University of Bern
-
Much in the same way humans can become addicted to online gaming or internet gambling, dogs can become addicted to their toys. That's the finding of new research that examined the behaviors of 105 pups in a laboratory setting.
-
The question of whether life once existed on Mars may be answered by a new laser instrument from the University of Bern. The device can be carried by a rover to zap samples of the Red Planet to see if they contain traces of microfossils.
-
When it comes to protein sources that are more eco-friendly than traditional livestock, two of the most promising candidates are insects and microalgae. Scientists have now devised a method of using waste from the former as food for the latter.
-
Farmers have long known that it's a good idea to rotate crops. A Swiss study now indicates that wheat yields are boosted when those crops are planted in fields previously used to grow maize, which altered the soil's microbiome.
-
Astronomers have classified planetary systems into four distinct categories, based on the sizes and arrangements of their planets. As it turns out, the architecture of our own solar system is the rarest kind.
-
An artificial pancreas has been trialed in patients with type 2 diabetes for the first time. The device monitors a person’s blood glucose levels and automatically administers insulin when needed – and the results so far are promising.
-
Computer simulations have revealed that a hostile, tidally locked exoplanet roughly 45 light-years from Earth is capable of hosting tectonic activity — which is one of the key processes that contributes to making a world habitable — on a huge scale.
-
An intriguing new study, from a team of Swiss researchers, has revealed neural activity during REM sleep in a particular region of the brain known to affect appetite and feeding behaviors significantly influences waking eating patterns.
-
One of the many deteriorative effects of aging in humans is a decline in immune system function. But scientists may have uncovered a way to reverse this trend by transplanting a type of white blood cell from the young into the old.
-
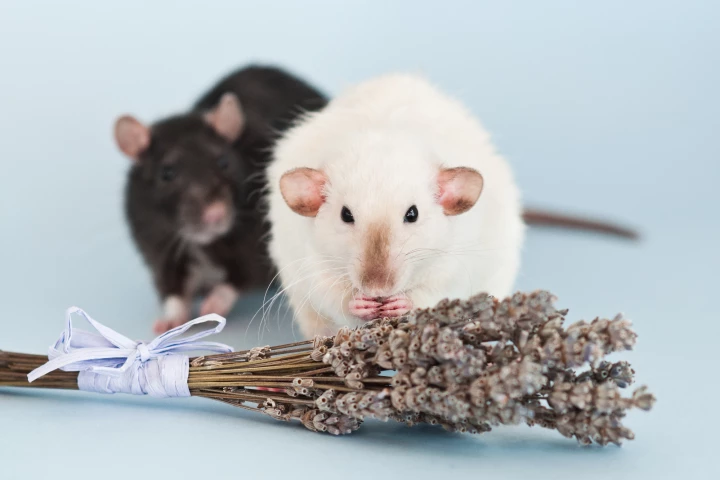
Scientists have already observed that rats will readily share food with other rats who are hungry. A new study now suggests that they do so not just based on what the other rat does, but also on how it smells.
-
An unexpected discovery is challenging our accepted understanding of how planets form. Astronomers have spotted a gigantic gas planet orbiting a small red dwarf star, which shouldn’t be possible according to current models.
-
Cancer might not be so difficult to kill if it didn’t have the terrifying ability to spread throughout the body. Now, researchers have discovered a particular protein signalling pathway that controls whether a tumor can spread or not, making it a good target for future drugs.
Load More