Ohio State University
-
VR is incredibly immersive for sight and sound, touch can be done, and even smell is starting to appear. That just leaves one sense – and whether or not anyone actually wants to taste virtual worlds, a new device is now tackling that final frontier.
-
Fighting fire usually involves water or foam, but they can be messy and environmentally destructive. Engineers at Ohio State University have now developed handheld tools that cleanly extinguish fires with 'ionic wind’ and vortex rings.
-
Some foods and beverages that are generally considered healthy – or healthier – contain hidden added sugars and saturated fats that can add up, leading people to unknowingly consume more than the recommended daily allowance, according to a new study.
-
It feels like back pain comes for many of us at some point in our lives, and it’s tricky to treat. A new gene therapy, which repairs damaged discs and reduces pain, has shown promise in mouse tests.
-
Engaging in activities that are designed to blow off steam when you’re angry probably isn’t going to be effective at reducing your anger, researchers have found. It’s better, they say, to try activities that decrease your physical arousal.
-
A new study has found the BA.2.86 variant of SARS-CoV-2 has a greater propensity for infecting certain lung cells than any prior Omicron variant. The research suggests BA.2.86 could potentially lead to COVID severity similar to the Delta variant.
-
American adults are eating 400-500 calories – roughly the same energy intake as a recommended main meal – in snacks every day, and it comes with little nutritional value yet a whole lot of sugar.
-
Spread by sandfly bites, the leishmania parasite causes ulcers that for many people are unexpectedly pain-free. For decades scientists have been puzzled by these painless lesions but new research is now homing in on the unusual analgesic mechanisms.
-
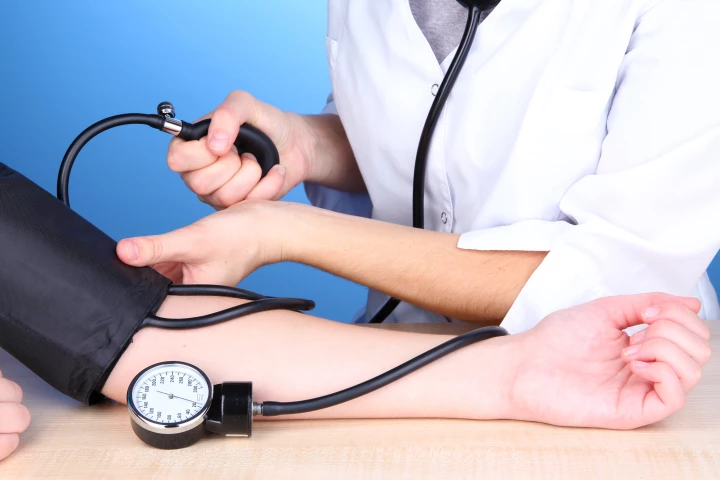
Half of the adult population has high blood pressure, but new research suggests that several million people may have elevated readings due to poor testing procedures. Experts call for a spotlight on how and where patients sit while in the cuff.
-
Despite studies showing pigeons are smart, they are perhaps more widely perceived as unintelligent 'rats with wings.' But now, scientists have demonstrated how these efficient learners solve problems just like artificial intelligence does.
-
Researchers have found that treating Special Ops veterans with psychedelics improved their mental health and, unexpectedly, their cognitive functioning, underscoring the benefits of psychedelic therapy for those with complicated trauma histories.
-
In order to optimize traffic flow through city streets, municipalities often install car-counting cameras or other sensors at a few set locations. A new study, however, suggests that using existing bus-mounted cameras may be a better way to go.
Load More