Type 2 diabetes
-
Adding to the growing body of research that proves our microbiome is a powerful ally in fighting disease, scientists have found that an easy-to-get nutrient in our food causes our guts to produce powerful insulin-regulating compounds.
-
Scientists have made a major breakthrough in understanding how fat cells grow in size, in response to accommodating larger droplets of fat. The findings unlock a new path in tackling obesity, by reducing the amount of fat our cells can store away.
-
Millions of people with type 2 diabetes might actually be undermining their efforts to improve their health, with researchers demonstrating that the commonly prescribed metformin blocks the cardiovascular benefits normally gained through exercise.
-
A large international study of more than 23,000 patients has found that common medicines used to treat high blood pressure and cholesterol, as well as heartburn, may be impacting cancer treatment effectiveness.
-
A promising “two-in-one” experimental drug could tackle both type 2 diabetes and heart disease by slashing cholesterol and inflammation, potentially offering a powerful new way to protect the heart and improve metabolism.
-
The age of the GLP-1 drug has reached yet another milestone, with the US Food and Drug Administration green-lighting Novo Nordisk's once-daily oral semaglutide pill to treat people at high risk of cardiovascular events like heart attack and stroke.
-
Compounds in green tea can reprogram muscle metabolism to boost insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance, according to new findings that further our understanding of why this ancient drink has long been linked to protect against obesity.
-
People living in areas of higher air pollution are at risk of more serious sleep apnea events, according to a large study spanning multiple countries. However, being aware of air quality means you can mitigate that risk to improve sleep and health.
-
Switching off a single enzyme in immune cells protected mice from obesity, type 2 diabetes, and fatty liver disease in a new study, offering a potential new treatment target for metabolic disorders.
-
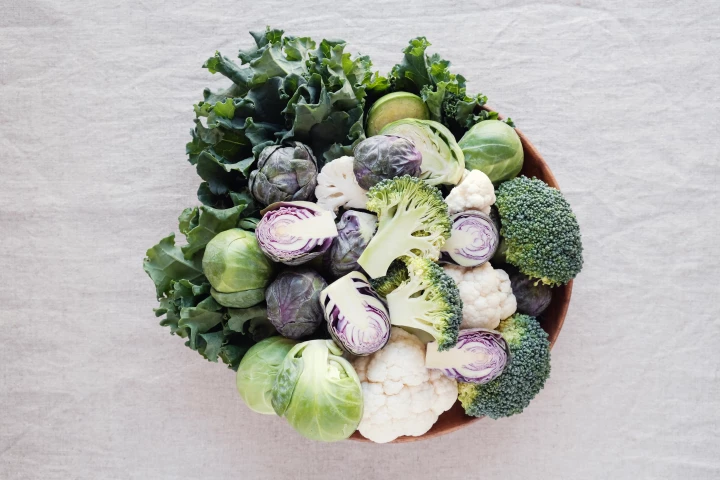
There's new evidence that cruciferous vegetables blunt spikes in blood sugar levels, which could be particularly important for those with type 2 diabetes or are at risk of developing it. And you only need a handful a day to reap the health benefits.
-
Scientists have identified a protein that acts as a kind of traffic cop for fat inside cells, revealing a mechanism that could help explain how the body regulates energy storage. The discovery provides a new avenue for tackling obesity and diabetes
-
Inflammation may predict how well people with diabetes respond to depression treatment, and the effects differ dramatically between type 1 and type 2 diabetes, according to a new study that offers a path towards personalized mental health care.
Load More