Treatment
-
A new study from Northwestern University offers hope to Alzheimer's patients and their caregivers. If researchers there are correct, their new small-molecule NU-9 drug may be able to stop the disease long before it begins ruining lives.
-
Magnetic bioactive nanocomposites can eliminate tumors through magnetic arson while helping build new bone. Integrating bioactivity with magnetic performance may be key step in creating smart nanomaterials for oncology and medical regeneration.
-
Researchers at Switzerland’s EPFL have created a new neurotherapy that vastly and non-invasively improves vision for patients with hemianopia-related vision loss. Previously, patients suffering from the condition simply had to learn to live with it.
-
Scientists found that nearly every cancer harbors its own distinct community of microbes – tiny passengers that can influence how tumors start, spread, and respond to treatment, paving the way for a new era of precision medicine.
-
Scientists who won a 2024 IgNobel Prize for "discovering that many mammals are capable of breathing through their anus" have now completed a successful trial based on this, using a technique that gets oxygen into the blood via an unconventional route.
-
Precision-targeted radiation is proving a match for surgery in early-stage lung cancer, offering patients similar long-term survival with less invasiveness, and potentially transforming how this common cancer is treated.
-
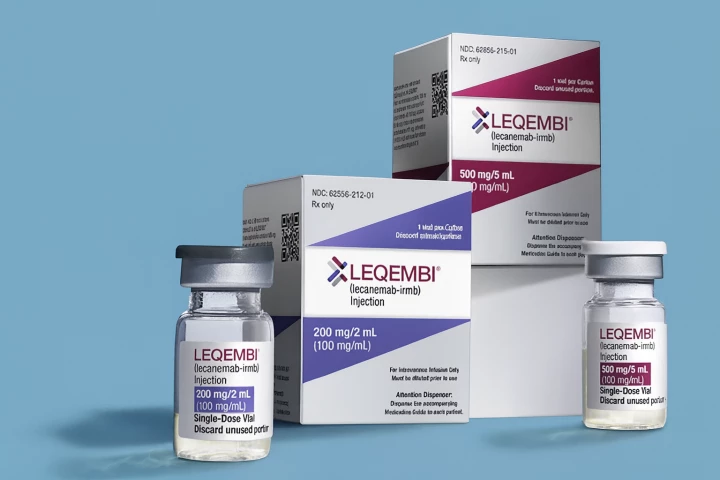
The FDA has approved a new version of an Alzheimer’s disease drug that can be given as a quick at-home weekly injection, offering patients a more convenient option than lengthy infusion-center visits. It will be widely available from October 6, 2025.
-
It's an inconvenient fact that many drugs have to be administered in the form of a slow intravenous (IV) drip, as opposed to a single quick injection. That may be about to change, however, thanks to a new take on an existing "spray drying" technique.
-
Having hypersensitive teeth can be quite the hassle, making it painful to consume hot, cold, sweet and/or acidic foods and beverages. Tiny new "robots" are here to help, by permanently plugging tunnels in the teeth for less discomfort.
-
Recurring kidney stones can be an agonizing, debilitating problem, particularly if they can't be treated by orally-administered medication. There may be new hope on the horizon, in the form of a tiny magnetically-steerable stone-dissolving "robot."
-
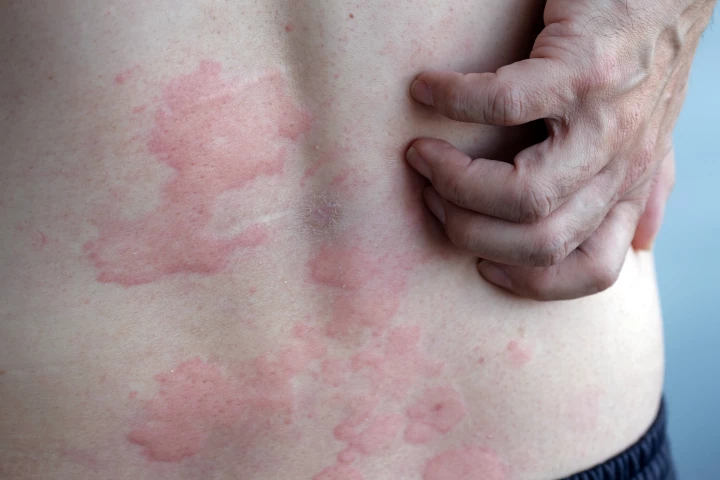
A massive global study has ranked the best and safest treatments for chronic hives when antihistamines fall short. The findings provide a clear treatment roadmap for both patients and clinicians alike.
-
A promising new treatment to combat "undruggable" cancers has been green-lit for a human trial. It's hoped the novel drug will be able to stunt the growth and enable the effective treatment of cancers driven by the MYC oncogene and its MYC protein.
Load More