Traumatic Brain Injury
-
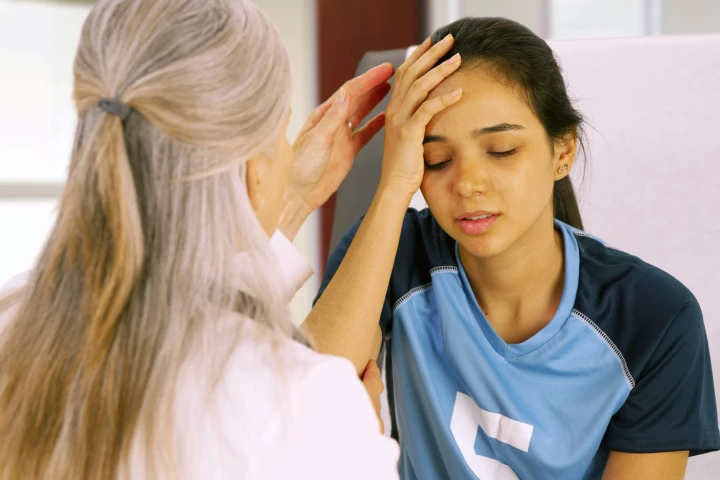
Not all concussions are created equal. A new study has revealed nine early warning signs that a mild head injury might linger longer than expected, and why spotting them within hours could change recovery outcomes.
-
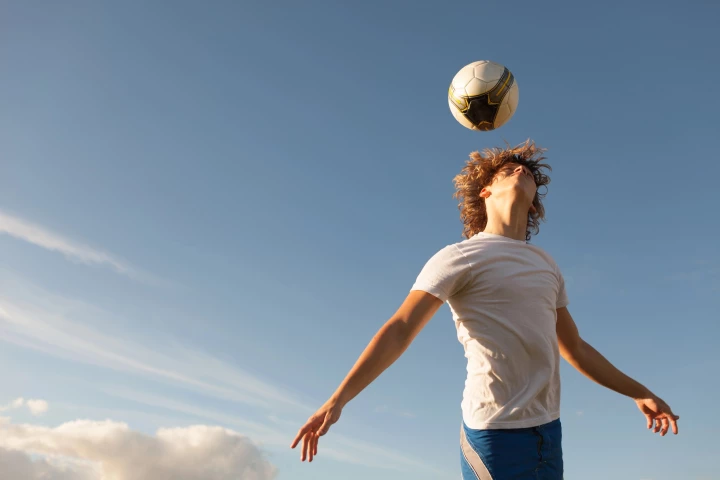
Soccer heading has long been suspected of impacting brain health, but where and how it leaves a mark has been a blind spot. Now, for the first time, scientists have a clear picture of the damage and why repeated impacts can impair cognition over time.
-
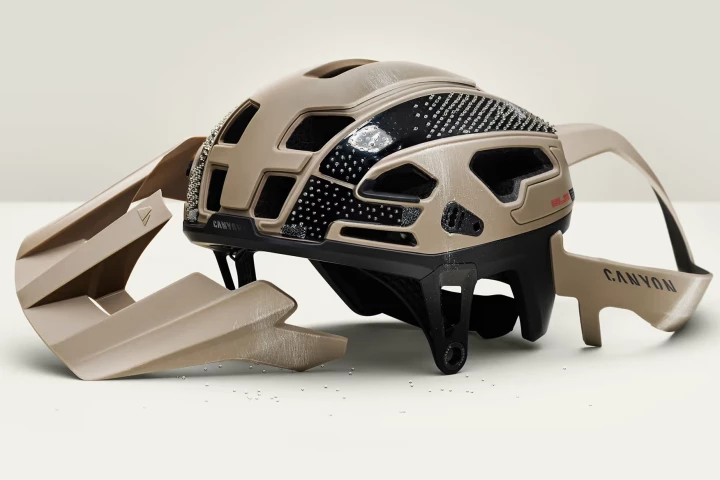
Foam may protect you from whacks on the head, but it's not sufficient when you're cycling at speed. That's where RLS bike helmet tech comes in. It offers 4x the concussion protection of a regular helmet, via ball bearings and panels that pop off.
-
A new study has found that psilocybin, the psychedelic ingredient in magic mushrooms, could be an effective treatment for repeated mild concussions because of its brain-healing properties. It could be the first medical treatment for the condition.
-
A new study has found that a kid who has suffered a concussion – even a mild one – is 15% less likely to go on to higher education in adulthood. It highlights the long-term impact of traumatic brain injury on learning, regardless of severity.
-
Individuals who suffer head trauma from sports, accidents, or other causes often go on to develop neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson's or Alzheimer's. A new study sheds light on why that might be and offers a way to prevent it.
-
A new study has demonstrated that a tiny bundle of optical fibers can continuously, accurately, and simultaneously measure six biomarkers of brain health, helping to prevent serious complications that can follow a traumatic brain injury.
-
Researchers found that soccer players who use their head to control the ball show abnormalities in their brains similar to CTE – not the news 275 million soccer players around the world want to hear.
-
New research found that even an old mild concussion can have long-lasting effects in otherwise healthy people. The study adds to a growing understanding of traumatic brain injury and is relevant to the evolving legal landscape around brain injuries in sports.
-
A severe brain injury can leave patients unresponsive to stimuli, but they may be more aware than we realize. A new study of brain activity has shown that up to a quarter of unresponsive patients may exhibit “hidden consciousness.”
-
Damaged brain tissue can be re-grown using a new method that lets researchers guide stem cells into exactly the type of brain cells they need for a particular spot. They're targeting new treatments for stroke, traumatic brain injury and MS.
-
Researchers have worked with biology rather than against it, fitting microparticle 'backpacks' to important inflammatory cells called macrophages to significantly reduce lesion size and inflammation caused by traumatic brain injury.
Load More