University of Bristol
-
In the world of dogs and cats, it wouldn't be a stretch to say that canines seem more optimistic and felines less so. But a dog's optimism can apparently be dampened by their human's emotional state, according to new research.
-
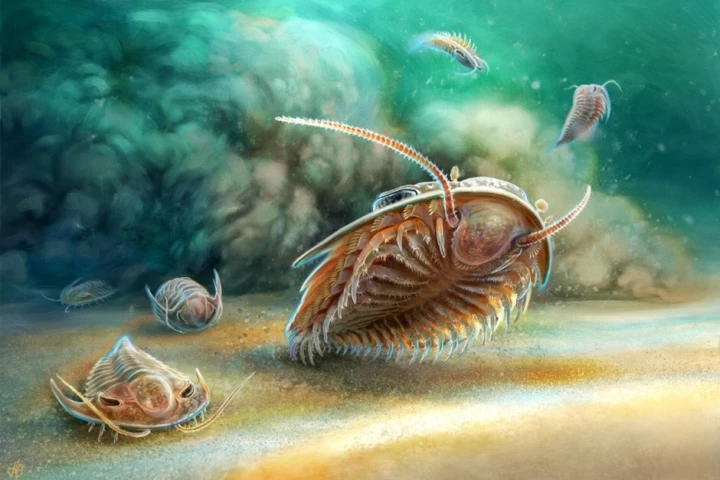
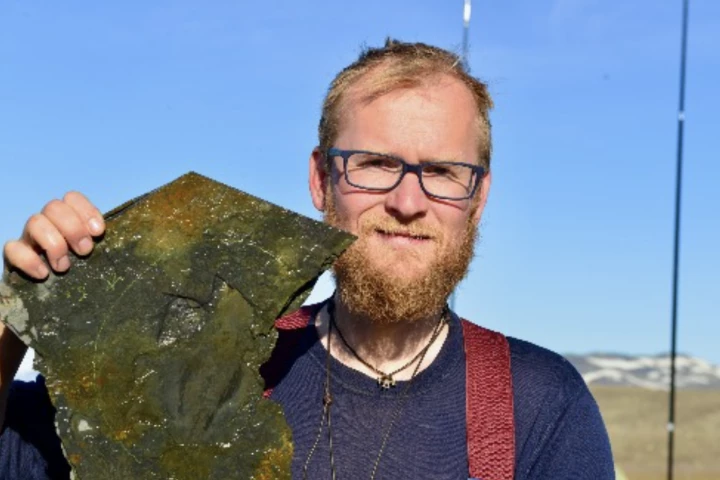
Scientists have just revealed their findings on what are being described as the most pristine trilobite fossils ever found. The fossils, which show both hard exterior features and soft inner tissues, shed new light on the fascinating creatures.
-
Snails are great at climbing vertical surfaces, even though they have just a single wet suction-cup foot. A new robot climbs walls by mimicking that simple yet effective mechanism, although thankfully it leaves a trail of water instead of mucus.
-
While we don't like to talk ill of the dead, new analysis has called into question the intelligence of the king of the dinosaurs. It upends last year's findings that likened the cognitive skills of the Tyrannosaurus rex to that of a primate.
-
Carbon dioxide is key to how long airborne viruses hang around in the air and, therefore, their likelihood of spreading. Opening a window may be a more scientific way to avoid the spread of respiratory viruses than first anticipated.
-
A new octopus-sucker-inspired suction cup could make it much easier and more energy-efficient for robots to lift and release rough-surfaced objects. The secret lies in using water to mimic octopus mucus.
-
Researchers have identified a novel inhibitor drug that, when given to mice, prevented both eye and kidney complications commonly seen in diabetics. Further research is being done to advance the drug to clinical trials.
-
Scientists have uncovered a new huge predatory worm species thought to have hunted in the Earth’s water column around 518 million years ago. They also believe this worm, whose name means terror beast, was one the earliest carnivorous swimming animals.
-
A study has found a link between higher consumption of ultra-processed foods and the risk of developing some cancers. However, they found that obesity, often caused by eating too much of these foods, was not a large contributing factor.
-
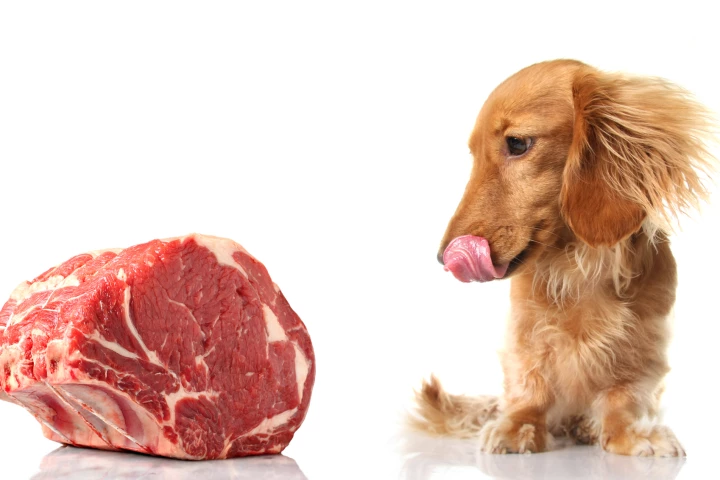
A new study has found that feeding dogs uncooked meat increases their risk of excreting E. coli that is resistant to a widely-used antibiotic, thereby increasing the potential that the bacteria will be passed on to owners and cause illness.
-
Desynchronizing the circadian rhythm in rats had a significant impact on appetite and feeding behavior, a study has found. The findings have important implications for night shift workers and those suffering jet lag and chronic sleep disturbances.
-
People suffering from dementia not only get confused, they can also become highly anxious and even aggressive. In order to catch such behaviors before they escalate out of control, a British scientist has developed a pair of sensor-packin' socks.
Load More