Microbiome
-
A herbal mouthwash selectively killed off bad bacteria in the mouth while preserving the good strains, according to a new study. It's proposed as an alternative to conventional mouthwashes, which were found to kill indiscriminately and damage gum tissue.
-
Alternating between a calorie-restricted plan and one high in fat and sugar, resulting in weight gain, is not just down to psychology and behavior. This kind of weight-loss-gain cycle – yo-yo dieting – has a surprising biological driver: The gut.
-
A small daily dose of kombucha made from black tea has been shown to meaningfully reshape the gut microbiome in adults – particularly those with obesity – without any dietary changes. It also reveals a lot about the importance of micro-biodiversity.
-
Even without noses, octopuses are able to determine which food sources are good to eat and which have gone past their prime simply by touching them. The secret, says a new study, lies with surface microbiomes and some very sensitive suckers.
-
If you have an aversion to the bitterness of foods like cabbage or broccoli, you might be a "super-taster," carrying a specific genetic code that dials up taste sensitivity. It may also put you at higher risk of kidney disease and bipolar disorder.
-
Researchers have found an indication of depression in a slightly unexpected place – the microbiome inside our mouths. The finding opens a new route of inquiry that could lead to novel antidepressant treatments and help other ailments as well.
-
A new study has found that diet-driven weight gain triggers impaired cognitive functioning an symptoms of anxiety, adding to the growing body of evidence that there's an intrinsic biological link between our gut health and our mental health.
-
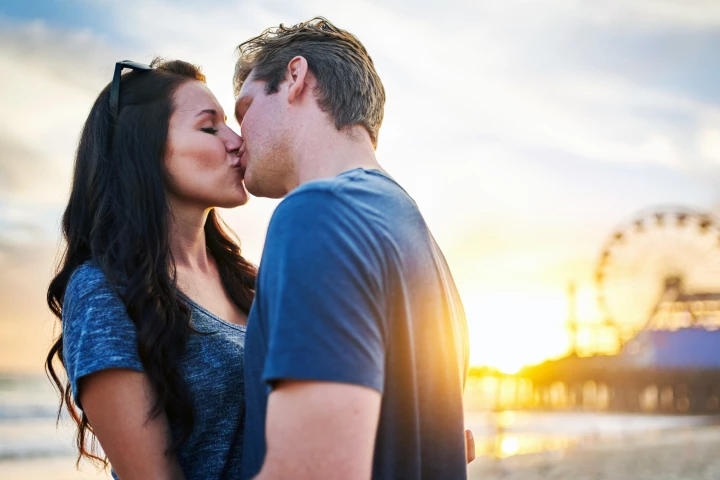
In a study of newlywed couples, researchers found that depression and anxiety can be passed from one spouse to the other via the oral microbiome, which is transferred during close contact, such as kissing.
-
A large-scale human clinical trials is currently underway testing a wild idea. Can fecal transplants reduce a person's cravings for alcohol by altering their microbiome? Early studies are indicating this could be possible.
-
What does gut fermentation and neuroinflammation have in common? A lot, according to new research that uncovers how the post-stroke microbiome directly influences brain health and recovery. It opens the door to new ways of restoring cognitive function.
-
Juicing as a way of fasting, cleansing, or detoxing can unbalance the health-affecting bacteria in the gut and mouth, according to a new study. After only three days, there was an increase in bacteria responsible for inflammation and disease.
-
Driven by a fascination with bacteria, microbiologist Julie Kopczyńska has trawled through existing research on the gut microbiome and created an easy-to-use gut health calculator. She says it's a good way to keep tabs on health and well-being.
Load More