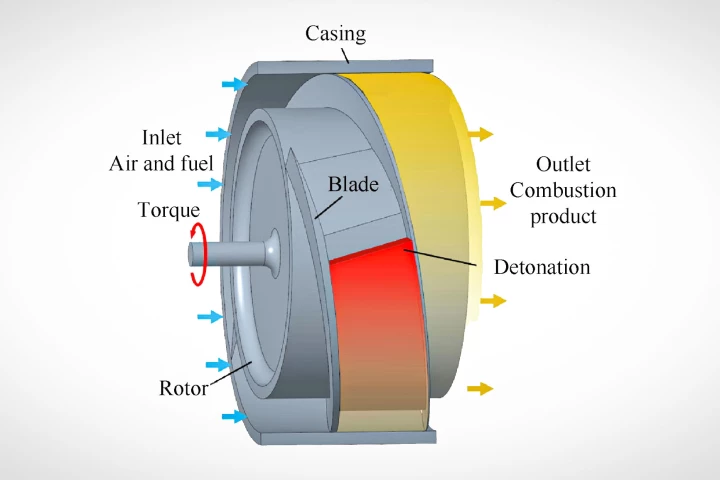
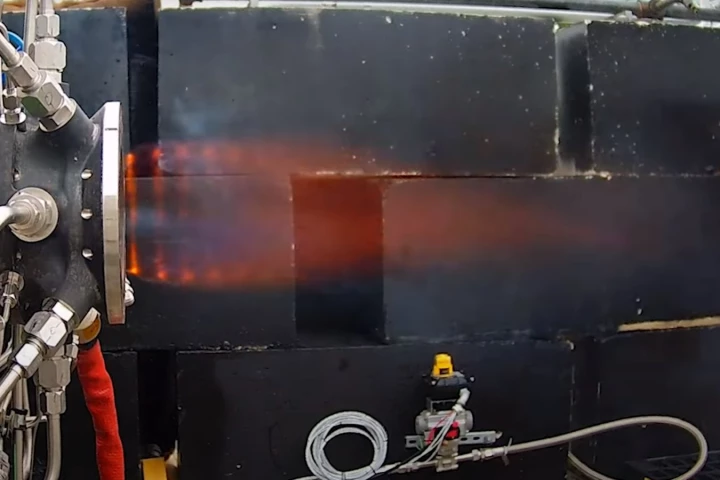
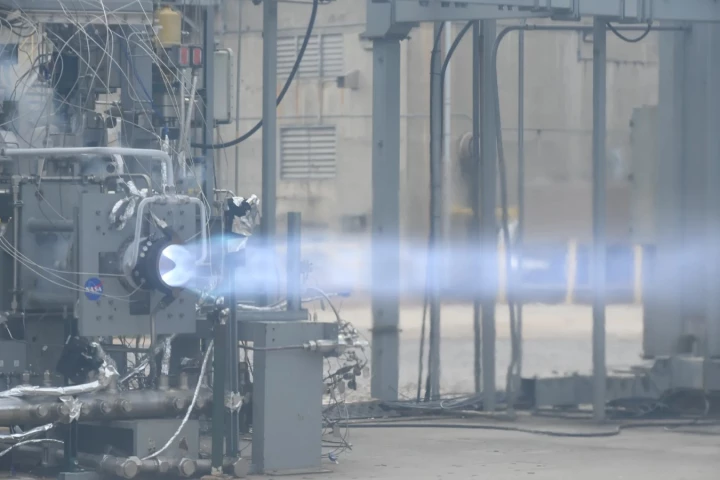
Rotating Detonation Engines
First developed in the 1950s at the University of Michigan, these rocket engines use powerful and chaotic detonations, self-propagating thanks to hypersonic shockwaves travelling around a ring-shaped combustion chamber, in place of slower, more controllable combustion reactions, to create powerful, high efficiency rockets and engines.
-
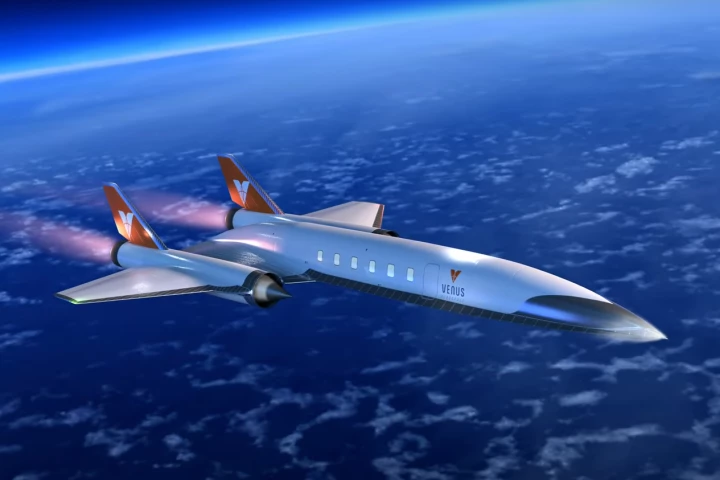
In what may be a world first, Venus Aerospace has, for the first time in the US, successfully flown a Rotating Detonation Rocket Engine (RDRE) that uses supersonic explosions to create thrust. Such engines could help propel future hypersonic vehicles.
-
A self-propagating series of explosions, contained between the blades of a high-speed rotor, promises a leap in power and efficiency during hypersonic flight – provided this radical new engine can be built strong enough to withstand its own power.
-
When is an empty tube not an empty tube? When it's a ramjet that uses rotating detonation technology to propel aircraft at hypersonic speeds. A case in point is Venus Aerospace's new Venus Detonation Ramjet 2000 lb Thrust Engine (VDR2).
-
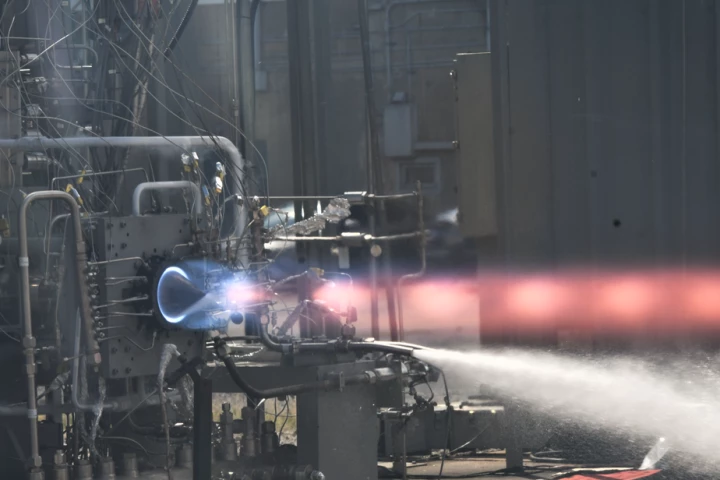
A revolutionary alternative to conventional rockets that uses controlled explosions has completed its first long-duration engine test as part of Venus Aerospace's partnership with DARPA to develop a Rotating Detonation Rocket Engine.
-
NASA has pushed forward a revolutionary new rocket technology at its Marshall Space Flight Center in Alabama. Engineers at the facility fired the 3D-printed Rotating Detonation Rocket Engine (RDRE) for a record 251 seconds with 5,800 lb of thrust.
-
GE Aerospace has demonstrated what it claims is the world's first hypersonic Dual-Mode Ramjet (DMRJ) rig test using Rotating Detonation Combustion (RDC) in a supersonic flow stream that could one day give hypersonic missiles longer range.
-
DARPA has contracted Raytheon to develop a practical version of a revolutionary air-breathing rotating detonation engine called Gambit, which would have no moving parts and could lead to lighter missiles with longer ranges at lower cost.
-
Explosions get you much more bang from your fuel buck than combustion – if your engine can withstand them. NASA believes the rotating detonation engine could be the future of deep space travel, and it's getting strong results in prototype testing.
-
A Florida team working with the US Air Force says that it's built and tested an experimental model of a rotating detonation rocket engine, which uses a spinning series of chaotic explosions inside a ring channel to create super-efficient thrust.
-
The U.S. Navy is examining the potential of using Rotating Detonation Engines (RDEs) to improve fuel consumption and cut costs.