New York University
-
Researchers have found an indication of depression in a slightly unexpected place – the microbiome inside our mouths. The finding opens a new route of inquiry that could lead to novel antidepressant treatments and help other ailments as well.
-
By eliminating the essential amino acid cysteine from the diets of mice, and disabling their ability to produce it, scientists have induced rapid and dramatic weight loss. The technique opens a new pathway to explore in weight-loss science.
-
Memories can form outside of the brain, according to new research. Non-brain cells exposed to chemical pulses similar to the ones that brain cells are exposed to when presented with new information caused the non-brain cells to switch on a gene critical for memory formation.
-
Studying a species of microscopic worms exposed to high radiation from the 1986 Chernobyl disaster, researchers couldn’t find signs of genetic damage caused by the exposure. The findings are set to forge a path towards a better understanding of cancer.
-
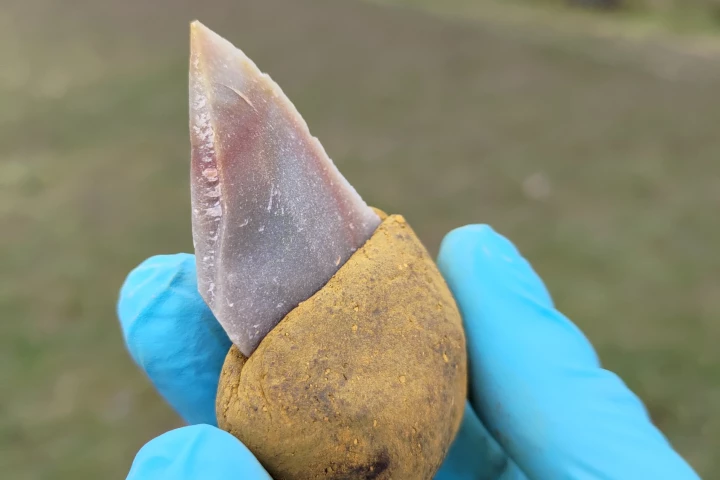
Neanderthals were gluing handles onto their tools over 100,000 years ago, possibly making the species even smarter than previously thought. So says a new study that discovered the use of adhesives on ancient stone tools that were previously overlooked.
-
Researchers have demonstrated a programmable nano-scale robot, made from a few strands of DNA, that's capable of grabbing other snippets of DNA, and positioning them together to manufacture new UV-welded nano-machines – including copies of itself.
-
After screening 27 million compounds, researchers have found a small-molecule drug that performed as well as a common painkiller with no side effects in rodent tests. The hope is that the finding could lead to better pain management for humans.
-
While insecticide-treated bed nets do help protect against malaria-carrying mosquitos, the chemicals are becoming less effective as the insects develop a resistance to them. It now appears that microwaving one such insecticide makes it "good" again.
-
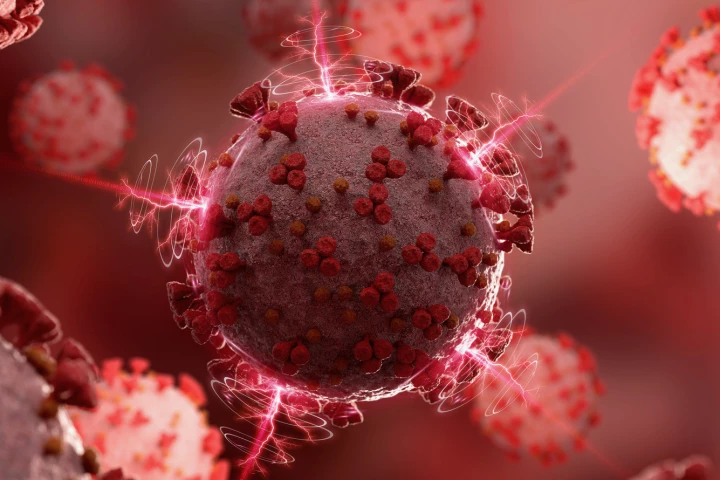
In the neverending human-vs-virus battle, scientists often focus on disrupting the protein coating on the bugs. New research shows an alternative: using certain compounds to act as molecular "pins" that pop the membranes holding viruses together.
-
A third of the US population lives with chronic pain. While the economic burden is well known, it also has a huge impact on mental health, opioid misuse and quality of life. Scientists now say they know the genetic hack to cut off the pain entirely.
-
A new long-term study by researchers at NYU has found that regular internet usage by older adults is linked with a decreased risk of dementia. But it’s about striking a balance, with evidence excessive use can be harmful to cognitive health.
-
Even though some conditions cause people to lose their appetite, those folks have to keep eating in order to recover. A new "electroceutical" ingestible capsule could help, by making them feel hungry … and it was inspired by a lizard's skin.
Load More