Treatment
-
A promising new treatment to combat "undruggable" cancers has been green-lit for a human trial. It's hoped the novel drug will be able to stunt the growth and enable the effective treatment of cancers driven by the MYC oncogene and its MYC protein.
-
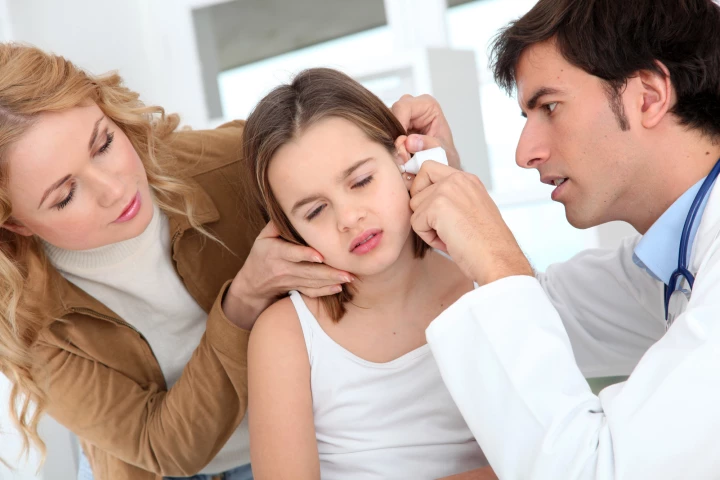
Babies and small children are prone to middle ear infections, which typically have to be treated with orally administered antibiotics. A new fast-acting topical gel could soon replace such drugs, however, potentially reducing unpleasant side effects.
-
In the ongoing search to find an intervention that does away with opioids, a new game-based system has shown huge promise in tackling chronic neuropathic pain. Using a game and a headset, it "trains" patients to rewire brain signals to relieve pain.
-
A landmark study has found that a workable exercise plan significantly improves survival and health of people who have survived colorectal cancer. So much so that, as one researcher notes, "Our findings will change the way we treat colon cancer."
-
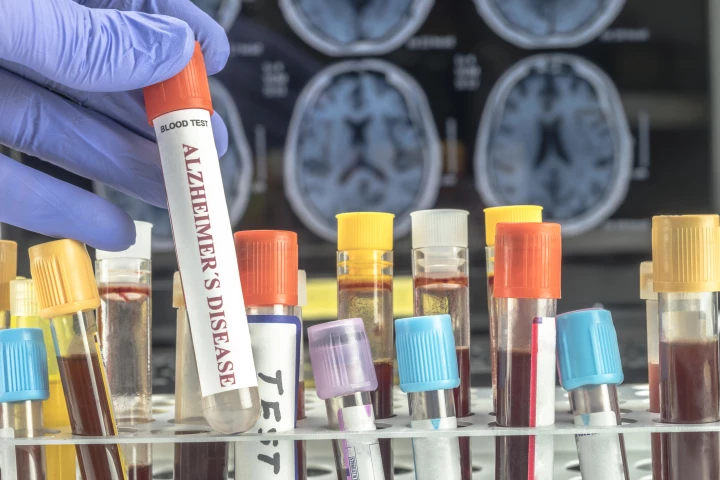
The first blood test for Alzheimer's disease detection has been green-lit by the US Food and Drug Administration, providing a simpler, quicker and less invasive method of diagnosis and speedier intervention. It's a milestone moment for medical science.
-
The Hailie Smartinhaler improves asthma control by ensuring inhalers are used effectively and at the right time. It has been assisting American asthmatics since 2017; now its makers want it to be available to Aussie asthmatics, too.
-
Pupil dilation and subtle facial changes in response to sound can reveal how severe tinnitus is. Through this, researchers have discovered a new way to objectively gauge how bad the condition is, more accurately diagnosing tinnitus and treating it.
-
Using an existing steroid-free topical foam daily significantly improved the signs and symptoms of psoriasis on the scalp and the body, according to a recent clinical trial. It could be a game-changer for people with the condition in both places.
-
Clinical trials of a minimally invasive treatment for degenerated spinal discs have produced impressive results, significantly reducing back pain severity and improving function. It may mean delaying surgical intervention or preventing it altogether.
-
Nerve or neuropathic pain has long been a tricky condition to treat effectively. However, a new study has comprehensively evaluated current drug and non-drug therapies to provide up-to-date guidelines to inform treatment options.
-
Researchers have reviewed non-drug treatments for low back pain to assess which ones are more likely to reduce pain and improve function. What the review makes clear is that more research into effective low back pain treatments is needed.
-
The treatment of kidney stones could soon be getting much faster, easier, and safer. Scientists have devised a method of non-invasively tearing the objects apart, using what are known as "acoustic vortex beams."
Load More