RMIT University
-
Researchers have developed a new method for preventing bacteria from adhering to surfaces, such as medical devices. It relies on the unique properties of resilin, a natural insect protein that enables fleas to jump hundreds of times their body length.
-
Researchers at Australia's RMIT University have devised a simple and clever contraption that could make drinking water available in disaster-stricken areas, by pulling it out of thin air.
-
Deep-sea sponges have a secret: their light lattice-like forms are astonishingly stiff and strong. Inspired by these creatures, RMIT researchers have developed a new structure to make significantly stronger materials for more durable buildings.
-
Tubular structures that fold flat for storage may not take up much room in that form, but they also tend not to be very strong when deployed. That isn't a problem with an experimental new type of tube, that's inspired by both origami and bamboo.
-
A diet low in carbs and high in fat, which has gained popularity for shedding weight, can increase type 2 diabetes risk by 20%, according to a new study. The research team behind the study say their findings highlight the need to eat a balanced diet.
-
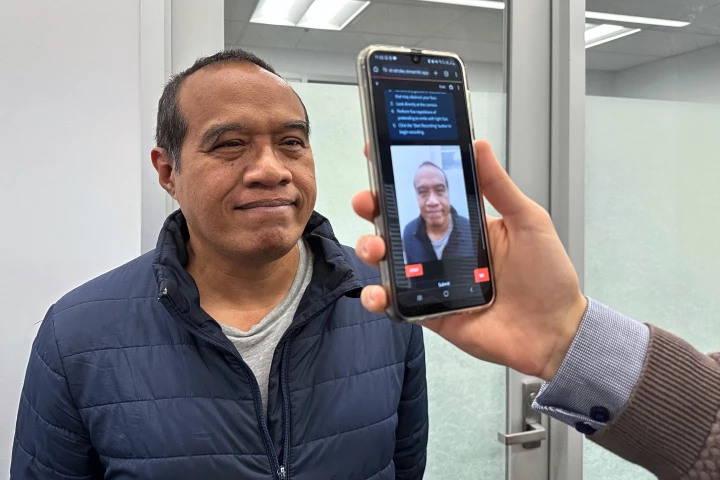
If someone has suffered a stroke, the sooner they get the appropriate medical attention, the better. A new smartphone tool may help ensure that happens, by allowing first responders to determine if a patient has indeed experienced a stroke.
-
A new international study has revealed that the prevalence of image-based abuse, so-called ‘sextortion,’ among adult men and women is more common than was first thought, with a high degree of overlap between perpetrators and victims.
-
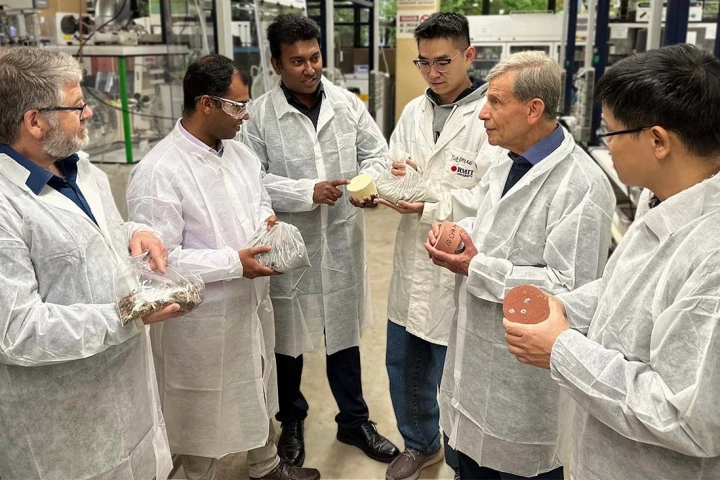
In a world first, the researchers who used waste coffee grounds to make concrete that’s 30% stronger are putting their innovative material to the test by laying sidewalks made of the stuff to see how it fares when it's subjected to foot traffic.
-
Bricks made of discarded glass and recycling-waste ash have been shown to insulate better than regular bricks, while also requiring less energy to produce. And of course, they additionally use materials which would otherwise end up in landfills.
-
While there are already clothing materials that help keep wearers cool simply by allowing heat to escape, an experimental new fabric coating goes a step further. Utilizing a whole bunch of nanodiamonds, it actually draws heat away from the body.
-
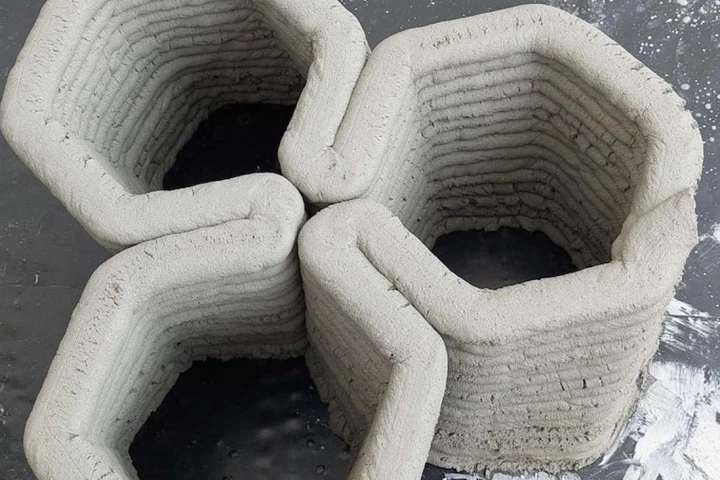
3D-printed concrete structures are claimed to be faster and cheaper to build than their traditional counterparts, but they're not always as strong. That problem may soon be solved by adding a pinch of graphene oxide, which could also be used to detect cracks.
-
Cybersecurity is a growing concern as more critical infrastructure can be exposed to hacks. Now Australian engineers have developed and demonstrated a new technique called “ineffable cryptography,” which treats keys like the Coca-Cola secret formula.
Load More