Refrigeration
-
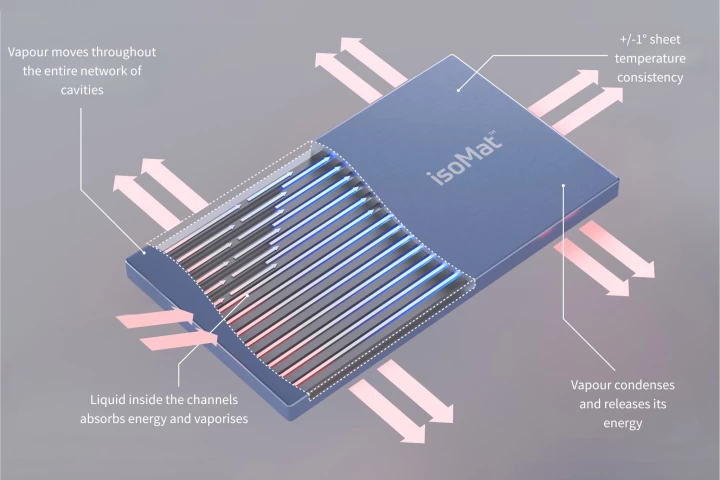
How's this for a set of promises? Flint Engineering claims its new, flat, thermal-transfer "IsoMat" can power entire homes, cut refrigerator energy consumption by 30%, and radically speed up EV charging while also extending battery life.
-
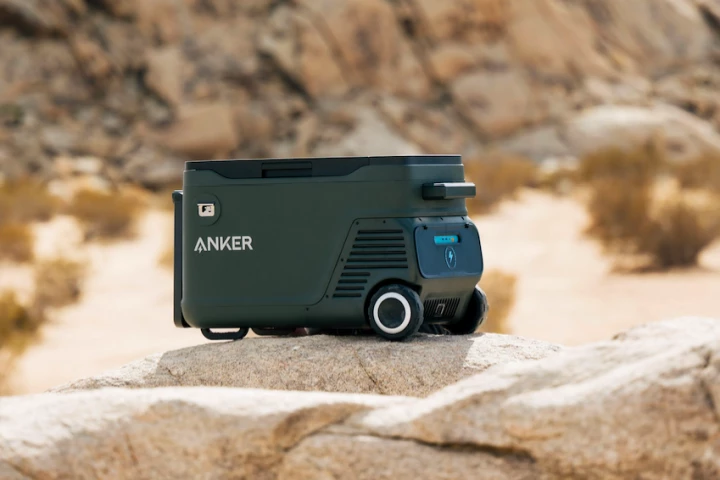
Anker has already established itself as a major player in portable power, and now it uses that expertise to launch a more convenient camping fridge. Its new EverFrost fridge uses a swappable lithium battery for more convenient go-anywhere cooling.
-
Heating and cooling systems are among the biggest guzzlers of energy. Berkeley Lab has now developed a new technology that heats and cools by switching a material between solid and liquid states, inducing a large temperature change from a small voltage.
-
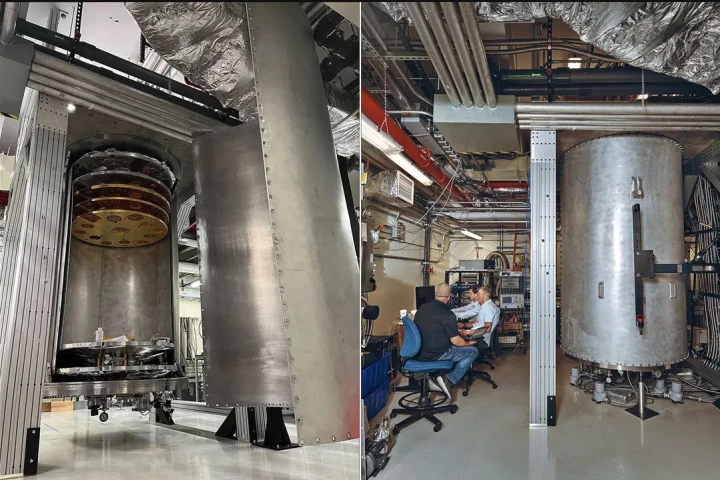
Quantum computing requires extremely cold temperatures. To that end, IBM has built and demonstrated a huge “super-fridge” codenamed Project Goldeneye that chills things colder than outer space.
-
Besides keeping your food cold, there’s not much more we need from a fridge, but manufacturers keep cramming new features in there. The latest example from LG is the MoodUP, a fridge that sports speakers and LED doors that can change color on demand.
-
Gases used as refrigerants in cooling systems can leak into the atmosphere and become major contributors to climate change. Now engineers at Harvard have demonstrated a new prototype cooling device that uses a solid-state material as a refrigerant.
-
Refrigeration and air conditioning could use a boost in efficiency. On that road, researchers have now developed an unusual new technique that could lead to "twist fridges", which cool by unraveling fibers that are tensely twisted.
-
Scientists led by the University of Cambridge have developed a way to replace the organic gases used in most conventional refrigerators with plastic crystals. By using crystals of neopentyl glycol under pressure, it may be possible to build safer, greener, and more efficient cooling systems.
-
Refrigerator technology hasn’t changed much in decades. Now researchers in Europe have shown promising early results with an experimental cooling system that uses magnetic fields and shape-shifting memory alloys.
-
The days of the rackety, energy-gobbling refrigerator may be numbered with the advent of more efficient systems that cool with the use of magnets. Cooltech Applications has launched the first magnetic refrigeration system (MRS) for commercial use.
-
In an effort to make a greener, more energy efficient cooling system, a team of engineers from Germany's Saarland University is turning to shape memory materials to replace the refrigerant gases used in conventional cooling technologies.
-
GE researchers have developed a new type of refrigeration technology using magnets that is more environmentally friendly and is predicted to be 20 to 30 percent more efficient that current technology ... and could be in household fridges by the end of the decade.
Load More