Princeton University
-
We know autism is not a single, homogeneous condition. Instead it's shaped by different traits, genes, and life experiences. Scientists have now discovered four distinct types of autism, each with its own biological signature.
-
While obesity significantly increases the risk of many cancers, scientists have now uncovered that there are specific dietary fat drivers that impede the body's ability to fight tumors. This landmark reveals that not all fats are created equal.
-
Researchers have found a way to take waste concrete from demolition sites and turn it into fresh new concrete that has a strength not seen before from such a product. The breakthrough could lead to significant emissions reductions in the building sector.
-
Many objects are made of black plastic, which has so far proven to be very hard to recycle. US scientists have devised a new method of recycling black polystyrene, however, using sunlight and an ingredient that's already present in the plastic.
-
Seeking to improve the tokamak fusion reactor known as ITER, researchers have found a way to stop rogue tungsten atoms from shearing off the walls and messing with the plasma. The finding is another important milestone on fusion's road to success.
-
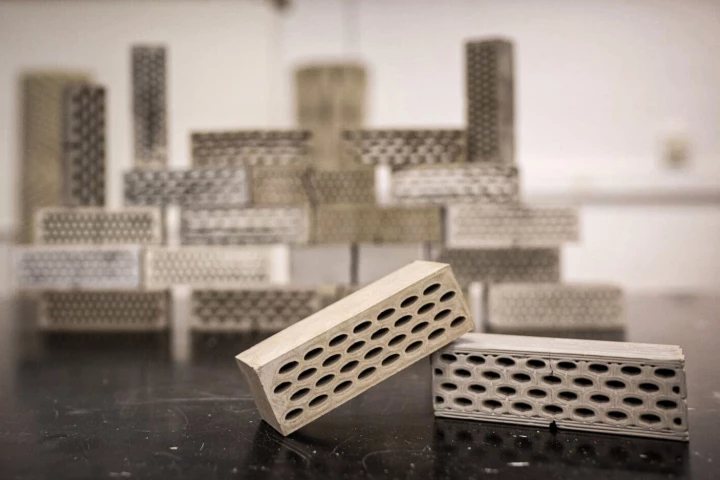
A pair of Princeton engineers have developed a new kind of concrete that promises more than 5 times the damage resistance of the usual stuff, by poking holes in its structure.
-
Inspired by the shiny lining of mollusk shells, researchers created a cement composite 19 times more flexible and 17 times more crack-resistant than regular cement. Its properties could be applied to brittle ceramic materials like porcelain and concrete.
-
If a soft-bodied robot uses rigid actuators to move its body, then it isn't really soft now, is it? An experimental new caterpillar-inspired bot gets around that conundrum by using soft, collapsible origami segments to squirm and steer its way into our hearts.
-
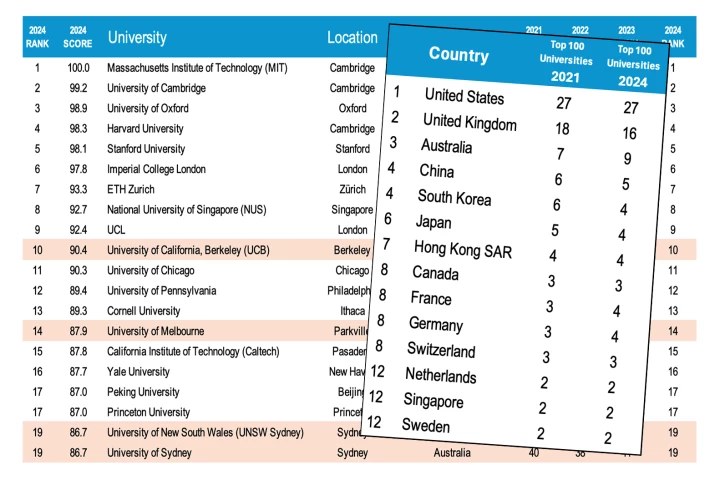
The 2024 QS World University Rankings were released this week, and with three new key metrics added to the scoring process, several universities have rocketed to the international forefront, while traditional icons are being pushed below the fold.
-
Americans aged 25-65 years are dying at far higher rates than their peers from other high-income countries, even surpassing death rates in Central and Eastern Europe. A new study examines what's caused the three-decade rise in midlife mortality.
-
For anyone who thinks that all electric boats are really just aquatic golf carts, well … think again. A Princeton University student team recently broke a world speed record for electric-powered boats, with an average speed of 114.2 mph (183.8 km/h).
-
Although lithium can be found in hard mineral ores, it's more often extracted from very salty (aka briny) groundwater. The latter task could soon be much quicker and eco-friendlier, thanks to a new string-based extraction technique.
Load More