Regenerative
-
In a major breakthrough for regenerative medicine, MIT scientists have developed a way to convert skin cells directly into brain cells extremely efficiently, without needing to go through the intermediate step of converting them to stem cells first.
-
Eye injuries that damage the cornea are usually irreversible and cause blindness. But a new clinical trial has repaired this damage in patients thanks to a transplant of stem cells from their healthy eyes.
-
Heart attacks are dangerous not just because of the initial event, but the long-term damage afterwards. Now scientists have discovered a dormant gene that could be reactivated to regenerate heart tissue, preventing the progression to heart failure.
-
Scientists have engineered a hybrid mouse with a gene that predates all animal life. The team replaced a single gene in the mouse stem cells with a version from an ancient, single-celled ancestor, and successfully grew healthy live mice from it.
-
The body has a remarkable ability to heal injuries, but it has its limits. Now scientists have developed a way to improve on the natural process, making implants created from a patient’s own blood to regenerate injuries, even repairing bone.
-
Scarring of heart tissue can be slowed but not stopped, and can lead to heart failure. But a new study has shown that an existing immunotherapy could stop scar tissue formation after heart attacks.
-
Imagine being horribly maimed and the only way to survive was to merge your damaged flesh with another injured human. Scientists have discovered this startling ability in comb jellies, which can fuse together to share a nervous and digestive system.
-
Where there's relative movement, there's a chance to generate electricity, and vehicle wheels move up and down on their suspension the entire time they're in motion. We first encountered regenerative suspension 15 years ago – so how's it going?
-
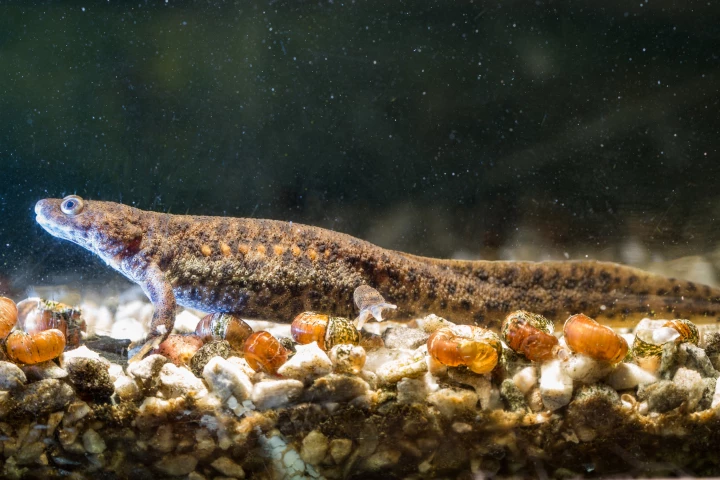
It might sound like something out of the X-men but it came from a lab in California: mutant newts that grew perfect limbs after defective appendages were cut off. The findings help science get one step closer to understanding how regeneration works.
-
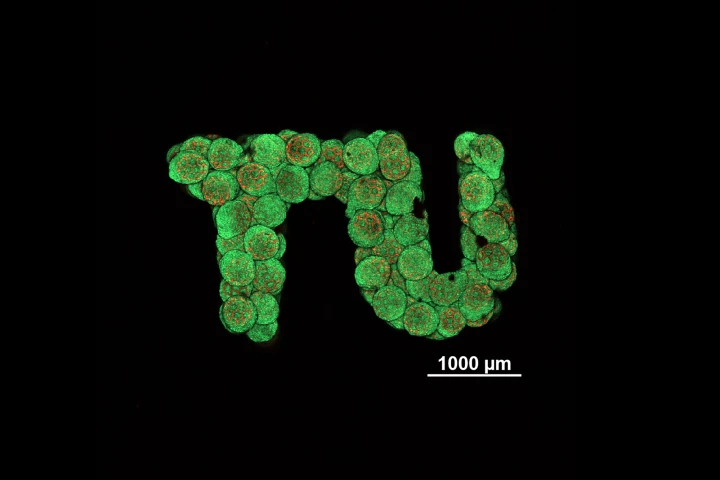
Researchers at TU Wien have developed a new way to grow cartilage from stem cells and guide it into basically any shape required. The breakthrough could lead to better ways to patch up injuries.
-
Heart tissue normally can't regenerate after an injury. But now, scientists at Max Planck have shown in mice that reprogramming the energy metabolism of the heart allows it to regenerate after a heart attack, which could open new therapies.
-
A complete spinal cord injury results, tragically, in total paralysis of all limbs and muscles below the injury site. But now, scientists at EPFL have demonstrated in mice a new gene therapy that can regenerate nerves and restore the ability to walk.
Load More