trial has repaired this damage in patients thanks to a transplant of stem cells from their healthy eyes.
-
A study of over 220,000 people that looked at the consumption of butter versus plant oils has reached a conclusion that shows just how much better for you one is than the other. Making the switch might be one of the easiest ways to extend your life.
-
The first successful transplant of a genetically modified pig kidney into a human recipient is still being regarded as a medical milestone and success – even though the recipient, Rick Slayman, suddenly passed away over the weekend.
-
A genetically edited pig kidney has been successfully transplanted into a living patient for the first time. Reports indicate the man is doing well a few weeks on, raising hopes for a wider pool of donated organs in future.
-
Most of us have woken up with an aching back after a sleepless night, only for that pain to then keep us awake the next night. Now Harvard scientists have discovered a possible link between pain and poor sleep, and maybe even a way to break the loop.
-
A drug that treats excessive daytime sleepiness and obstructive sleep apnea could be repurposed to relieve debilitating symptoms of attention deficit hyperactive disorder, without the serious health risks that stimulants may hold for older adults.
-
A group of US and Canadian anesthesiologists has sounded the alarm on the new class of weight-loss drugs, this time warning that they can increase the risk of serious complications for patients under sedation on the operating table.
-
For those who struggle to find time to exercise during the week, preferring to do most of it on the weekend, a new study has found that being a “weekend warrior” is still effective at reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease.
-
Getting your cat spayed is a normal part of pet ownership, but it can be expensive, invasive and not very practical on strays. Now scientists have tested a new method that renders female cats permanently sterile with a single gene therapy injection.
-
People suffering from ALS (amyotrophic lateral sclerosis) often have difficulty raising their arms, due to deterioration of cells in their brain and spinal cord. A new wearable system is designed to help, utilizing a pair of under-arm balloons.
Load More