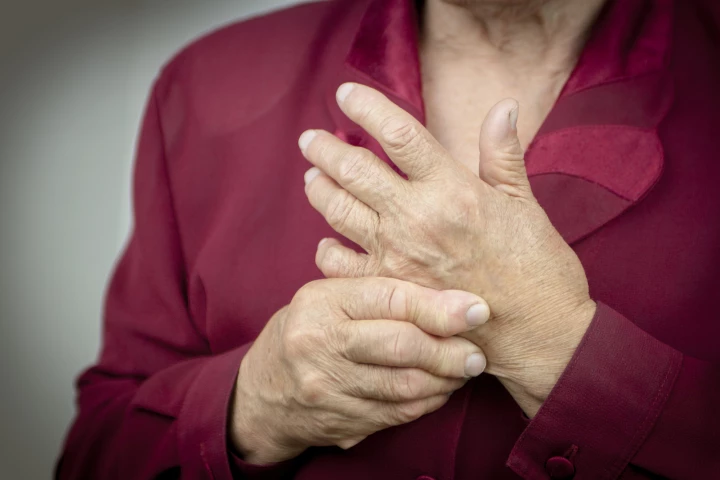
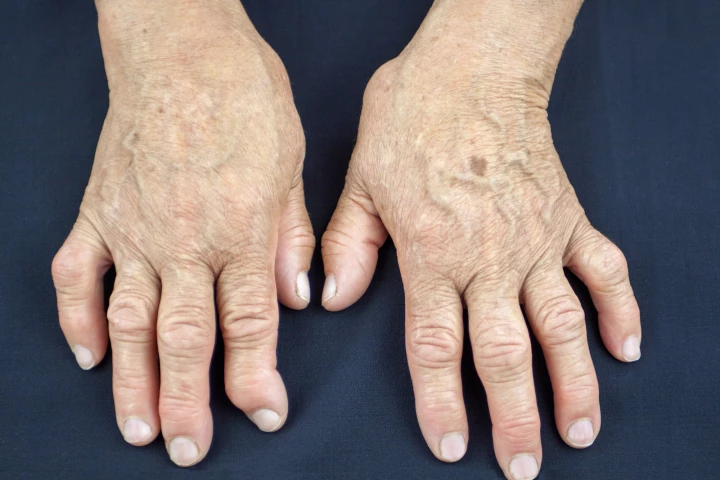
Rheumatoid arthritis
-
A drug currently used as a second- or third-line treatment for those with rheumatoid arthritis has shown huge promise as a preventative, stopping the onset of the debilitating and painful disease in 92.8% of at-risk participants after 12 months.
-
In 2023, researchers were focused on better understanding the disease process underlying arthritis, and the treatment and relief of symptoms. Here are the year’s top arthritis stories appearing on New Atlas.
-
They’ve been approved in the US since 2012, but Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors are still the new kid on the block in terms of rheumatoid arthritis treatment. A new study lays to rest the doubts some had over their effectiveness beyond clinical trials.
-
When a person with rheumatoid arthritis receives healthy antibodies intravenously, it can reduce inflammation. Researchers have, for the first time, discovered the molecular pathways that underlie this effect, paving the way for new treatments.
-
Autoimmune diseases such as MS and rheumatoid arthritis affect almost four percent of the global population. A new study has now identified a naturally occurring compound that may provide a new way of treating these debilitating diseases.
-
Instead of injections or pills, why not engineer bacteria to secrete therapeutic molecules from within our gut? A new study is showing how a genetically modified probiotic can produce an anti-inflammatory molecule to treat rheumatoid arthritis in rats.
-
Immune suppression can help relieve symptoms of autoimmune diseases, but it can cause complications. A new nanoparticle therapy selectively targets problematic immune cells, and was able to significantly delay and even prevent arthritis in mice.
-
A new study has provided more evidence gut bacteria plays a role in the development of rheumatoid arthritis. The research suggests an abnormal immune response to a common species of gut bacteria could influence the development of the disease.
-
Scientists studying the activity of a drug used to treat rheumatoid arthritis have discovered some surprising metabolic functions, some of which may be useful when it comes to countering diabetes and obesity.
-
A research team has discovered a novel mechanism in which a key protein drives the inflammatory damage associated with rheumatoid arthritis. The foundational finding could lead to entirely new pathways to treat this autoimmune disease affecting millions.
-
Positive Phase 3 trial results for a new antibody treatment targeting rheumatoid arthritis have recently been reported. The therapy is hoped to offer a new option to patients struggling with current treatments and should be available within the next year.
-
A new study from scientists in Japan and the US has identified a form of inter-neuron communication as a key mechanism in the way inflammation spreads between joints in conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.
Load More