UC Davis
-
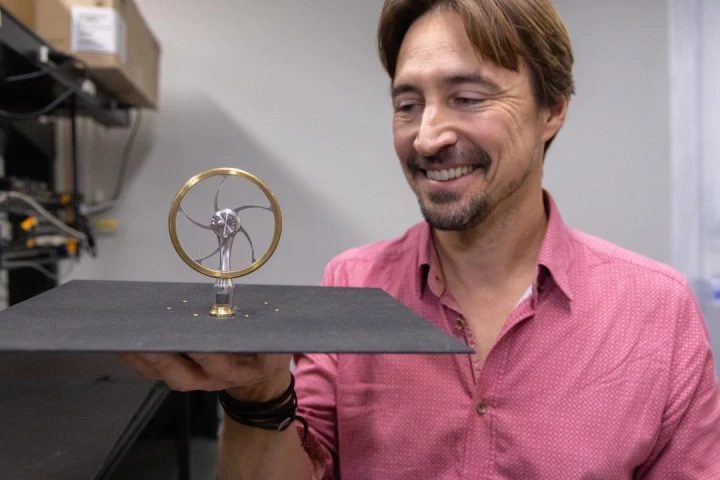
What if you could draw energy from the night sky without effort? That's the question that researchers at the University of California, Davis are trying to answer with a new engine that generates power simply by sitting under the clear starry heavens.
-
Fruit smoothies have become a huge trend in healthy lifestyle world – and for good reason. They are a quick source of vitamins, fiber, and antioxidants, and they take just a few minutes to make! Bananas are the number-one ingredient for a good smoothie. Creamy and naturally sweet, they seem to pair well with pretty much every other fruit ... or do they?
-
In another advancement in the field of brain-computer interfaces, a new implant-based system has enabled a paralyzed person to not only talk, but also 'sing' simple melodies through a computer – with practically no delay.
-
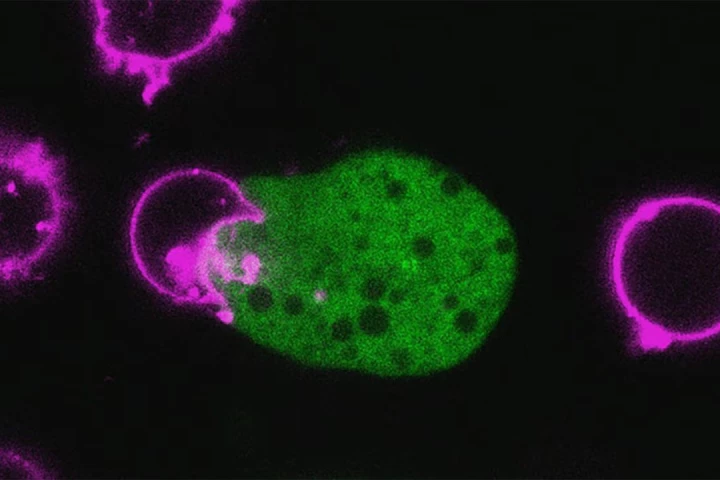
One type of parasite, Entamoeba histolytica, has developed a very intriguing way to evade the defences of our immune system. It rips pieces off human cells and steals the proteins to wear them as a disguise.
-
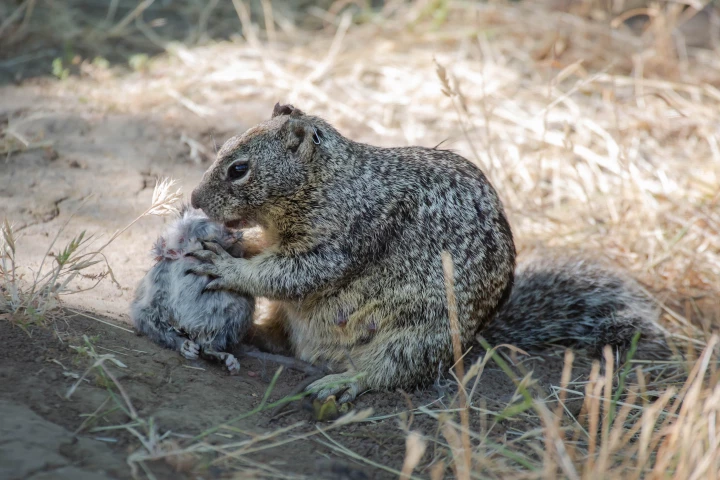
Unless you're a nut, cute little squirrels pose little threat – but they could have a surprising murderous streak. After watching squirrels in California for 12 years, scientists have seen them actively hunt and kill small rodents this past summer.
-
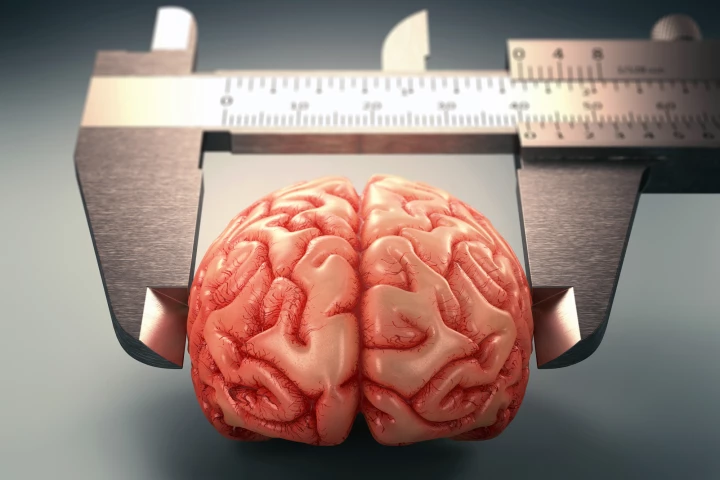
In the human species, bigger brains suggest better brain health and cognitive function. And since the 1930s, our brains have been growing. Now, a new study shows how this is affecting our risk of developing dementia, particularly Alzheimer's disease.
-
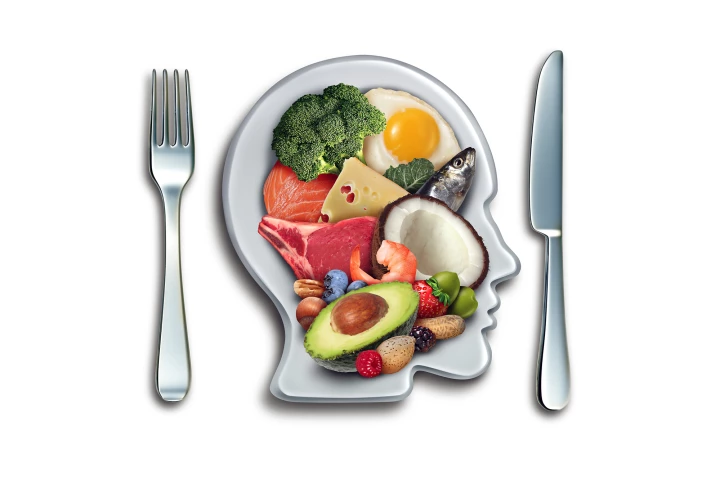
Eating a keto diet prevented the mild cognitive impairment often seen in the early stages of Alzheimer’s disease, new research has found. The researchers suggest that adopting the diet may be a way of delaying the onset of full-blown Alzheimer's.
-
The 102-year-old tuberculosis vaccine shrank liver cancer tumors in mice, which suggests it may be replicated in a human trial. If this was the case, the vaccine might prove successful in tackling this notoriously hard-to-treat cancer.
-
Researchers have identified an accurate ‘signature’ that may signal a person’s risk of dementia five to 10 years before symptoms appear. The biomarker could provide an early diagnosis, allowing therapeutic interventions to slow the disease’s progress.
-
Research has found that some personality traits increase the risk of a dementia diagnosis, whereas others reduce it. The findings suggest that targeting these traits earlier in life may be a way of reducing dementia risk in the long term.
-
For centuries red wine has been thought to trigger headaches more than other drinks, and it's been unclear exactly why this is the case. Now researchers think they've solved the mystery, and the culprit is a chemical previously thought to be beneficial.
-
The way a sunflower bends to follow the Sun across the sky each day can be quite dramatic. Now, scientists have uncovered something equally dramatic: it does it through unique genetic transcription, which rewrites what we know about its special Sun dance.
Load More