UC Riverside
-
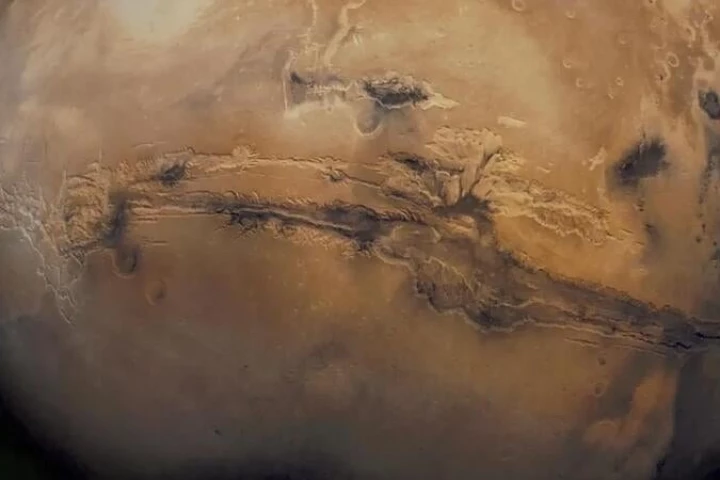
Why did the ice ages occur? If you need a scapegoat, a new study by Stephen Kane of UC Riverside suggests pointing the finger at Mars. According to computer models, the pull of the Red Planet may have altered the Earth's orbit until things got nippy.
-
The evolutionary ladder is meant to be climbed one rung at a time with an organism shedding some traits and gaining others on the way up. However, in a very surprising twist, some tomatoes on the Galapagos islands are inching back down the ladder.
-
Finding alien life won’t be a flying saucer landing at the White House – NASA scientists will hold a press conference to excitedly show off a chart that’s incomprehensible to most people. Now we’re a step closer to that boring but groundbreaking day.
-
A new review has highlighted how skin tone can affect the safety and effectiveness of some medications and why the current way we run clinical drug trials needs to change to include more historically underrepresented populations.
-
Thanks to a recent discovery regarding marine algae, scientists have developed crop plants that absorb a fuller spectrum of sunlight, resulting in better growth. The finding could also lead to increased production of biofuels.
-
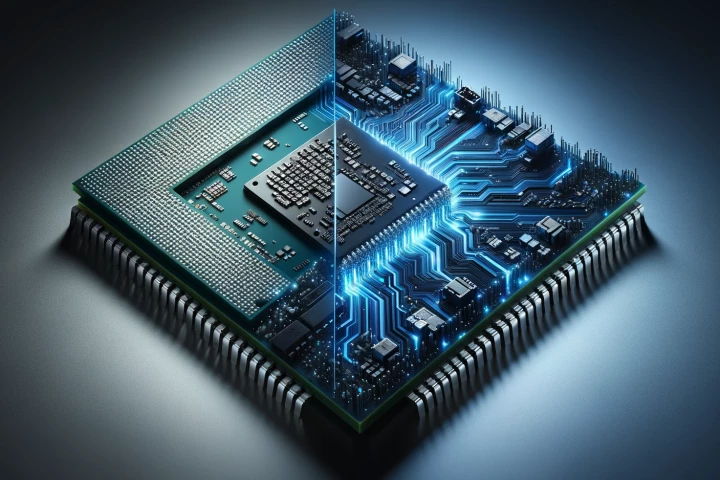
Existing processors in PCs, smartphones and other devices can be supercharged for enormous power and efficiency gains, according to UC Riverside. With no changes to hardware, this new approach to the software squeezes extra juice out of your system.
-
A simple, cheap pretreatment promises to radically cut the price of sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) made from waste wood biomass – potentially making it cost-competitive with fossil-based jet fuel, while cutting down emissions by up to 80%.
-
Hard though it may be to believe, there has apparently never been a confirmed sighting of a live newborn great white shark. Such may no longer be the case, however, thanks to recently analyzed aerial drone footage shot in California.
-
Researchers have developed a peptide that targets a protein implicated in 75% of human cancers and found that it slowed the proliferation of cancer cells in the lab. It’s the first step towards developing an effective treatment for a range of cancers.
-
Checking for pollutants in the environment via soil sampling and other traditional methods can be a laborious process, but what alternatives are there? Well, scientists have now engineered a plant to turn red when exposed to specific toxic chemicals.
-
As any car-chase action movie will tell you, the gasoline used in our vehicles is flammable, explosive stuff. Scientists have created a new combustible fuel, however, which stays safely non-flammable for transport and storage.
-
Researchers have identified how the virus that causes COVID-19 takes advantage of cellular machinery to spread in the body, and a way to stop it. The finding could lead to a new class of antiviral therapies to treat a range of other viruses as well.
Load More