Purdue University
-
Using scented products indoors changes the chemistry of the air, producing as much air pollution as car exhaust does outside, according to a new study. Researchers say that breathing in these nanosized particles could have serious health implications.
-
While some pet owners may disagree, it's widely accepted that around 80% of dogs will "play fetch" with their humans. But scientists have now discovered that almost half of house cats will also chase and return objects to their owners.
-
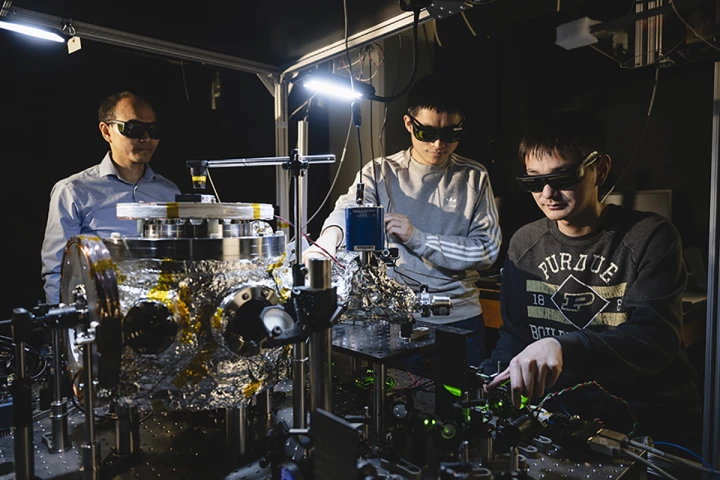
Physicists have levitated nanoscale diamonds, hit them with lasers to make them flash and spun them at an incredible 1.2 billion rpm. The experiments aren’t just about creating the “world’s smallest disco” but could help the study of quantum physics.
-
The ravages of smoking cigarettes on human health have long been established. Now a new study says that contact with cigarette smoke, even if it's on your clothes after coming from a smoky environment, can damage your dog's health as well.
-
Getting glue to stick in dry conditions is relatively easy, but having it maintain a bond underwater is much more difficult. That said, a new bio-based glue not only works underwater, it actually gets stronger when immersed.
-
Hog barns typically aren't the nicest places to be at the best of times, but try living in one during a heat wave. Scientists at Indiana's Purdue University have developed a self-activating hog-cooling pad for just such situations.
-
Strength and flexibility are two opposites that usually need to be balanced in steel. But now engineers at Purdue University and Sandia Labs have developed a new treatment that can be applied to steel alloys to boost both strength and ductility.
-
You may have noticed that on some drink cup lids, there are small domes that can be "popped down" to indicate what sort of beverage is in the cup. Scientists now believe that similar domes could help drones monitor the air pressure on their wings.
-
Scientists have demonstrated a technique to allow quantum computers to store more information in photons of light. The team encoded eight levels of data into photons and read it back easily, representing an exponential leap over previous systems.
-
Last year, engineers at Purdue University used their expertise in materials science to produce the world’s whitest paint, and have now made some tweaks to the recipe and produced a version that is thinner and lighter.
-
Is there microbial life floating around in the clouds of Venus? Scientists have long pondered this question and soon we may get some answers, starting with a cloud-skimming mission in 2023 to search for signs of life.
-
A new advance in EV research leverages an advanced cooling technology to take the heat out of the charging cable, allowing it to handle the type of current needed to charge up an electric car in under five minutes.
Load More