University at Buffalo
-
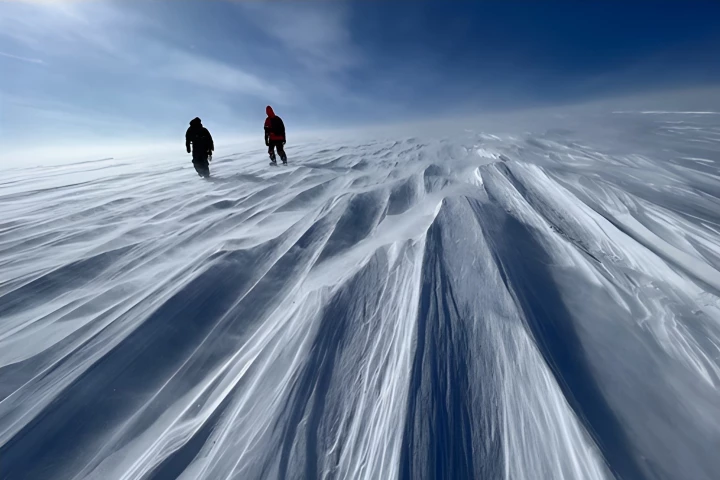
In northwestern Greenland, researchers working on the GreenDrill project have cored through a 500-meter-thick ice dome. They found something startling: the dome completely disappeared 7,000 years ago. And it might do it again.
-
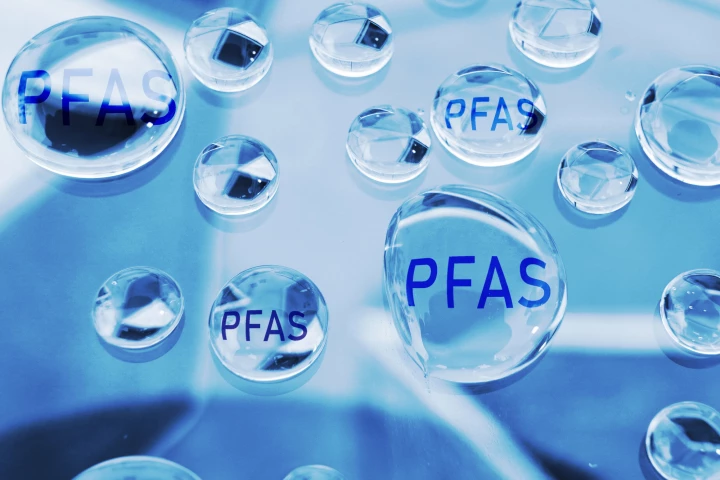
Toxic ‘forever chemicals’ are increasingly showing up in the environment, our food and drinking water, and our bodies. But we might have a new weapon: scientists have identified a bacterium that can eat these chemicals, as well as their byproducts.
-
To find black holes we usually have to look thousands of light-years away. But a new study suggests we could find evidence of them right here on Earth, as tiny tunnels they’ve carved out in rocks or old buildings.
-
You might not hear it, but rodents are known to speak to each other in voices so high-pitched that human ears can’t pick them up. Now scientists have found that these vocalizations might have a second purpose – they help them smell better.
-
One in five older Americans have been diagnosed with heart disease, and age-related cardiovascular decline is the biggest killer of adults over 65. Now, further research into light therapy opens the door to staving off this deadly condition.
-
While it's handy to be able to control our devices via voice commands, speaking those commands out loud can be problematic. The EarCommand system offers an alternative, as it "reads" users' silently mouthed words by monitoring their ear canal.
-
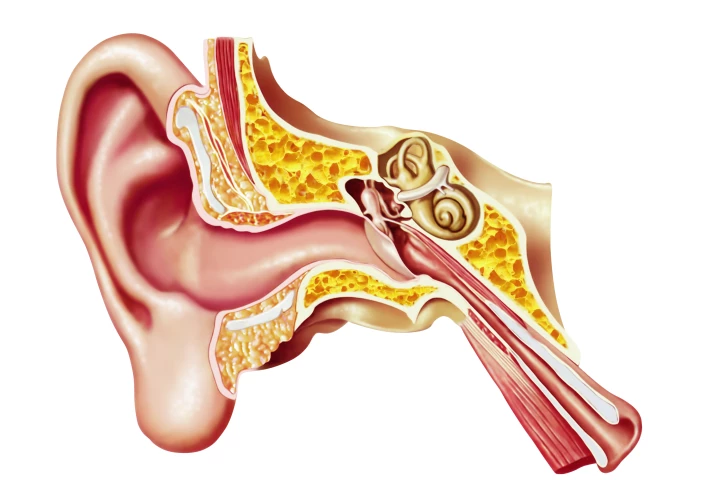
Researchers at the University at Buffalo have used Bluetooth earbuds and a deep learning AI system to diagnose three common ear conditions with a simple, non-invasive audio test that uses a sonar-like audio chirp to map out the ear structure.
-
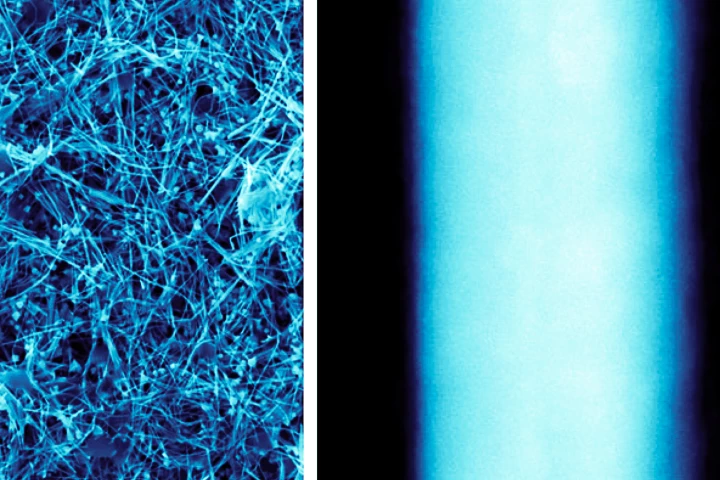
Copper is known for its ability to kill microbes on contact, which is why it's often professionally coated onto commonly touched items. A copper nanowire spray may allow everyday folks to give existing surfaces the same treatment, using a spray can.
-
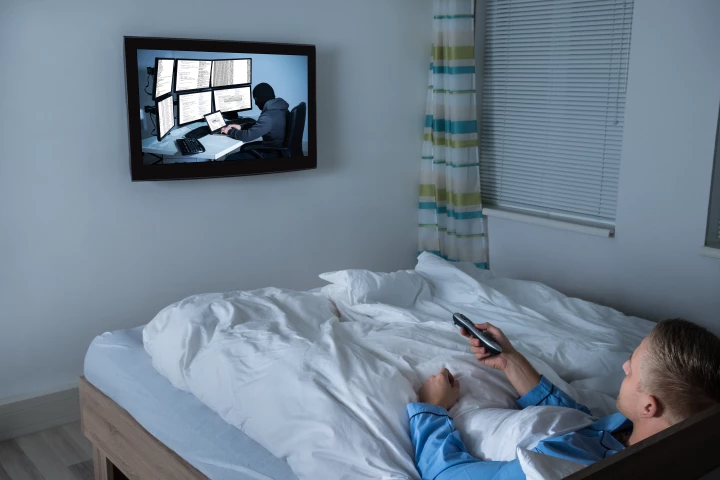
A pair of recent studies have upended the common belief that watching screens before going to sleep disturbs the quality or duration of your slumber. The research indicates some people may actually get more rest by watching something before going to sleep.
-
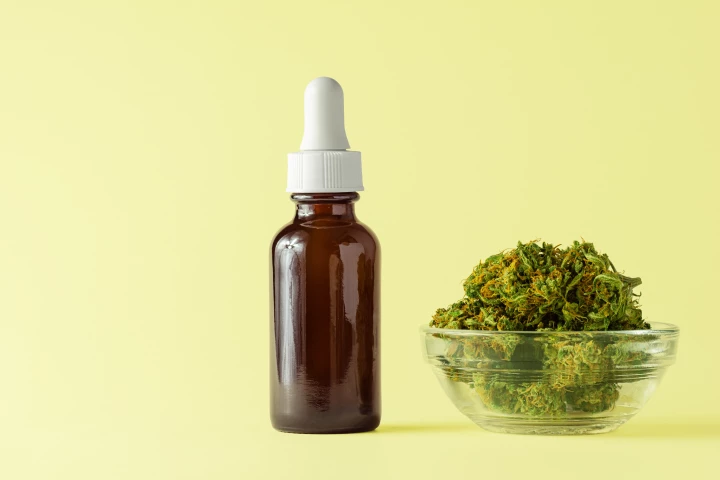
Delta-8 THC is similar to its commonly known psychoactive cousin, delta-9 THC, and new studies are offering the first large-scale insights into what kinds of effects people are experiencing with this unique and under-researched drug.
-
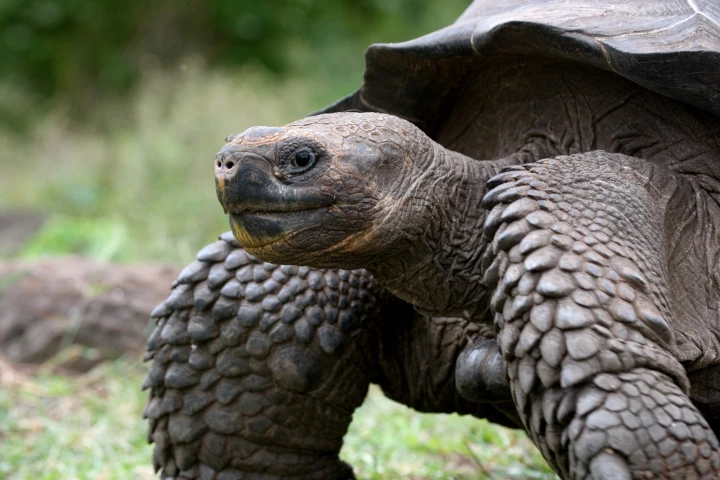
Galapagos giant tortoises are some of the longest-living animals on Earth, but how do they pull off the feat? A new study has examined the genome of the species and found duplicate genes that may protect them from aging-related diseases like cancer.
-
The immune system is a powerful weapon, but sometimes it can attack things that are trying to help us. A new preclinical treatment could one day help, using a kind of “reverse vaccine” to train the immune system to ignore specific drugs or molecules.
Load More