The Rockefeller University
-
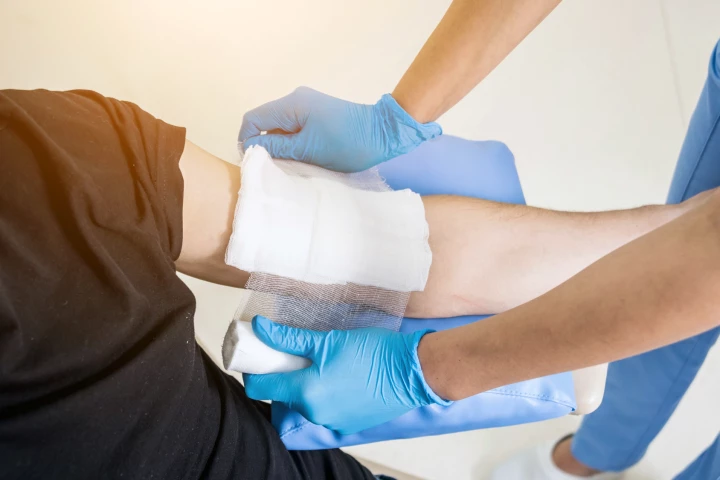
When the skin is injured, a stem cell’s survival instincts kick in. New research reveals that a simple amino acid, serine, helps push stem cells to abandon hair growth in favor of wound healing, opening the door to new therapies for chronic wounds.
-
Researchers have developed a quick, cheap, and highly sensitive blood test to detect a telltale protein produced by cancer cells. The test can pick up a range of cancers before symptoms appear and could be key to early diagnosis of the disease.
-
Fruit flies differ from us in many ways, including the fact that they can't move their eyes relative to the rest of their head. That's not a problem, however, as new research shows that they move their retinas within their unmoving eyes instead.
-
Scientists have studied what makes mosquitoes more attracted to some humans over others, and uncovered strong association between being a so-called mosquito magnet and elevated levels of a fatty acids on the skin.
-
Algorithms have helped uncover a new antibiotic that shows promise against some nasty bacteria, using a novel mode of attack that should be hard for them to develop resistance to. Most importantly it could unlock a whole new arsenal of antibiotics.
-
An international team of scientists has published the first complete, gap-free sequence of the human genome. The new reference genome adds hundreds of millions of base pairs to earlier drafts, filling in crucial gaps to improve studies of disease.
-
Our sense of smell seems to be the least understood. To help shed some light on the system, researchers at Rockefeller University have taken the first cryo-electron microscope images of an olfactory receptor at work in the simple system of an insect.
-
Our brains are extremely fast at recognizing the faces of people important to us. Now, a new study has identified a previously unknown population of brain cells that may be hybrids of sensory and memory neurons, which enable this quick recall.
-
A new study has affirmed the link between the presence of brown fat and improved cardiac or metabolic health, validating the relatively new hypothesis that the type of adipose tissue commonly referred to as brown fat confers broad health benefits.
-
It’s long been thought that our cells stop dividing as we age as a natural preventative measure against cancer. Now a new study has found intriguing evidence supporting this hypothesis in genomes from several particularly cancer-prone families.
-
Researchers looking for biomarkers to predict rheumatoid arthritis flare-ups have discovered a never-before-seen type of cell. Dubbed PRIME cells, they accumulate in the bloodstream seven days before a flare, but strangely disappear during the flare.
-
As researchers rekindle a more than 100-year-old therapy, using blood from recovered COVID-19 subjects as a treatment for newly infected patients, a team in New York is thrusting this old, experimental treatment into the 21st century.
Load More