TU Wien
-
Scientists around the world have been one-upping each other in a bid to create the smallest QR code that can be reliably read. Now, researchers have set the bar real high with a QR code so tiny, you'll need an electron microscope to see it.
-
From washing urinals to tidying up the beach, we can already see a future where our robot servants help keep our world a little cleaner. Now, a robotic arm has mastered the surprisingly complex task of sink washing, showing off its ability to learn.
-
Atomic clocks are our most accurate timekeepers, losing only seconds across billions of years. But nuclear clocks could steal their thunder, speeding up GPS and the internet. Now, scientists have built and tested the first prototype nuclear clock.
-
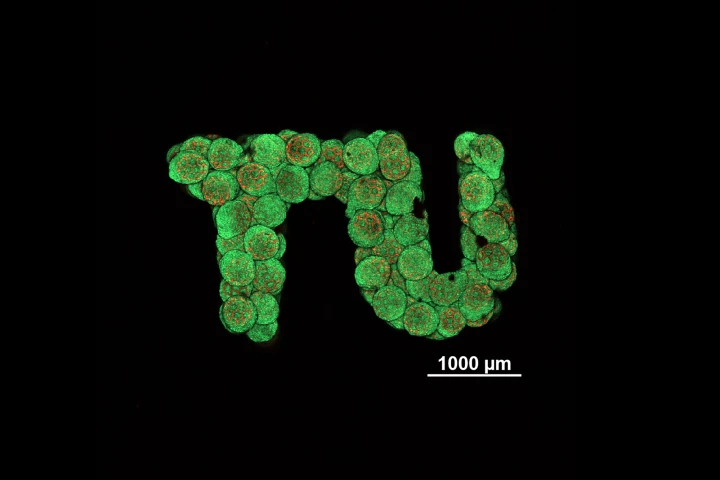
Researchers at TU Wien have developed a new way to grow cartilage from stem cells and guide it into basically any shape required. The breakthrough could lead to better ways to patch up injuries.
-
It may seem like electronics will always get faster, but at some point the laws of physics intervene. Scientists have now calculated the absolute speed limit – the point at which quantum mechanics prevents microchips from getting any faster.
-
The ivory trade has been banned for over 30 years now, which means that technicians restoring ivory artifacts have to get creative in finding alternative materials. A new 3D-printable substance known as Digory appears to fit the bill nicely.
-
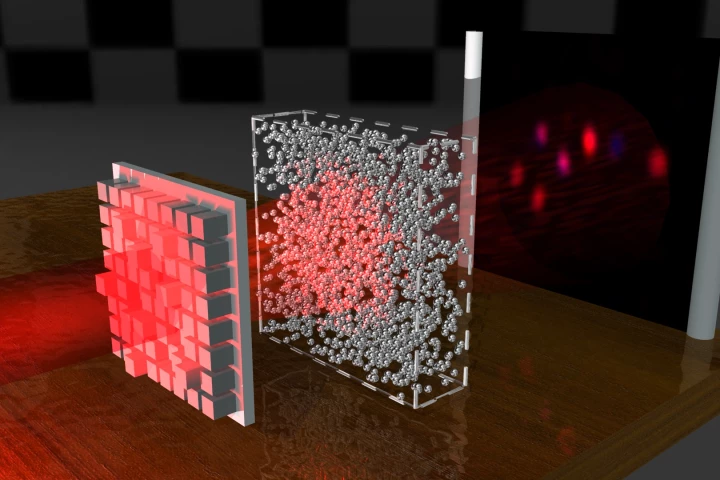
Clouds or sugar cubes block light because they’re disordered media that scatter light waves. Now scientists have found a way to manipulate light waves to pass through, projecting an image on the other side as clearly as if the obstacle wasn’t there.
-
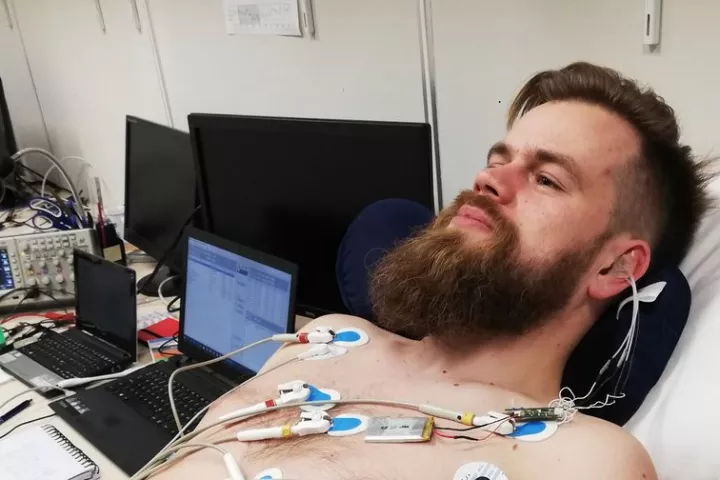
As some readers may already know, in-ear stimulation of the vagus nerve can help relieve pain in other parts of the body. Thanks to new research by Austrian scientists, such treatments could soon be more effective than ever.
-
An imaginative new approach to bridge-building was demonstrated for the first time in Austria last week. The novel construction method, likened to opening an umbrella, is designed to save considerable time, money and impact on the local landscape.
-
While we've certainly heard of epoxy resins that harden when exposed to light, usually all of the substance has to be exposed. A new additive causes resin to solidify when even only a bit of it gets lit up, however – plus it works underwater.
-
Terahertz radiation is extremely useful but, traditionally, tricky and expensive to generate. Scientists at TU Wien have come up with a new source of terahertz radiation that they claim breaks records for efficiency and the breadth of its spectrum.
-
According to researchers from the Vienna University of Technology, propelling conventional wheelchairs puts users' joints in unnatural and potentially injury-causing positions. They've developed what is claimed to be a more ergonomic alternative, in the form of a hand-cranked wheelchair.
Load More