RMIT University
-
When it comes to systems for cleaning up marine oil spills, most of them simply float in place, waiting for the oil to come to them. A new robot, however, could proactively move through oil slicks – and it's inspired by both a dolphin and a sea urchin.
-
Scientists have developed a new eyedrop that can ferry protective compounds all the way to the retina, paving the way for a less-invasive – and injection-free – method of managing sight-stealing diseases such as age-related macular degeneration.
-
Giant solidified masses of fat, grease, and other waste threaten to clog sewer lines and cause huge spillages in cities worldwide. Researchers at RMIT have developed two novel ways to prevent these blocks of waste from forming.
-
In a landmark 14-year study, researchers found that artificially sweetened drinks raise the risk of developing type 2 diabetes by more than a third, higher than those with sugar. It challenges the perception that diet drinks are healthier options.
-
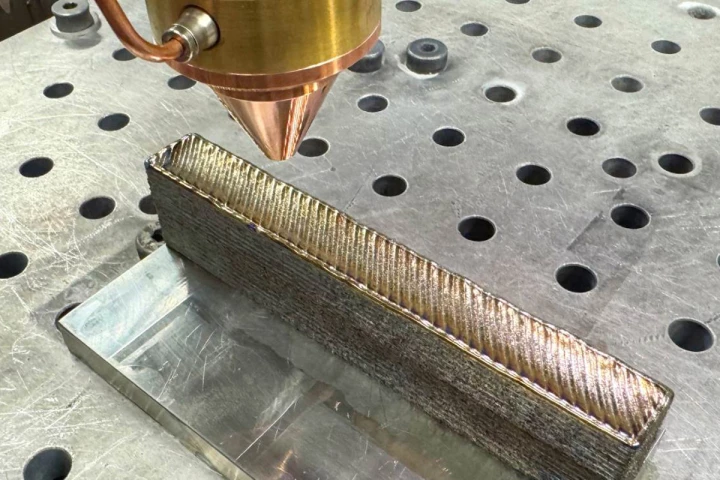
Researchers in Australia have developed a titanium alloy that's 30% cheaper to produce than standard titanium, and is stronger and more ductile than other titanium alloys.
-
Researchers have developed a new method for preventing bacteria from adhering to surfaces, such as medical devices. It relies on the unique properties of resilin, a natural insect protein that enables fleas to jump hundreds of times their body length.
-
Researchers at Australia's RMIT University have devised a simple and clever contraption that could make drinking water available in disaster-stricken areas, by pulling it out of thin air.
-
Deep-sea sponges have a secret: their light lattice-like forms are astonishingly stiff and strong. Inspired by these creatures, RMIT researchers have developed a new structure to make significantly stronger materials for more durable buildings.
-
Tubular structures that fold flat for storage may not take up much room in that form, but they also tend not to be very strong when deployed. That isn't a problem with an experimental new type of tube, that's inspired by both origami and bamboo.
-
A diet low in carbs and high in fat, which has gained popularity for shedding weight, can increase type 2 diabetes risk by 20%, according to a new study. The research team behind the study say their findings highlight the need to eat a balanced diet.
-
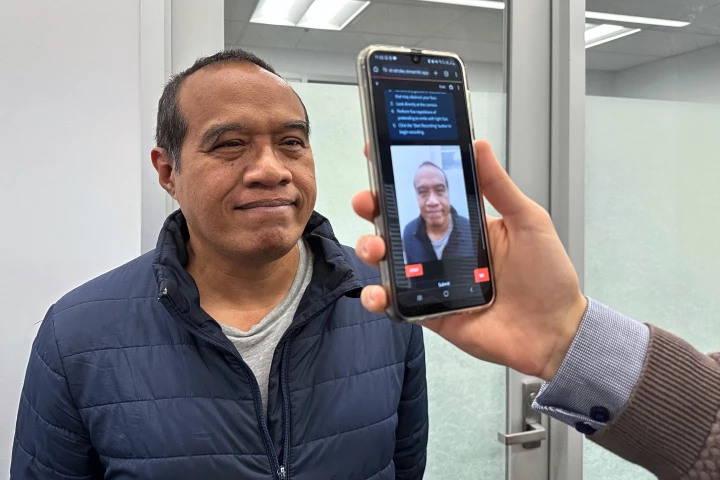
If someone has suffered a stroke, the sooner they get the appropriate medical attention, the better. A new smartphone tool may help ensure that happens, by allowing first responders to determine if a patient has indeed experienced a stroke.
-
A new international study has revealed that the prevalence of image-based abuse, so-called ‘sextortion,’ among adult men and women is more common than was first thought, with a high degree of overlap between perpetrators and victims.
Load More