University College London
-
We know what they look like, and even sound like, but there’s one question you might not have pondered: what do ancient Egyptian mummies smell like? Whether you wanted to know or not, scientists have now given us an answer.
-
In the first study of its kind, scientists have used extensive data to identify that adults with ADHD have a significantly lower life expectancy than their neurotypical peers. This unprecedented research should serve as a serious wake-up call.
-
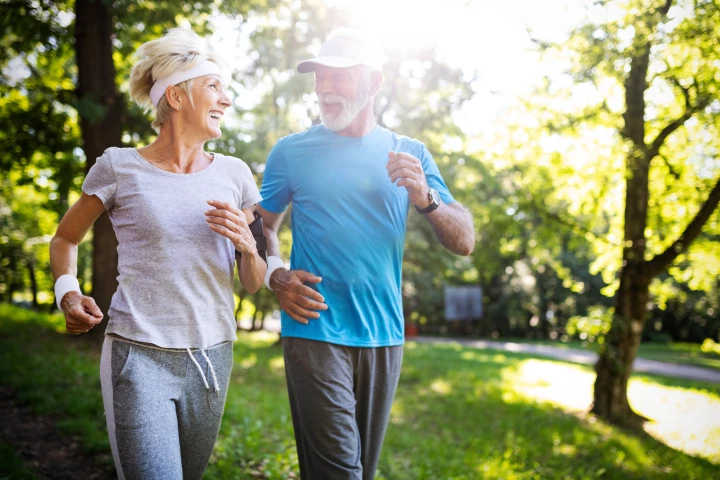
Declining brain function is a natural part of the aging process, but that doesn’t mean it can’t be delayed. A new study found that physical activity can boost brain function for up to 24 hours and, independent of exercise, so can a good night’s sleep.
-
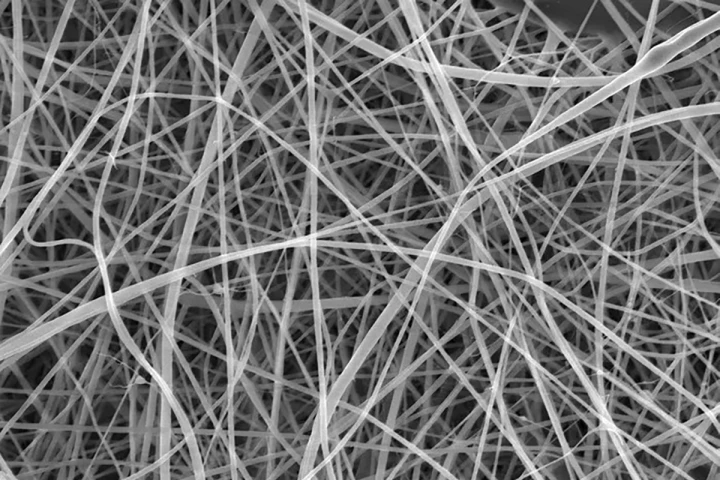
The world's thinnest spaghetti is 200 times thinner than a human hair, which means you'd have a hard time eating it. It's actually a nanofiber developed to help heal wounds. Besides, you'd probably overcook it in a second anyway.
-
Finding time to exercise each day is a challenge for many people, but a new study of nearly 15,000 men and women has discovered that adding just five minutes of daily activity that gets your heart rate up is enough to lower your blood pressure.
-
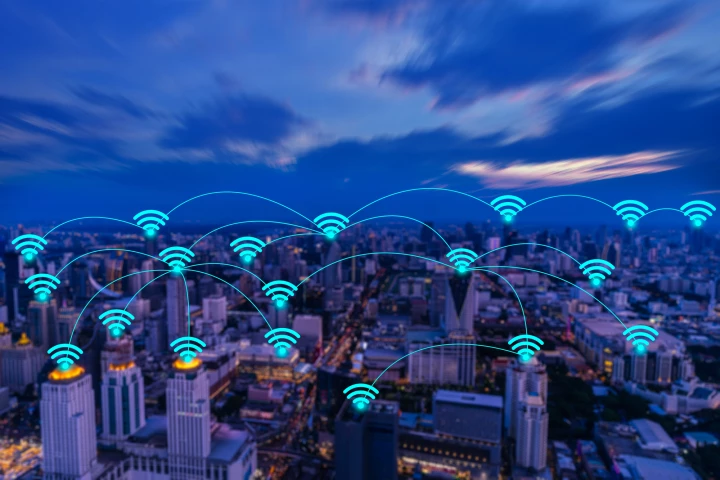
Scientists at the University College London have set a new world record in wireless data transmission speeds, sending a blistering 938 Gigabits per second (Gbps) over the air through a combo of radio and light technology.
-
Exercise’s positive effect on depression is well-known, but not how it produces its anti-depressant effects. After reviewing a broad range of studies into how depression and physical activity affect motivation, researchers have now come up with a hypothesis.
-
A group of volunteers in the UK let scientists put the SARS-CoV-2 virus up their noses for research investigating why some of us naturally avoid getting COVID-19. This first-of-its-kind study opens the door to better vaccines and treatments.
-
A lengthy trip to Mars, which exposes astronauts to a combination of cosmic radiation and weightlessness, could result in permanent kidney damage, according to a new study. It's the largest analysis to date on how spaceflight affects kidney health.
-
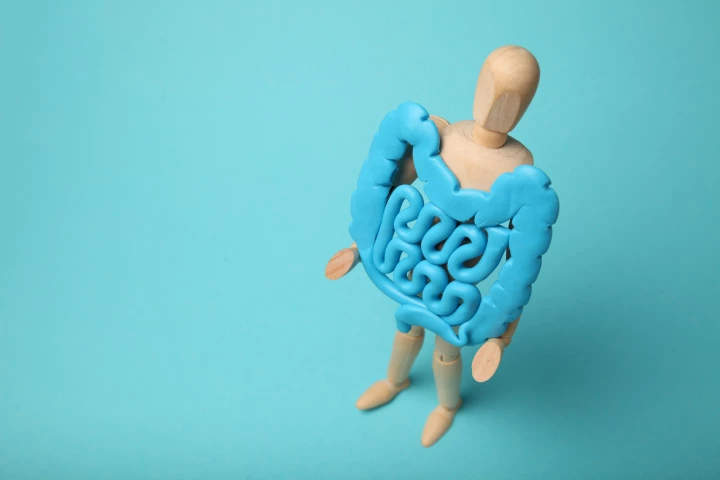
For the first time, a major trigger in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and related conditions has been identified, and existing drugs are capable of blocking it. It's a "massive step" in successfully treating these debilitating lifelong conditions.
-
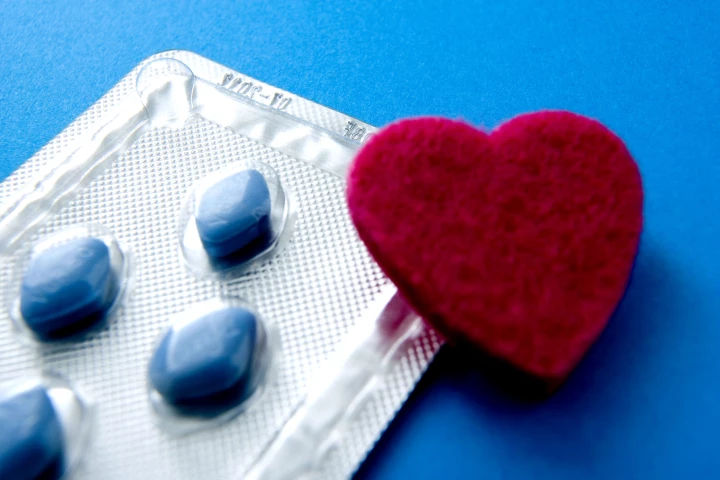
Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors such as Viagra are best known for treating erectile dysfunction, but a study of nearly 270,000 men has added to the growing body of evidence that they may also protect the brain against developing Alzheimer's disease.
-
A team has reported the first-ever evidence of human-to-human transmission of Alzheimer’s disease, demonstrating how a human growth hormone treatment transplanted toxic proteins into children and caused the development of early-onset Alzheimer’s.
Load More