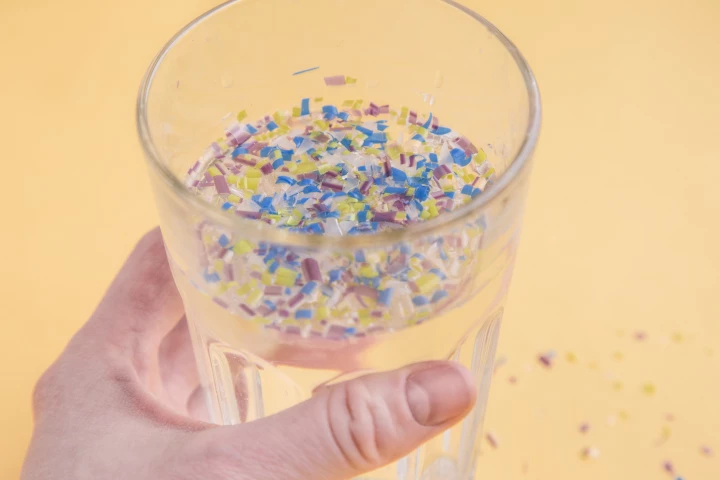University of British Columbia
-
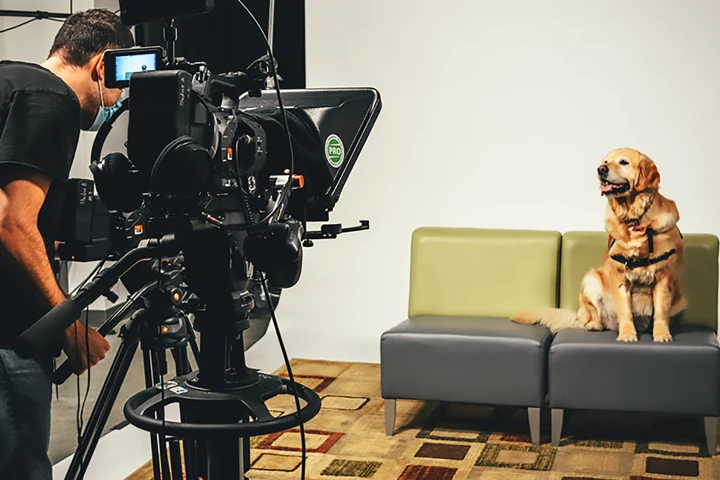
Watching a video of a therapy dog for just five minutes can meaningfully lower stress levels, a new study shows, offering a simple, stigma-free option for those reluctant to seek traditional mental health support.
-
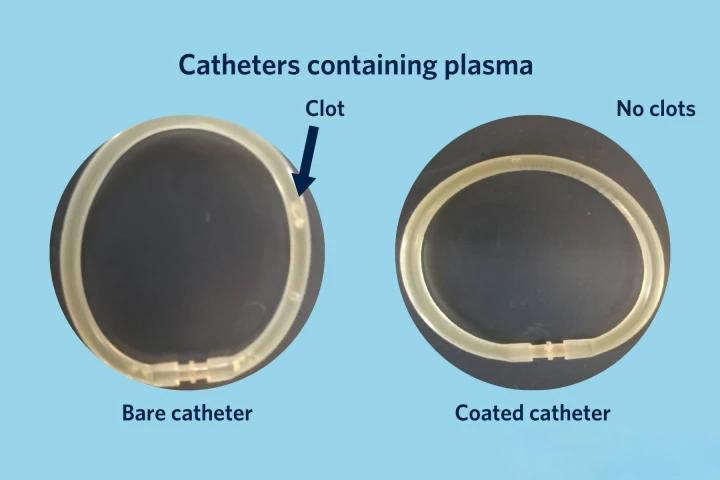
When a patient's blood flows through catheters, stents or other medical devices, there's always a risk that harmful clots may form. An experimental new bio-inspired coating could keep that from happening, without the use of blood-thinning drugs.
-
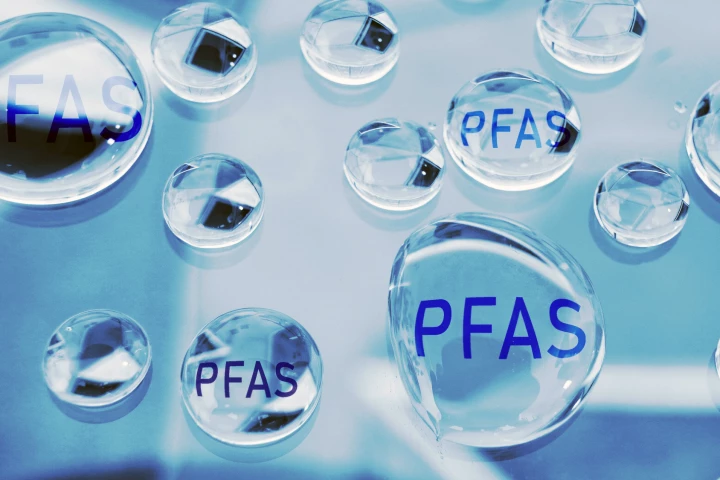
Proposed methods of removing toxic ‘forever chemicals’ from water have either only trapped the chemicals or broken them down. A new study has demonstrated a method that does both effectively. And it's quick and cheap.
-
While people are becoming concerned about microplastic pollution in their drinking water, it's one of those things that the average person can't check for themselves. That could soon change, however, if a new prototype device reaches production.
-
Vantablack, which is the world's darkest material, could be in for some competition. Canadian scientists have created a super-black substance that has the potential to be cheaper, hardier and easier to manufacture … and it's made out of wood.
-
Some people produce more insulin in response to proteins and fats than carbs, new research has found. Suggesting that insulin production is more individualized than first believed, the findings pave the way for treating conditions through a tailored diet.
-
Diabetics sick of daily injections may have renewed hope for a less invasive alternative. Scientists at the University of British Columbia (UBC) have developed a new delivery method for insulin where users just place a few drops under their tongue.
-
New research has found that daily users of crystal methamphetamine who turned to cannabis to manage their cravings used the stimulant drug less, especially female users. The findings suggest a new harm-reduction strategy is needed.
-
A study has linked elevated blood insulin levels and pancreatic cancer. The researchers say their findings may lead to new cancer prevention strategies and targeting treatments to slow or prevent the progression of the cancer.
-
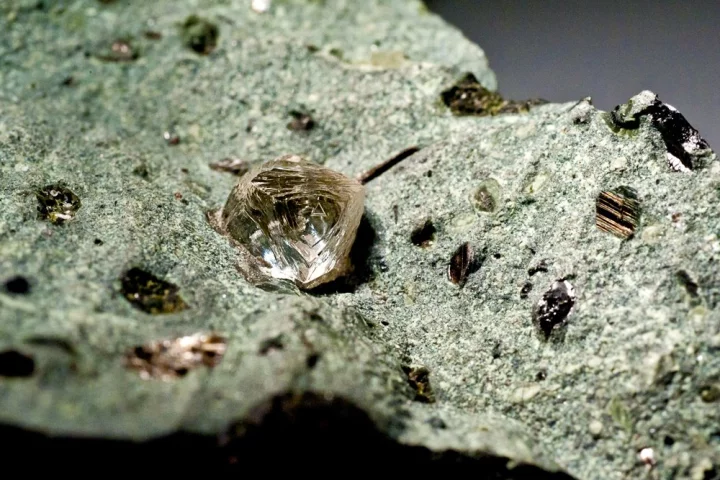
Locating diamond deposits in the earth isn't always an exact science, so the greater the number of methods of doing so, the better. A new study now suggests that soil microbes may point the way to such buried treasures.
-
A new study has found that four major childhood allergies share a common feature: an imbalance of gut bacteria during infancy. Researchers say that correcting this imbalance could potentially prevent lifelong allergic diseases.
-
Researchers may have found an effective, green way to remove microplastics from our water using readily available plant materials. Their device was found to capture up to 99.9% of a wide variety of microplastics known to pose a health risk to humans.
Load More