Tokyo Institute of Technology
-
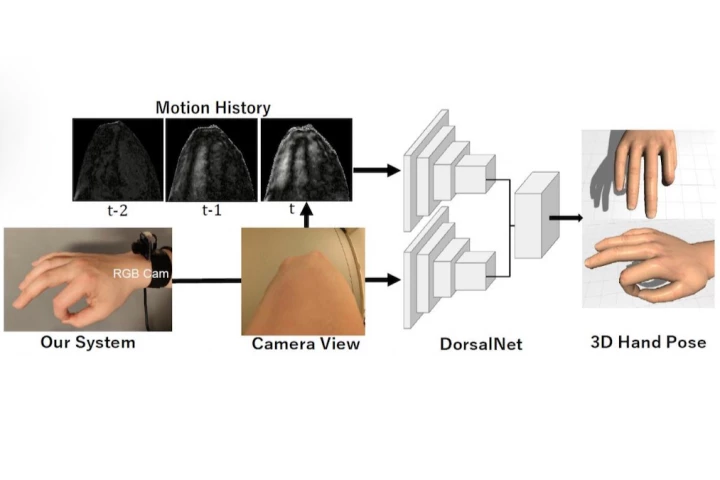
When it comes to tracking the positions of a person's moving hand, sensor-equipped gloves are often used. An experimental new system, however, utilizes a wrist-mounted camera … which doesn't even "see" the user's fingers.
-
Typically, motion capture systems are confined to one studio containing multiple cameras, and they require subjects to wear sensor-equipped body suits. A new setup, however, is based around a single chest-mounted camera.
-
Scientists have uncovered an unfortunate feedback loop that could make things worse for the climate. According to a new study, ocean acidification seems to increase the amount of nitrous oxide, a potent greenhouse gas, that’s released into the air.
-
The biggest missing link lies between non-living matter and the earliest living cells. A new study has found a mechanism that may have helped droplets transition into early cells, taking place in ponds, puddles and waterways that dried out and refilled repeatedly over time.
-
One of the largest natural sources of renewable energy could be right under our feet – literally – with geothermal energy. Now researchers at Tokyo Institute of Technology and Sanoh Industrial have developed a new type of battery cell that can directly convert heat energy into electricity.
-
Red dwarf stars are of particular interest to astronomers hunting down distant worlds. The latest study of Kepler data has now identified 15 new exoplanets around red dwarfs, including a system of three “Super-Earths” – one of which appears to be orbiting within the host star’s habitable zone.
-
By using super-high pressures and temperatures to duplicate conditions at the Earth's core, scientists at the Tokyo Tech have discovered that there may be quartz crystals there that help explain how the Earth gets the power to generate its field.
-
The Tokyo Institute of Technology and Bridgestone Tires have developed a new hydraulic robotic muscle that is lightweight, yet is five to ten times as strong as conventional electric motors.
-
Researchers have developed a tiny origami robot that is swallowed as a capsule, then unfolds in true Transformer style to patch a wound or remove foreign objects, such as button batteries.
-
A new resin makes it possible to create tiny, custom-shaped electrodes and other conductive microstructures.
-
Researchers at the Tokyo Institute of Technology are developing a cooking simulator that lets users cook up a virtual steak.
-
Researchers at the Tokyo Institute of Technology are developing a humanoid robot called Sumanoid, which is able to reproduce realistic swimming strokes.
Load More