Nanotubes
-
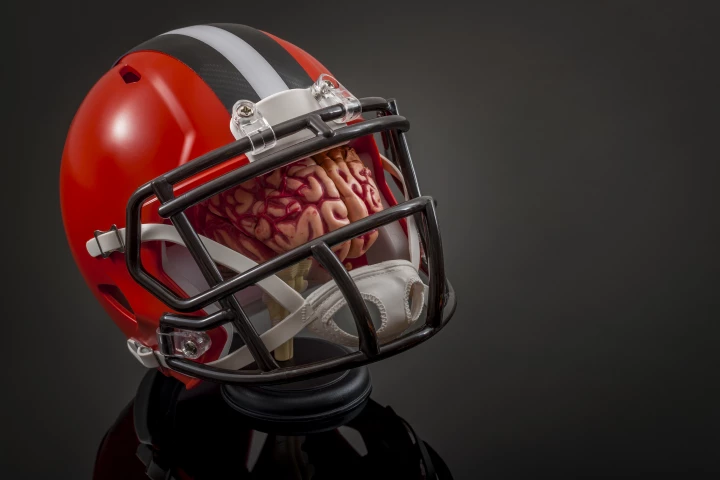
Researchers have developed a new, lightweight foam made from carbon nanotubes that, when used as a helmet liner, absorbed the kinetic energy caused by an impact almost 30 times better than liners currently used in US military helmets.
-
Researchers tricked glioblastoma cancer cells in mice into taking up iron-filled carbon nanotubes. They then shredded those cells by spinning the tubes using magnetic force. The technique has the researchers hopeful for a similar result in humans.
-
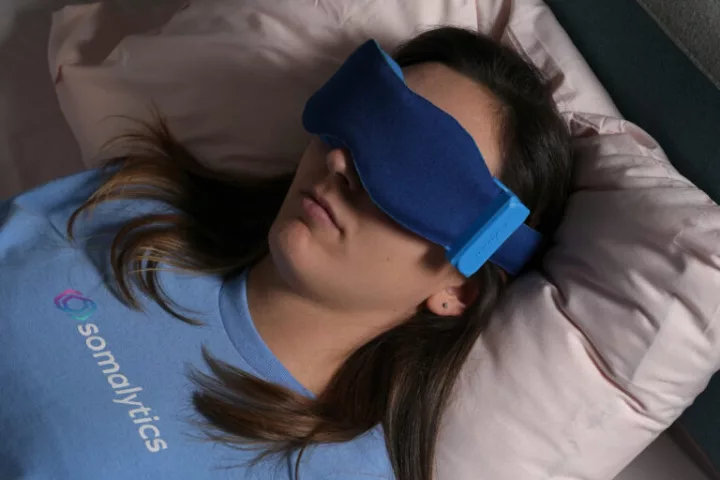
The REM stage of sleep plays an important role in learning, memory and brain development. Currently, lab-based tests are required to gauge how much REM sleep a person is getting. The SomaSleep mask, however, is claimed to let users do so at home.
-
Carbon nanotubes have found use in everything from smart bandages to more efficient solar cells. Now, scientists at the University of Wisconsin-Madison have used them in a helmet lining foam that offers better impact protection than regular foams.
-
Engineers at EPFL have inserted carbon nanotubes into photosynthetic bacteria, greatly improving their electrical output. They even pass these nanotubes down to their offspring when they divide, through what the team calls “inherited nanobionics.”
-
Engineers in the US and Mexico have developed a way to use soot from emissions to improve solar thermal devices. The coatings are not only cheaper to produce but more efficient than using materials like graphene, while reducing pollution.
-
Because nanoscale objects are so incredibly small, they don't reflect enough light for even the best microscopes to discern details such as their color. A new lighting system, however, addresses that problem by acting as a tiny spotlight.
-
Rice University researchers have produced a "smart" shirt that uses interwoven carbon nanotube fibers to provide steady electrical contact with the skin, allowing for ongoing gathering of data on heart activity.
-
Audeze helped design a pair of headphones to facilitate communication between doctor and patient during an MRI scan, without affecting the imagery produced. And this led to the development of the CRBN Electrostatic headphones for audiophiles.
-
MIT has developed a device that generates electricity using a completely new mechanism. “Particles” made of carbon nanotubes are dunked in an organic solvent, which induces a current to potentially power small robots or drive chemical reactions.
-
While it's important to check wounds for infections, removing the dressing in order to do so can be disruptive to the healing process. A new smart bandage could help, by "glowing" in a certain way if an infection is beginning.
-
France's Nawa Technologies is setting up operations in the United States, and bringing its fast, affordable vertically aligned carbon nanotube (VACNT) manufacturing process into a new application: making carbon fiber composites much stronger.
Load More