Ultrasound
-
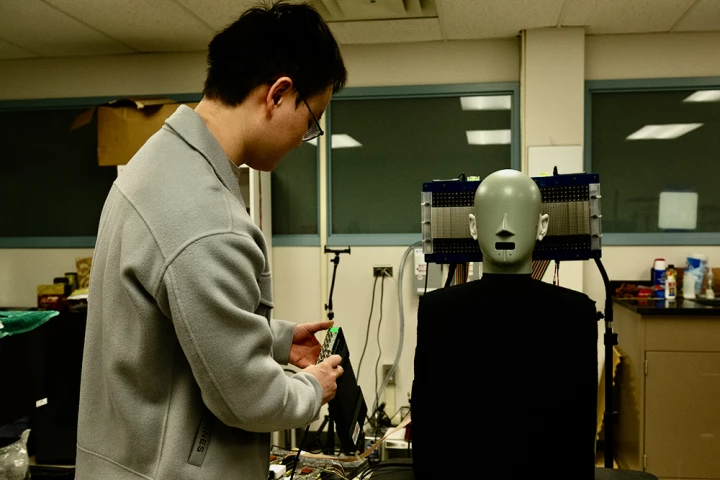
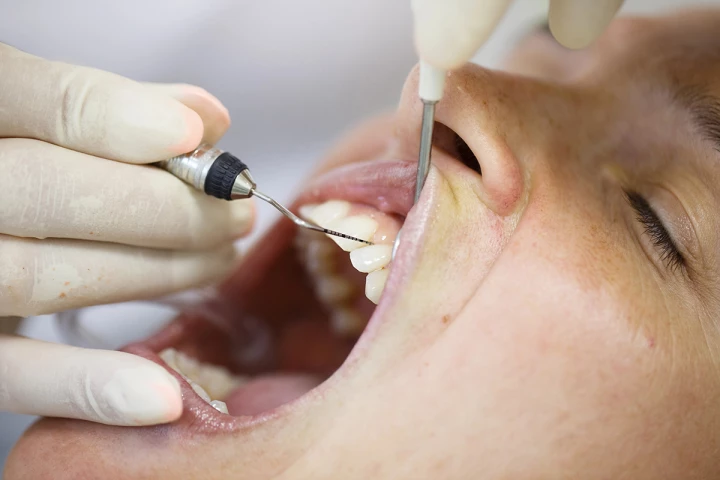
When it comes to dental checkups, no one likes having their gums poked with the periodontal probe. Well, they may soon no longer have to, thanks to a gum-assessing toothbrush-shaped mini ultrasound transducer.
-
Imagine being able to listen to music or other audio that no one else can hear, without having to wear headphones. Doing so is now possible via so-called "audible enclaves," which already exist in functional prototype form.
-
The treatment of kidney stones could soon be getting much faster, easier, and safer. Scientists have devised a method of non-invasively tearing the objects apart, using what are known as "acoustic vortex beams."
-
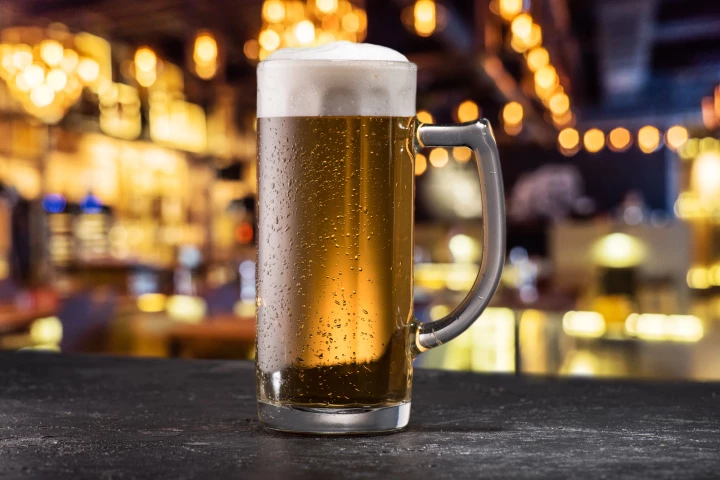
Using ultrasonic waves and a salt bath, a research team has altered the surface of glass. The brand-new method may lead to glass made without the use of harsh chemicals for self-cleaning windshields, germ-busting surfaces, or maybe even better beer.
-
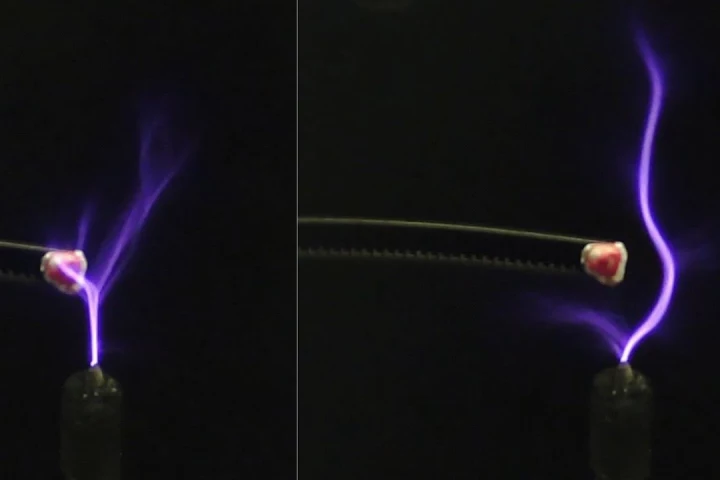
Electricity is chaotic, and we normally need to constrain it to wires and circuits to make use of it. Scientists in Europe and Canada have now managed to guide sparks through thin air and even around obstacles using ultrasound waves.
-
A new kind of cancer gene therapy can be remotely activated at a specific part of the body. The team developed a version of CRISPR that responds to ultrasound, and demonstrated how it can be used to clear cancer in mice.
-
Last year, xMEMS Labs embarked on a mission to replace legacy coil-based speakers in wireless ANC buds with silicon-based solid-state micro-speakers. Now the company has a new full-range flavor for open-fit earphones.
-
You might not hear it, but rodents are known to speak to each other in voices so high-pitched that human ears can’t pick them up. Now scientists have found that these vocalizations might have a second purpose – they help them smell better.
-
It's always best if farmers can detect drought stress before crop plants become wilted, weakened and lower-yielding. An experimental new portable device could help in that regard, as it uses ultrasound to spot such stress in its earliest stages.
-
Currently, when doctors wish to continuously monitor a patient's blood pressure, they insert a catheter into one of the individual's arteries. There could soon be a safer alternative, however, and it was inspired by the tuning of guitar strings.
-
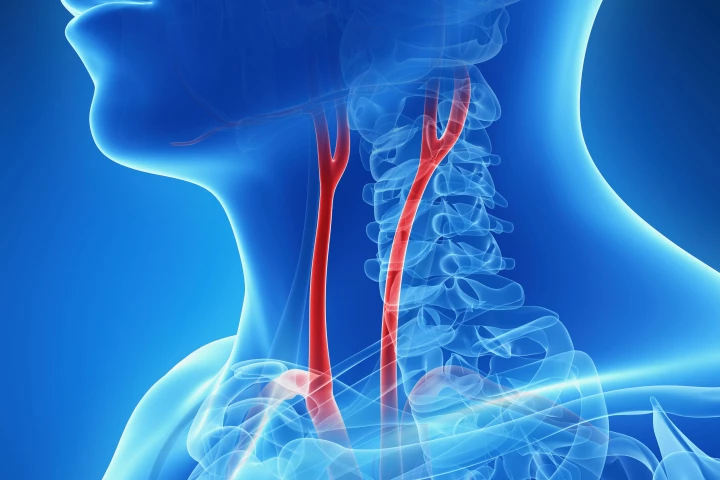
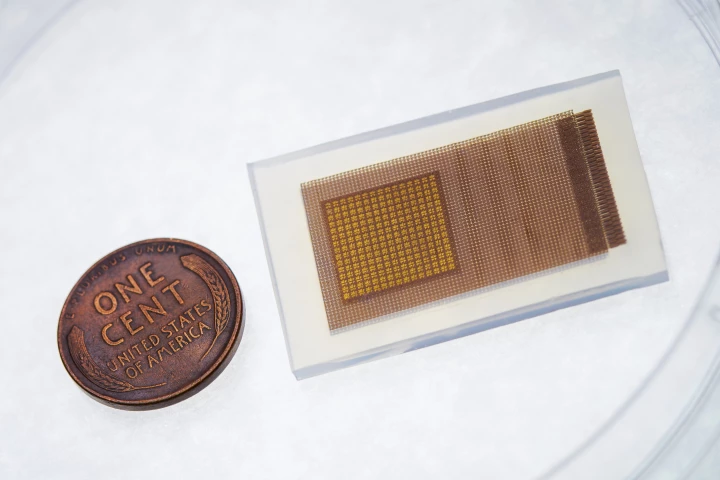
A wearable ultrasound patch could soon be saving lives, by monitoring the blood flow in hospital patients' brains. The device is only about the size of a postage stamp plus it works continuously, unlike traditional methods.
-
A fresh cup of coffee in the morning can be vital for facing the day ahead, but what if you had to wait a day to get your caffeine hit? That's on the menu if you like your Joe brewed cold, but researchers have used ultrasound to cold brew in minutes.
Load More